
The line \[y = mx + c\] passes through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\]. Find \[m\] and \[c\].
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: To find the value of \[m\] and \[c\] for the line \[y = mx + c\] which passes through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\], we will first put the point \[(2,5)\] and then \[(4,13)\] in the equation of line \[y = mx + c\]. Putting these points will give two linear equations in terms of \[m\] and \[c\]. We will solve these obtained linear equations to find the value of \[m\] and \[c\].
Complete step by step answer:
The given two points on coordinate axes are shown below.
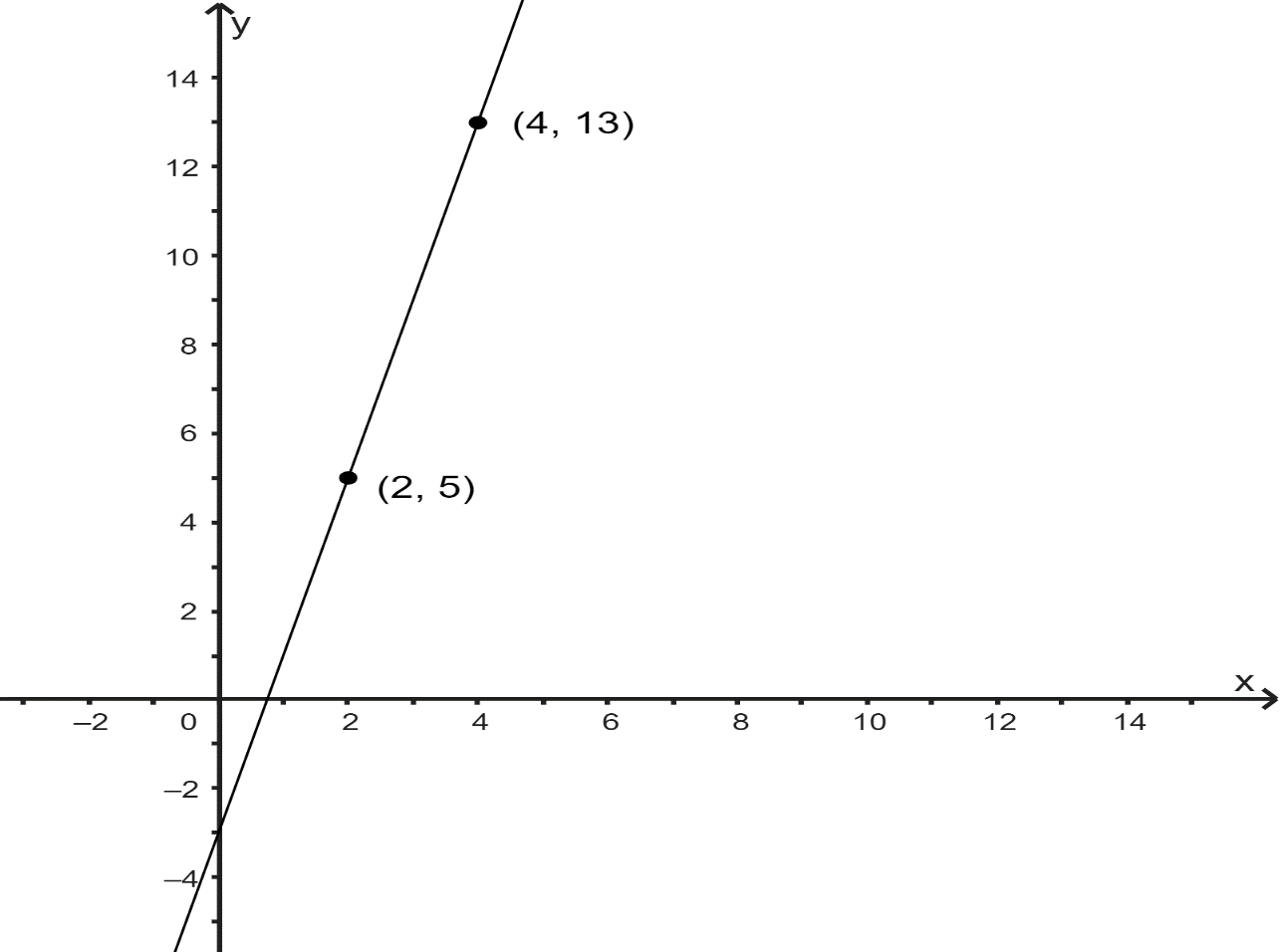
Putting \[(2,5)\] in equation \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = m \times 2 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 2m + c\]
On rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2m + c = 5\]
Taking \[2m\] from L.H.S. to R.H.S., we get
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - 2m - - - (1)\]
Putting \[(4,13)\] in equation \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 13 = m \times 4 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 13 = 4m + c\]
On rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4m + c = 13 - - - (2)\]
Putting \[(1)\] in \[(2)\],
\[ \Rightarrow 4m + \left( {5 - 2m} \right) = 13\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow 2m + 5 = 13\]
Taking \[5\] from L.H.S. to R.H.S.
