
The leaves are modified into tendrils, hooks, pitcher, and bladder in the following plants respectively.
(a) Sweet pea, cat’s nail, Nepenthes,. Utricularia.
(b) Sweet pea, cat’s nail, Utricularia, Nepenthes.
(c) Nepenthes,. cat’s nail, Sweet pea, Utricularia.
(d) Nepenthes,. Sweet pea, cat’s nail, Utricularia.
(e) Utricularia, Nepenthes,. cat’s nail, Sweet pea.
Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: All the mentioned modifications of leaves are the important parts of the plants that help in the performance of various functions. They are helpful in supporting the plants, acting as their defence mechanism, or helping in the process of making food, etc.
Complete answer:
The leaves are the site for the process of photosynthesis to occur, this process is performed by the plants to make their own food. But the plants have other roles as well to which are performed by the leaves but in a modified manner. This type is called the modifications of leaves. They perform different functions according to their structure.
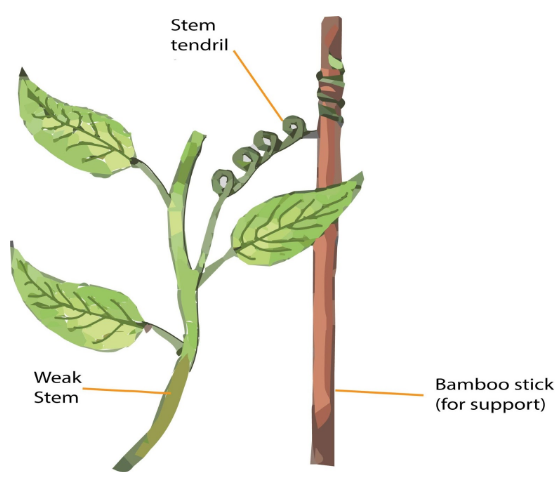
The tendrils are the wiry, skinny, thread-like structures that are curled once they come in contact with an object. They help in providing support to the plants and are generally observed in the case of the pea plants. Hooks are the leaf modification where the end of the leaflets develops a hook-like structure which gives the plants support and helps them in climbing, it is mostly observed in the case of the flowering plants. Example: Cat’s nail, Aloe, etc.
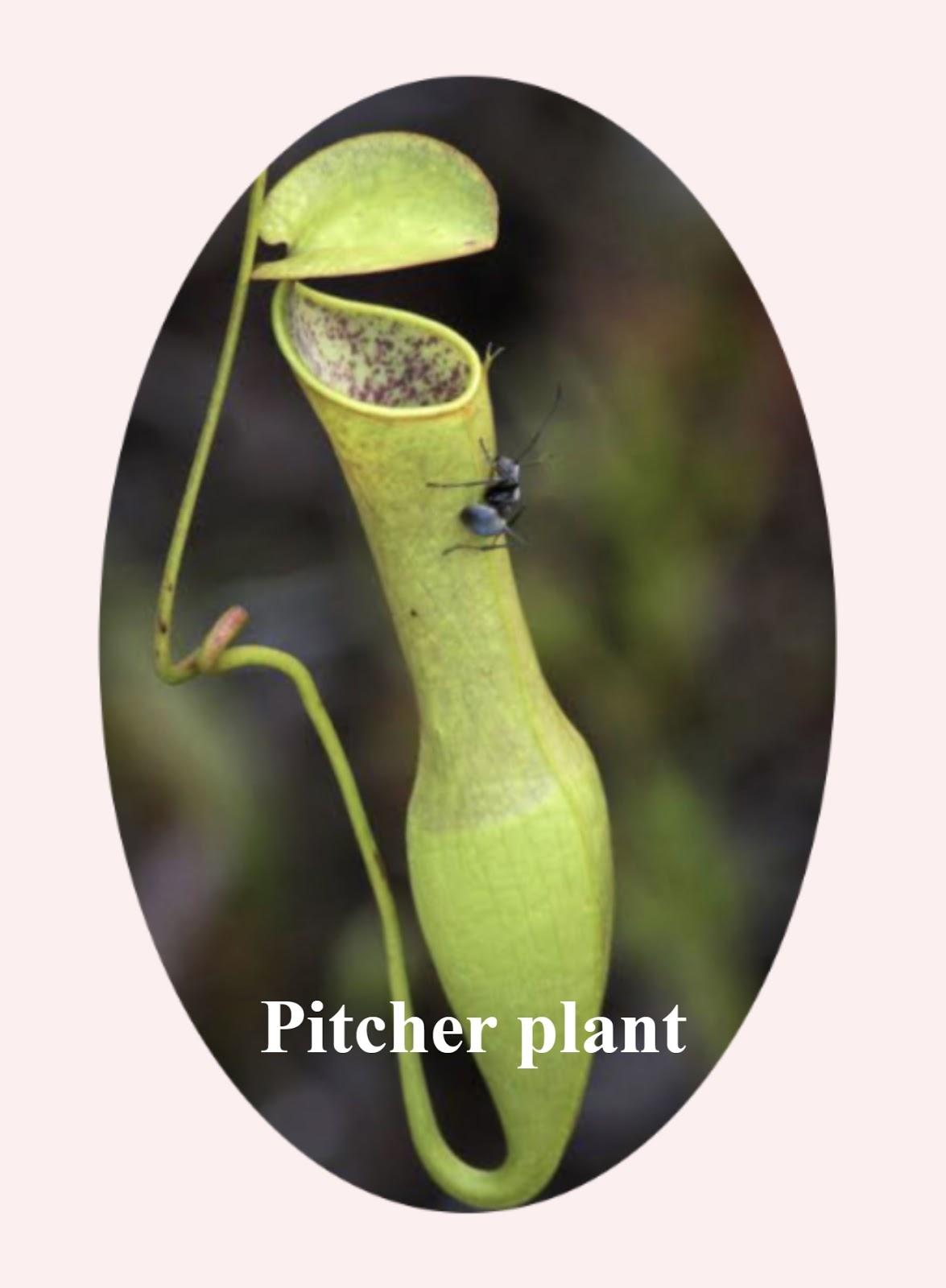
The pitcher is the structure that is formed by certain leaves when they get modified which helps them in catching their prey. This type of plant will be called the carnivorous plant as they trap the insects inside their modified leaves. Example: Nepenthes,. etc. The bladder is performed as a leaf modification in the leaves of the aquatic plants that are found under the water. These bladders help in trapping the insects or their prey inside them. Example: Utricularia.

