
The largest set of real values of ‘x’ for which \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\le x\] is
(A) \[\left( -1,\infty \right)\]
(B) \[\left( -1,0 \right)\cup \left( 0,\infty \right)\]
(C) \[\left[ 0,\infty \right)\]
(D) \[\left( 0,\infty \right)\]
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Assume \[f\left( x \right)=\ln \left( 1+x \right)-x\] . For \[f\left( x \right)\le 0\] , \[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)\le 0\] . For \[x < -1\] , the expression
\[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. For \[-1 < x < 0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is negative. For \[x=0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is equal to zero. For \[x > 0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. Now, use wavy-method and get the intervals of x where the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is zero or greater than zero. We also know the property that ‘a’ must be greater than zero for \[\ln a\] . So, for \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\] , \[\left( 1+x \right) > 0\] . Now, take the intersection of intervals of x and conclude the answer.
Complete answer:
According to the question, we are given an expression and we are asked to calculate the set of real values of x.
The given expression is \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\le x\] .
On modifying the above expression, we get
\[\ln \left( 1+x \right)-x\le 0\] ……………………………………..(1)
Let us assume that \[f\left( x \right)=\ln \left( 1+x \right)-x\] …………………………………..(2)
On differentiating equation (2), we get
\[\dfrac{df\left( x \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left\{ \ln \left( 1+x \right)-x \right\}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{1+x}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1-\left( 1+x \right)}{1+x} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-x}{1+x}\] ………………………………………(4)
For \[f\left( x \right)\le 0\] we have \[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)\le 0\] …………………………………….(5)
Now, from equation (4) and equation (5), we get
\[\dfrac{-x}{1+x}\le 0\]
\[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\ge 0\] ……………………………………(6)
Using wavy-curve for the above equation, we get
For \[x < -1\] , the numerator as well as the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is positive.
For \[-1 < x < 0\] , the numerator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is negative whereas the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is negative.
For \[x=0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is also equal to zero.
For \[x > 0\] , the numerator as well as the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is positive.
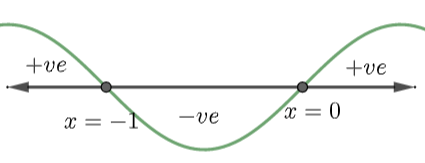
In equation (6), we can observe that we need the expression is greater than zero. So, in wavy-curve, we have to take those intervals where positive sign is lying and from the above diagram, the intervals where positive sign is lying is \[\left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] . So, \[x\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] ……………………………..(7)
We also know the property that ‘a’ must be greater than zero for \[\ln a\] ……………………………..(8)
Now, from equation (1) and equation (8), we have
\[\left( 1+x \right) > 0\]
\[x > -1\] …………………………………….(9)
Now, from equation (7) and equation (9), we get
\[x\in \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] .
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
In this question, one might do a silly mistake and conclude the intervals of x after calculating from wavy-curvy method and miss the point that for defining the function \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\] , \[\left( 1+x \right)\] must be greater than zero. So, whenever this type of question appears, also calculate the intervals where the function is defined.
\[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. For \[-1 < x < 0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is negative. For \[x=0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is equal to zero. For \[x > 0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. Now, use wavy-method and get the intervals of x where the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is zero or greater than zero. We also know the property that ‘a’ must be greater than zero for \[\ln a\] . So, for \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\] , \[\left( 1+x \right) > 0\] . Now, take the intersection of intervals of x and conclude the answer.
Complete answer:
According to the question, we are given an expression and we are asked to calculate the set of real values of x.
The given expression is \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\le x\] .
On modifying the above expression, we get
\[\ln \left( 1+x \right)-x\le 0\] ……………………………………..(1)
Let us assume that \[f\left( x \right)=\ln \left( 1+x \right)-x\] …………………………………..(2)
On differentiating equation (2), we get
\[\dfrac{df\left( x \right)}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left\{ \ln \left( 1+x \right)-x \right\}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{1+x}-1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{1-\left( 1+x \right)}{1+x} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-x}{1+x}\] ………………………………………(4)
For \[f\left( x \right)\le 0\] we have \[{{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)\le 0\] …………………………………….(5)
Now, from equation (4) and equation (5), we get
\[\dfrac{-x}{1+x}\le 0\]
\[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\ge 0\] ……………………………………(6)
Using wavy-curve for the above equation, we get
For \[x < -1\] , the numerator as well as the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is positive.
For \[-1 < x < 0\] , the numerator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is negative whereas the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is negative.
For \[x=0\] , the expression \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is also equal to zero.
For \[x > 0\] , the numerator as well as the denominator of \[\dfrac{x}{1+x}\] is positive. It means that the whole expression is positive.

In equation (6), we can observe that we need the expression is greater than zero. So, in wavy-curve, we have to take those intervals where positive sign is lying and from the above diagram, the intervals where positive sign is lying is \[\left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] . So, \[x\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] ……………………………..(7)
We also know the property that ‘a’ must be greater than zero for \[\ln a\] ……………………………..(8)
Now, from equation (1) and equation (8), we have
\[\left( 1+x \right) > 0\]
\[x > -1\] …………………………………….(9)
Now, from equation (7) and equation (9), we get
\[x\in \left[ 0,\infty \right)\] .
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
In this question, one might do a silly mistake and conclude the intervals of x after calculating from wavy-curvy method and miss the point that for defining the function \[\ln \left( 1+x \right)\] , \[\left( 1+x \right)\] must be greater than zero. So, whenever this type of question appears, also calculate the intervals where the function is defined.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




