
The length of the diagonal of the square is \[\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]. Then find the length of a side of the square.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint:
Here, we will first draw the diagram of the square and divide it into two right triangles using the diagonal. Then we will apply the Pythagorean Theorem, in one of the triangles and find the required length of the side of the square. Pythagoras theorem states that the square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. Here, we will consider the diagonal as the hypotenuse.
Formula Used:
We will use the formula of the Pythagoras Theorem, \[{\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Given length of diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Now, let the side of the square be \[a\]
First of all, we will draw a square showing the given diagonal.
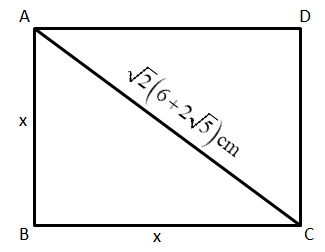
Here, we are having a square \[ABCD\] with sides \[x{\rm{cm}}\] and the length of the diagonal \[AC = \sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Now, in the right triangle \[ABC\], we will apply the Pythagoras. Therefore, we get
\[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
Substituting the values from the figure, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2}\]
Adding the like terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2{\left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)^2} = 2{x^2}\]
Cancelling out 2 from both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)^2} = {x^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides and neglecting the negative value because the length of side of a square can’t be negative, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 6 + 2\sqrt 5 {\rm{cm}}\]
Therefore, the required length of the side of the square is \[6 + 2\sqrt 5 {\rm{cm}}\]
Hence, this is the required answer.
Note:
An alternate way of solving this question is:
As we know, if the length of the side of a square is \[x\], then using Pythagoras theorem, the length of its diagonal is \[\sqrt 2 x\].
Now, if we compare the length of the side of a square and the length of its diagonal we can notice that, by multiplying the side of a square by \[\sqrt 2 \], we will be able to find the length of the diagonal.
Hence, alternatively, if we divide the length of the diagonal by \[\sqrt 2 \], then, we will be able to find the side of a square.
Using this property, we have the formula,
Side of a square \[ = \] Length of diagonal of the square \[ \div \sqrt 2 \]
Hence, in this question, the diagonal of the square is \[\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\].
Therefore, the required side of the square \[ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Hence, this is the required answer.
Here, we will first draw the diagram of the square and divide it into two right triangles using the diagonal. Then we will apply the Pythagorean Theorem, in one of the triangles and find the required length of the side of the square. Pythagoras theorem states that the square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. Here, we will consider the diagonal as the hypotenuse.
Formula Used:
We will use the formula of the Pythagoras Theorem, \[{\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Complete step by step solution:
Given length of diagonal of square \[ = \sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Now, let the side of the square be \[a\]
First of all, we will draw a square showing the given diagonal.

Here, we are having a square \[ABCD\] with sides \[x{\rm{cm}}\] and the length of the diagonal \[AC = \sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Now, in the right triangle \[ABC\], we will apply the Pythagoras. Therefore, we get
\[{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = {\left( {AB} \right)^2} + {\left( {BC} \right)^2}\]
Substituting the values from the figure, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2} + {\left( x \right)^2}\]
Adding the like terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2{\left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)^2} = 2{x^2}\]
Cancelling out 2 from both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)^2} = {x^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides and neglecting the negative value because the length of side of a square can’t be negative, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 6 + 2\sqrt 5 {\rm{cm}}\]
Therefore, the required length of the side of the square is \[6 + 2\sqrt 5 {\rm{cm}}\]
Hence, this is the required answer.
Note:
An alternate way of solving this question is:
As we know, if the length of the side of a square is \[x\], then using Pythagoras theorem, the length of its diagonal is \[\sqrt 2 x\].
Now, if we compare the length of the side of a square and the length of its diagonal we can notice that, by multiplying the side of a square by \[\sqrt 2 \], we will be able to find the length of the diagonal.
Hence, alternatively, if we divide the length of the diagonal by \[\sqrt 2 \], then, we will be able to find the side of a square.
Using this property, we have the formula,
Side of a square \[ = \] Length of diagonal of the square \[ \div \sqrt 2 \]
Hence, in this question, the diagonal of the square is \[\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\].
Therefore, the required side of the square \[ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right)}}{{\sqrt 2 }} = \left( {6 + 2\sqrt 5 } \right){\rm{cm}}\]
Hence, this is the required answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE





