
The largest synovial joint is
(a) Hip joint
(b) Knee joint
(c) Shoulder joint
(d) Ankle joint
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The largest synovial joint is a type of hinge joint. This synovial joint is present in that part of the body which is often considered to be vulnerable towards the injuries and osteoarthritis.
Complete answer:
The knee joint is the largest synovial joint. It consists of various connections between four bones. In the knee junction, the large femur bone of the thigh will connect with both the tibia and fibula of the leg, and as well as with the patella, or knee cap.
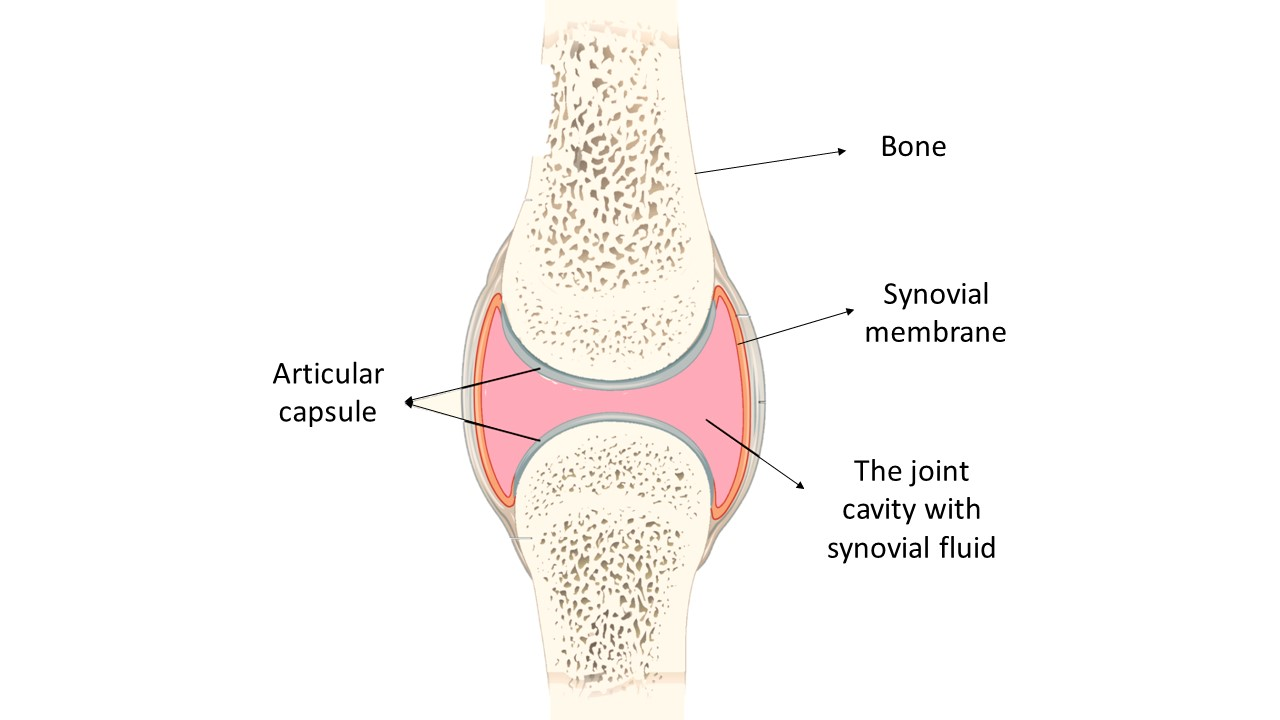
So, the correct answer is, ‘Knee Joint’.
Additional Information:
A joint is a place where two bones contact each other to bring about various movements in our body. The type of joint present will decide the nature and the extent of movement. We can walk, we can run, we can write, speak, etc., which are all made possible only because of the involvement of various joints present in our body.
Joints are classified depending on their structural and functional aspects.
Structural classification of joints
Structurally joints are classified into three types.
- Fibrous joints
- Cartilaginous joints
- Synovial joints
The following table gives the structural classification, nature of movements along with the examples of these joints.
Functional classification: Depending upon the nature and extent of movement, joints are classified into ball and socket joint, pivotal joint, hinge joint, condyloid joint, gliding joint, and saddle joint.
Note: Since the synovial joint allows flexibility in movement, it is vulnerable to injuries. One such example is Rheumatoid arthritis where the immune system will attack the synovial fluid and causes damage to the bones.
Complete answer:
The knee joint is the largest synovial joint. It consists of various connections between four bones. In the knee junction, the large femur bone of the thigh will connect with both the tibia and fibula of the leg, and as well as with the patella, or knee cap.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Knee Joint’.
Additional Information:
A joint is a place where two bones contact each other to bring about various movements in our body. The type of joint present will decide the nature and the extent of movement. We can walk, we can run, we can write, speak, etc., which are all made possible only because of the involvement of various joints present in our body.
Joints are classified depending on their structural and functional aspects.
Structural classification of joints
Structurally joints are classified into three types.
- Fibrous joints
- Cartilaginous joints
- Synovial joints
The following table gives the structural classification, nature of movements along with the examples of these joints.
| Structural classification of joints | Nature of these joints | Examples |
| Fibrous joints | Non- movable joints | The rib cage, upper jaw, the backbone |
| Cartilaginous joints | Partially movable joints | The Spinal cord |
| Synovial joints | Highly flexible joint | Neck joint, shoulder joint, knee joint |
Functional classification: Depending upon the nature and extent of movement, joints are classified into ball and socket joint, pivotal joint, hinge joint, condyloid joint, gliding joint, and saddle joint.
Note: Since the synovial joint allows flexibility in movement, it is vulnerable to injuries. One such example is Rheumatoid arthritis where the immune system will attack the synovial fluid and causes damage to the bones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




