
The larva of scypha is -
(a) Trochophore
(b) Glochidium
(c)Amphiblastula
(d) Coeloblastula
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: In half of the larval body, flagella is present while it is absent in the rest half. They are filter feeders that keep up the flow of water through their construction which passes out from a large opening called oscula. They have a breakable skeleton made up of stiff spicules.
Complete answer:
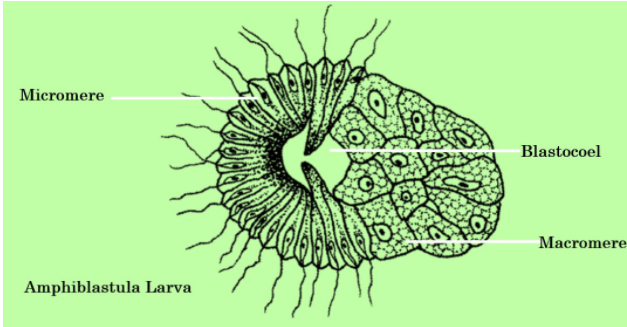
Amphiblastula is a typical free-swimming larva of scypha. Amphiblastula is oval and has a cavity in the middle. The front half of the larva is made up of cylindrical, flagellated cells, while the other half is made up of round cells without flagella. The larva swims keeping the flagellated portion forward.
The amphiblastula is preceded by a stage (stomoblastula) in which the blastula opens outward and is surrounded by round granular cells called macromere, which is distinguished from other cells with flagella (micromere). This is also called the inversion process.
A parenchymal is the most common larval form among the Demospongiae, whose outer layer is of flagellated cells and the inner mass is of non flagellated cells. This larva swims for a period that may vary from a few hours to a few days before it descends to find a surface suitable for attachment. After attachment, the larva metamorphoses into a young sponge through embolic gastrulation.
Scypha, formerly called sycon, belongs to the class Calcarea. It is also known as crown sponge, which is a small, marine sponge found attached to some submerged solid objects like rocks, shells of mollusks, and corals with the help of sticky secretion. It is found in shallow water up to a depth of 300 feet, where waves provide the animal with plenty of food and well-oxygenated water.
Scypha has a syconoid type of structure i.e,finger-like body shape, and is 2.5 to 7.5 cm in length. It has several cylinders, all the cylinders being connected to the base. It is grey or light brown. A single large opening is present at the distal or free end of each cylinder.
So, the correct answer is, ’amphiblastula’.
Note: - Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually.
-The blastula is the central cavity of a hollow mass of cells.
-Phylum Porifera has got Demospongiae the most diverse class. They are the sponges having a soft body that is covered by hard and often massive skeletons made of calcium carbonate, either aragonite or calcite.
- Gastrulation is an early stage in embryonic development during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a multilayered structure.
-Scypha is a branching colonial sponge, though solitary individuals also thrive, and are found in abundance near North Atlantic shores. The different species of Scypha are S. ciliatum, S. elegans, S. coronata, S. lingua, S. gelatinous, and S. Raphanus.
Complete answer:
Amphiblastula is a typical free-swimming larva of scypha. Amphiblastula is oval and has a cavity in the middle. The front half of the larva is made up of cylindrical, flagellated cells, while the other half is made up of round cells without flagella. The larva swims keeping the flagellated portion forward.
The amphiblastula is preceded by a stage (stomoblastula) in which the blastula opens outward and is surrounded by round granular cells called macromere, which is distinguished from other cells with flagella (micromere). This is also called the inversion process.
A parenchymal is the most common larval form among the Demospongiae, whose outer layer is of flagellated cells and the inner mass is of non flagellated cells. This larva swims for a period that may vary from a few hours to a few days before it descends to find a surface suitable for attachment. After attachment, the larva metamorphoses into a young sponge through embolic gastrulation.
Scypha, formerly called sycon, belongs to the class Calcarea. It is also known as crown sponge, which is a small, marine sponge found attached to some submerged solid objects like rocks, shells of mollusks, and corals with the help of sticky secretion. It is found in shallow water up to a depth of 300 feet, where waves provide the animal with plenty of food and well-oxygenated water.
Scypha has a syconoid type of structure i.e,finger-like body shape, and is 2.5 to 7.5 cm in length. It has several cylinders, all the cylinders being connected to the base. It is grey or light brown. A single large opening is present at the distal or free end of each cylinder.
So, the correct answer is, ’amphiblastula’.

Note: - Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually.
-The blastula is the central cavity of a hollow mass of cells.
-Phylum Porifera has got Demospongiae the most diverse class. They are the sponges having a soft body that is covered by hard and often massive skeletons made of calcium carbonate, either aragonite or calcite.
- Gastrulation is an early stage in embryonic development during which the single-layered blastula is reorganized into a multilayered structure.
-Scypha is a branching colonial sponge, though solitary individuals also thrive, and are found in abundance near North Atlantic shores. The different species of Scypha are S. ciliatum, S. elegans, S. coronata, S. lingua, S. gelatinous, and S. Raphanus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