\[ \Rightarrow 2m = 13 - 5\]
On solving we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2m = 8\]
Dividing both the sides by \[2\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m = 4\]
Putting the value of \[m\] in \[\left( 1 \right)\],
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - \left( {2 \times 4} \right)\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow c = - 3\]
Therefore, \[m\] is \[4\] and \[c\] is \[ - 3\] for the line \[y = mx + c\] which passes through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\].
Note:
We can also solve this problem by first finding the slope (\[m\]) of the line using given two points and then putting any one of the given points and the obtained value of slope in the equation \[y = mx + c\] to find the value of \[c\].
As we know that slope (\[m\]) of the line \[y = mx + c\] passing through \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\].
Therefore, slope (\[m\]) of the line \[y = mx + c\] passing through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\] is
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{13 - 5}}{{4 - 2}}\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m = 4\]
Therefore, \[m = 4\].
Now putting \[m = 4\] and \[(2,5)\] in the equation of the line \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 4 \times 2 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 8 + c\]
Taking \[8\] from R.H.S. to L.H.S.
\[ \Rightarrow 5 - 8 = c\]
\[\therefore c = - 3\]
Hence, the value of \[m\] is \[4\] and \[c\] is \[ - 3\].
Complete step by step answer:
The given two points on coordinate axes are shown below.
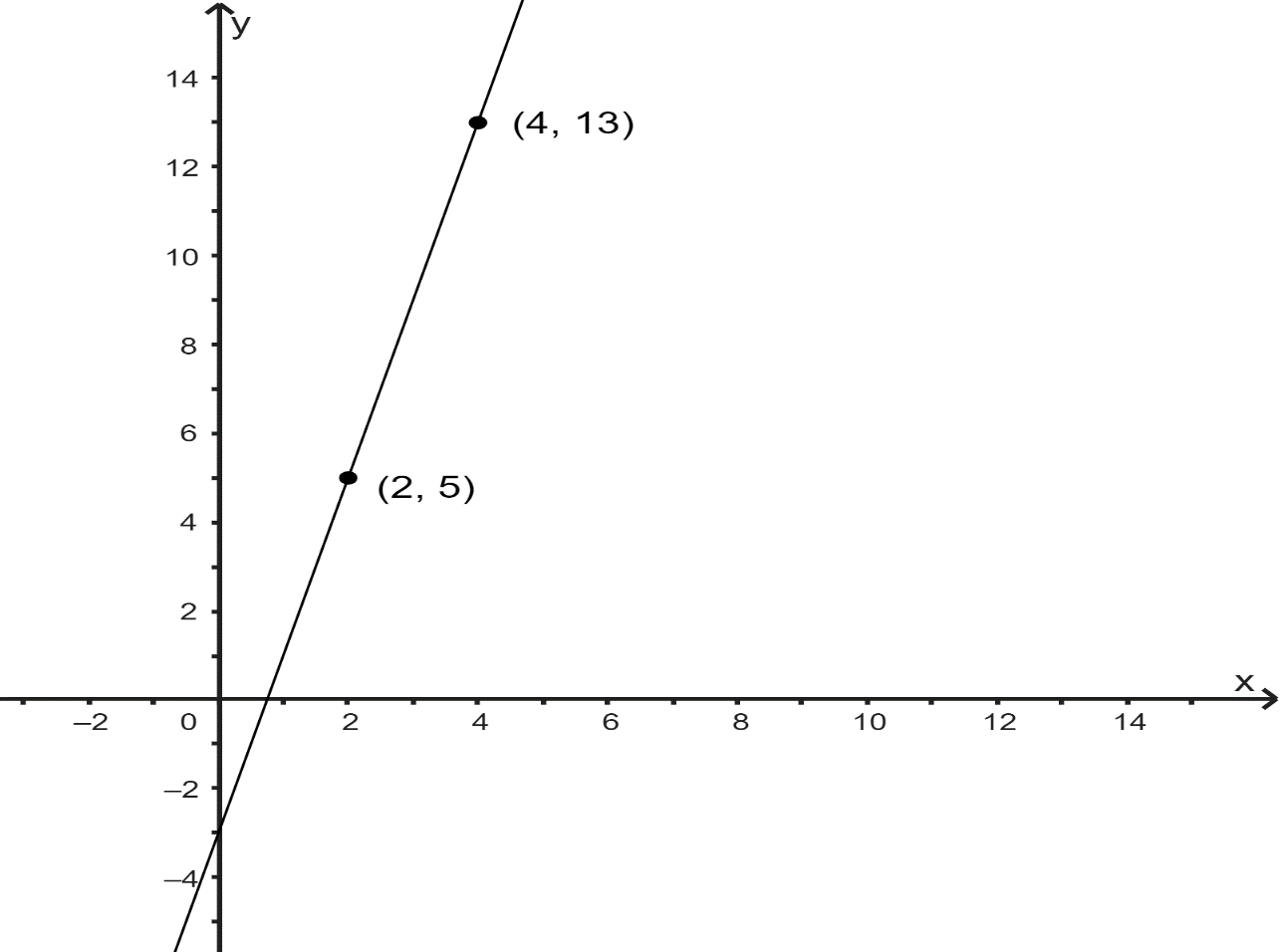
Putting \[(2,5)\] in equation \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = m \times 2 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 2m + c\]
On rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2m + c = 5\]
Taking \[2m\] from L.H.S. to R.H.S., we get
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - 2m - - - (1)\]
