
The length of a wall is 8 m and its height is 4 m. The wall is 35 cm thick. There is one door of size 2 m \[ \times \] 1 m, and two windows of size \[1.20\] m \[ \times \] 1 m. Find the expenditure of making the wall at the rate of ₹ 1500 per cubic meter.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to find the cost of making the wall. First, we will find out the volume of the cuboid of the given dimensions of the wall. Next, we will find the volumes of the cuboids that need to be removed from the wall for the door and the two windows. The cuboid will have thickness equal to the thickness of the wall. Then, we will use this to find the actual volume of the wall. Finally, we will multiply it with the given rate to find the cost of making the wall.
Formula used:
The volume of a cuboid is given by \[l \times b \times h\], where \[l\] is the length, \[b\] is the breadth, and \[h\] is the height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will draw a diagram as per the given information.
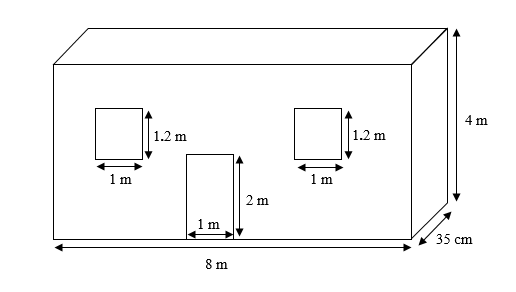
Let us convert all the given dimensions to metres.
We know that 1 centimetre is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{100}}\] metres.
Therefore, we get
Thickness of the wall \[ = 35{\text{ cm}} = 35 \times \dfrac{1}{{100}}{\text{ m}} = 0.35{\text{ m}}\]
Now, we need to find out the volume of the cuboid of the given dimensions of the wall.
The volume of a cuboid is given by the formula \[l \times b \times h\], where \[l\] is the length, \[b\] is the breadth, and \[h\] is the height.
Substituting \[l = 8\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 4\] m in the formula, we get
Volume of the cuboid for the wall \[ = 8 \times 0.35 \times 4{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of the cuboid for the wall \[ = 11.2{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
It is given that there is one door of size 2 m \[ \times \] 1 m, and two windows of size \[1.20\] m \[ \times \] 1 m in the wall.
For the door, a cuboid of size 2 m \[ \times \] 1 m, with thickness equal to the wall must be removed from the wall.
For the windows, two cuboids of size \[1.20\] m \[ \times \] 1 m, with thickness equal to the wall must be removed from the wall.
We will find the volumes of these cuboids and remove them from the total volume of the wall.
Substituting \[l = 2\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 1\] m in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the door \[ = 2 \times 0.35 \times 1{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the door \[ = 0.7{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Substituting \[l = 1.20\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 1\] m in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the window \[ = 1.20 \times 0.35 \times 1{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the window \[ = 0.42{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the equation by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the two windows \[ = 2 \times 0.42{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3} = 0.84{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Now, the volume of the wall can be found by removing the volumes of the cuboids removed for the windows and the door from the total volume of the cuboid of the wall.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the wall \[ = \left( {11.2 - 0.7 - 0.84} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Subtracting the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the wall \[ = 9.66{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Finally, we can calculate the cost of making the wall.
The total cost of making the wall is equal to the product of the volume of the wall in cubic meters, and the cost per cubic meter of making the wall.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total cost of making the wall \[ = 9.66 \times 1500 = 14,490\]
Therefore, we get the cost of making the wall as ₹ 14,490.
Note: We should ensure that all units are in either millimetres or centimetres. A common mistake is to use the 35 cm and multiply it with 4 m and 8 m to get the volume of the wall as 1120 metres. This is incorrect.
Formula used:
The volume of a cuboid is given by \[l \times b \times h\], where \[l\] is the length, \[b\] is the breadth, and \[h\] is the height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will draw a diagram as per the given information.

Let us convert all the given dimensions to metres.
We know that 1 centimetre is equal to \[\dfrac{1}{{100}}\] metres.
Therefore, we get
Thickness of the wall \[ = 35{\text{ cm}} = 35 \times \dfrac{1}{{100}}{\text{ m}} = 0.35{\text{ m}}\]
Now, we need to find out the volume of the cuboid of the given dimensions of the wall.
The volume of a cuboid is given by the formula \[l \times b \times h\], where \[l\] is the length, \[b\] is the breadth, and \[h\] is the height.
Substituting \[l = 8\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 4\] m in the formula, we get
Volume of the cuboid for the wall \[ = 8 \times 0.35 \times 4{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Volume of the cuboid for the wall \[ = 11.2{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
It is given that there is one door of size 2 m \[ \times \] 1 m, and two windows of size \[1.20\] m \[ \times \] 1 m in the wall.
For the door, a cuboid of size 2 m \[ \times \] 1 m, with thickness equal to the wall must be removed from the wall.
For the windows, two cuboids of size \[1.20\] m \[ \times \] 1 m, with thickness equal to the wall must be removed from the wall.
We will find the volumes of these cuboids and remove them from the total volume of the wall.
Substituting \[l = 2\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 1\] m in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the door \[ = 2 \times 0.35 \times 1{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the door \[ = 0.7{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Substituting \[l = 1.20\] m, \[b = 0.35\] m, and \[h = 1\] m in the formula, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the window \[ = 1.20 \times 0.35 \times 1{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the window \[ = 0.42{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Multiplying the equation by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the cuboid removed for the two windows \[ = 2 \times 0.42{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3} = 0.84{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Now, the volume of the wall can be found by removing the volumes of the cuboids removed for the windows and the door from the total volume of the cuboid of the wall.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the wall \[ = \left( {11.2 - 0.7 - 0.84} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Subtracting the terms in the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \]Volume of the wall \[ = 9.66{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^3}\]
Finally, we can calculate the cost of making the wall.
The total cost of making the wall is equal to the product of the volume of the wall in cubic meters, and the cost per cubic meter of making the wall.
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Total cost of making the wall \[ = 9.66 \times 1500 = 14,490\]
Therefore, we get the cost of making the wall as ₹ 14,490.
Note: We should ensure that all units are in either millimetres or centimetres. A common mistake is to use the 35 cm and multiply it with 4 m and 8 m to get the volume of the wall as 1120 metres. This is incorrect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





