
The lengths in km (rounded to nearest hundred)
of some major rivers of India are given below:
Draw a bar graph to represent the above information.
River Length in (km) Narmada 1300 Mahanadi 900 Brahmaputra 2900 Ganga 2500 Kaveri 800 Krishna 1300
| River | Length in (km) |
| Narmada | 1300 |
| Mahanadi | 900 |
| Brahmaputra | 2900 |
| Ganga | 2500 |
| Kaveri | 800 |
| Krishna | 1300 |
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: We recall shapes of the bar plot and we draw the bars vertically. We take vertical bars of equal width at equal distance with each other on the horizontal axis and take the length of the rivers in kilometers in the vertical axis on the left side with a small division equal to 100 kilometers. \[\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that a bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents grouped data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically on the horizontal axis or horizontally on the vertical axis. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart. We observe the given table. \[\]
We see that in the left column we are given the names of the rivers and in the right column their length. We draw the bar for the river Narmada with any width (we have taken width 8 here) and draw height equal to $\dfrac{1300}{100}=13$ small divisions. Since each division is 100 km , 13 divisions will represent $13\times 100=1300$ km. \[\]
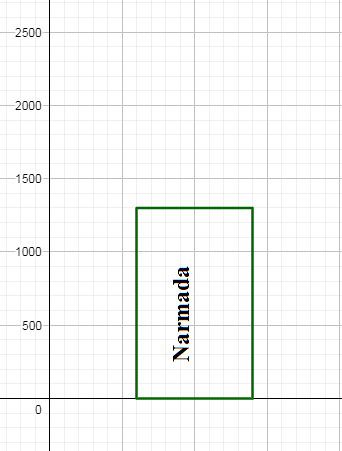
We draw the next bar for the river Mahanadi at some distance from the bar for Narmada with the same width we took for Narmada and height equal to $\dfrac{900}{100}=9$ small divisions. \[\]
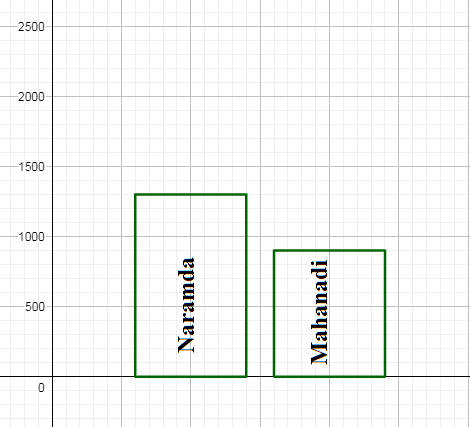
We similarly draw the bars the Brahmaputra, Ganga, Kaveri, Krishna river with the same width and equal distance with each other and height $\dfrac{2900}{100}=29,\dfrac{2500}{100}=25,\dfrac{800}{100}=8,\dfrac{1300}{100}=13$ small divisions respectively. We have the bar plot as, \[\]
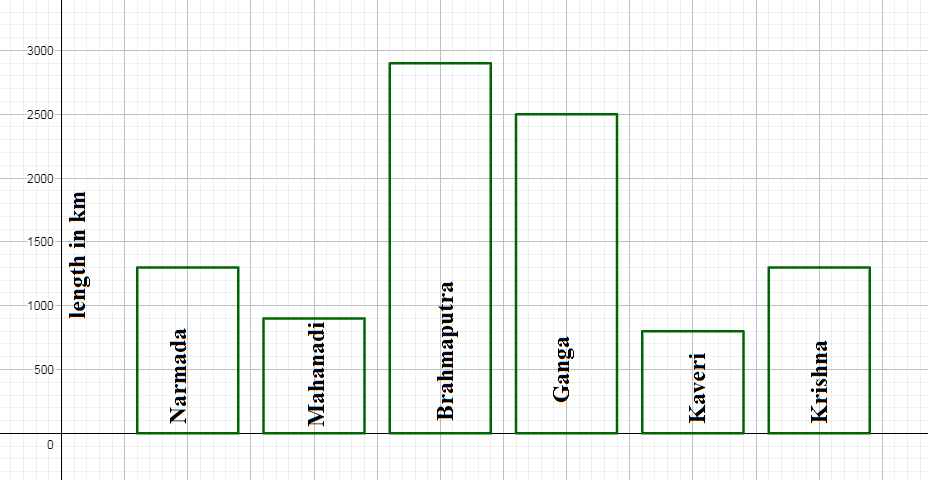

Note: We can also draw horizontal bars on the vertical axis. There are two other types of bar chart grouped bar charts where two or more colored bars close to each other and stacked bar charts where bars are on top of each other represent different groups. The histogram is a special type of vertical bar chart with continuous data on the horizontal axis where all the bars are close to each other.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that a bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents grouped data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. The bars can be plotted vertically on the horizontal axis or horizontally on the vertical axis. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart. We observe the given table. \[\]
| River | Length in (km) |
| Narmada | 1300 |
| Mahanadi | 900 |
| Brahmaputra | 2900 |
| Ganga | 2500 |
| Kaveri | 800 |
| Krishna | 1300 |
We see that in the left column we are given the names of the rivers and in the right column their length. We draw the bar for the river Narmada with any width (we have taken width 8 here) and draw height equal to $\dfrac{1300}{100}=13$ small divisions. Since each division is 100 km , 13 divisions will represent $13\times 100=1300$ km. \[\]

We draw the next bar for the river Mahanadi at some distance from the bar for Narmada with the same width we took for Narmada and height equal to $\dfrac{900}{100}=9$ small divisions. \[\]

We similarly draw the bars the Brahmaputra, Ganga, Kaveri, Krishna river with the same width and equal distance with each other and height $\dfrac{2900}{100}=29,\dfrac{2500}{100}=25,\dfrac{800}{100}=8,\dfrac{1300}{100}=13$ small divisions respectively. We have the bar plot as, \[\]

Note: We can also draw horizontal bars on the vertical axis. There are two other types of bar chart grouped bar charts where two or more colored bars close to each other and stacked bar charts where bars are on top of each other represent different groups. The histogram is a special type of vertical bar chart with continuous data on the horizontal axis where all the bars are close to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




