
The length of the shadow of a tower standing on level ground is found to be $2x$ metres longer when the sun’s elevation is ${{30}^{0}}$ than when it was ${{45}^{0}}$ . The height of the tower in metres is.
(a) $\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)x$
(b) $\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)x$
(c) $2\sqrt{3}x$
(d) $3\sqrt{2}x$
Answer
612.3k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem first we will draw the geometrical figure as per the given data. After that, we will use the basic formula of trigonometry $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\left( \text{length of the perpendicular} \right)}{\left( \text{length of the base} \right)}$ . Then, we will solve correctly to get the height of the tower and select the correct option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
It is given that the length of the shadow of a tower standing on level ground is found to be $2x$ metres longer when the sun’s elevation is ${{30}^{0}}$ than when it was ${{45}^{0}}$ . And we have to find the height of the tower.
Now, first, we will draw a geometrical figure as per the given data. For more clarity look at the figure given below:
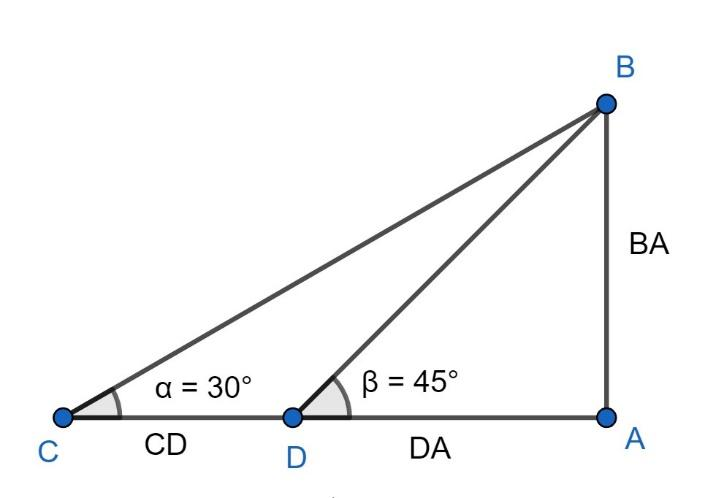
In the above figure BA represents the height of the tower, DA represents the length of the shadow of the tower when the elevation of the sun is equal to $\angle BDA=\beta ={{45}^{0}}$ and CA represents the length of the shadow of the tower when the elevation of the sun is equal to $\angle BCA=\alpha ={{30}^{0}}$ .
Now, as it is given that length of the shadow of a tower standing on level ground is found to be $2x$ metres longer when the sun’s elevation is ${{30}^{0}}$ than when it was ${{45}^{0}}$ . Then,
$CA=DA+2x...................\left( 1 \right)$
Now, consider $\Delta BDA$ in which $\angle BAD={{90}^{0}}$ , DA is equal to the length of the base, BA is equal to the length of the perpendicular and $\angle BDA=\beta ={{45}^{0}}$. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \angle BDA \right)=\dfrac{\left( \text{length of the perpendicular} \right)}{\left( \text{length of the base} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan {{45}^{0}}=\dfrac{BA}{DA} \\
& \Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{BA}{DA} \\
& \Rightarrow DA=BA................................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, consider $\Delta BCA$ in which $\angle BAC={{90}^{0}}$ , CA is equal to the length of the base, BA is equal to the length of the perpendicular and $\angle BCA=\alpha ={{30}^{0}}$. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \angle BCA \right)=\dfrac{\left( \text{length of the perpendicular} \right)}{\left( \text{length of the base} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{BA}{CA} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{BA}{CA} \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)................................\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute $DA=BA$ from equation (2) and $CA=\sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)$ from equation (3) into equation (1). Then,
$\begin{align}
& CA=DA+2x \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)=BA+2x \\
& \Rightarrow BA\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)=2x \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)} \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that $\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ so, we can write $\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)={{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}$ in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( {{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( 3-1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the length of the BA will be $x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)$ metres.
Thus, the height of the tower will be $x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)$ metres.
Hence, (a) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first try to understand what is asked in the problem. After that, we should try to draw the geometrical figure as per the given data. Moreover, we should apply the basic formula of trigonometry properly without any error and avoid calculation mistakes while solving to get the correct answer and then select the correct option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
It is given that the length of the shadow of a tower standing on level ground is found to be $2x$ metres longer when the sun’s elevation is ${{30}^{0}}$ than when it was ${{45}^{0}}$ . And we have to find the height of the tower.
Now, first, we will draw a geometrical figure as per the given data. For more clarity look at the figure given below:

In the above figure BA represents the height of the tower, DA represents the length of the shadow of the tower when the elevation of the sun is equal to $\angle BDA=\beta ={{45}^{0}}$ and CA represents the length of the shadow of the tower when the elevation of the sun is equal to $\angle BCA=\alpha ={{30}^{0}}$ .
Now, as it is given that length of the shadow of a tower standing on level ground is found to be $2x$ metres longer when the sun’s elevation is ${{30}^{0}}$ than when it was ${{45}^{0}}$ . Then,
$CA=DA+2x...................\left( 1 \right)$
Now, consider $\Delta BDA$ in which $\angle BAD={{90}^{0}}$ , DA is equal to the length of the base, BA is equal to the length of the perpendicular and $\angle BDA=\beta ={{45}^{0}}$. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \angle BDA \right)=\dfrac{\left( \text{length of the perpendicular} \right)}{\left( \text{length of the base} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan {{45}^{0}}=\dfrac{BA}{DA} \\
& \Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{BA}{DA} \\
& \Rightarrow DA=BA................................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, consider $\Delta BCA$ in which $\angle BAC={{90}^{0}}$ , CA is equal to the length of the base, BA is equal to the length of the perpendicular and $\angle BCA=\alpha ={{30}^{0}}$. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \angle BCA \right)=\dfrac{\left( \text{length of the perpendicular} \right)}{\left( \text{length of the base} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{BA}{CA} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{BA}{CA} \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)................................\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute $DA=BA$ from equation (2) and $CA=\sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)$ from equation (3) into equation (1). Then,
$\begin{align}
& CA=DA+2x \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{3}\left( BA \right)=BA+2x \\
& \Rightarrow BA\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)=2x \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)} \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that $\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ so, we can write $\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)={{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}$ in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& BA=\dfrac{2x}{\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)}\times \dfrac{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( {{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}} \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{\left( 3-1 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=\dfrac{2x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow BA=x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the length of the BA will be $x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)$ metres.
Thus, the height of the tower will be $x\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)$ metres.
Hence, (a) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first try to understand what is asked in the problem. After that, we should try to draw the geometrical figure as per the given data. Moreover, we should apply the basic formula of trigonometry properly without any error and avoid calculation mistakes while solving to get the correct answer and then select the correct option.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