Putting \[(4,13)\] in equation \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 13 = m \times 4 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 13 = 4m + c\]
On rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4m + c = 13 - - - (2)\]
Putting \[(1)\] in \[(2)\],
\[ \Rightarrow 4m + \left( {5 - 2m} \right) = 13\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow 2m + 5 = 13\]
Taking \[5\] from L.H.S. to R.H.S.
\[ \Rightarrow 2m = 13 - 5\]
On solving we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2m = 8\]
Dividing both the sides by \[2\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m = 4\]
Putting the value of \[m\] in \[\left( 1 \right)\],
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - \left( {2 \times 4} \right)\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow c = 5 - 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow c = - 3\]
Therefore, \[m\] is \[4\] and \[c\] is \[ - 3\] for the line \[y = mx + c\] which passes through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\].
Note:
We can also solve this problem by first finding the slope (\[m\]) of the line using given two points and then putting any one of the given points and the obtained value of slope in the equation \[y = mx + c\] to find the value of \[c\].
As we know that slope (\[m\]) of the line \[y = mx + c\] passing through \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[m = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}\].
Therefore, slope (\[m\]) of the line \[y = mx + c\] passing through \[(2,5)\] and \[(4,13)\] is
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{{13 - 5}}{{4 - 2}}\]
On solving,
\[ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m = 4\]
Therefore, \[m = 4\].
Now putting \[m = 4\] and \[(2,5)\] in the equation of the line \[y = mx + c\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 4 \times 2 + c\]
On simplification,
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = 8 + c\]
Taking \[8\] from R.H.S. to L.H.S.
\[ \Rightarrow 5 - 8 = c\]
\[\therefore c = - 3\]
Hence, the value of \[m\] is \[4\] and \[c\] is \[ - 3\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