Note:
A modification of the leaf is phyllode. They are modified petioles of leaves stems. They appear like a leaf and also function like one. In some plants, they may become widened and flattened while the leaf itself becomes reduced or disappears altogether. Phyllode serves the purpose of a leaf. Example: Acacia, Opuntia, etc.
Complete answer:
The leaves are the site for the process of photosynthesis to occur, this process is performed by the plants to make their own food. But the plants have other roles as well to which are performed by the leaves but in a modified manner. This type is called the modifications of leaves. They perform different functions according to their structure.
The tendrils are the wiry, skinny, thread-like structures that are curled once they come in contact with an object. They help in providing support to the plants and are generally observed in the case of the pea plants. Hooks are the leaf modification where the end of the leaflets develops a hook-like structure which gives the plants support and helps them in climbing, it is mostly observed in the case of the flowering plants. Example: Cat’s nail, Aloe, etc.
The pitcher is the structure that is formed by certain leaves when they get modified which helps them in catching their prey. This type of plant will be called the carnivorous plant as they trap the insects inside their modified leaves. Example: Nepenthes,. etc. The bladder is performed as a leaf modification in the leaves of the aquatic plants that are found under the water. These bladders help in trapping the insects or their prey inside them. Example: Utricularia.


Note:
A modification of the leaf is phyllode. They are modified petioles of leaves stems. They appear like a leaf and also function like one. In some plants, they may become widened and flattened while the leaf itself becomes reduced or disappears altogether. Phyllode serves the purpose of a leaf. Example: Acacia, Opuntia, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




