
The ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ of maleic acid is lesser than of ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ fumaric acid due to:
A. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in fumaric acid.
B. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid.
C. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid.
D. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in fumaric acid.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: In maleic acid two carboxylic groups are on the same side. In fumaric acid two carboxylic groups are on the opposite side. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is found between the groups within the molecule. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is found between two groups of two molecules.
Complete answer:
The structure of the maleic and fumaric acid is as follows:
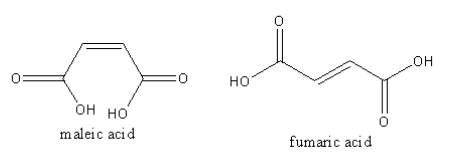
By releasing one proton maleic acid forms anion. Because both carboxylic groups are on the same side. The anionic oxygen forms hydrogen bonding with nearby hydrogen available at another carboxylic group. Similarly fumaric acid also forms anion but as both carboxylic groups are on the different side. So, the anion of fumaric acid cannot form hydrogen bonding. Hence anion of maleic acid is more stable than the anion of fumaric acid.
>The hydrogen bonding between two carboxylic groups of a maleic molecule, is known as intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
>The hydrogen bonding between two carboxylic groups of two fumaric acid molecules is known as intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
The intramolecular hydrogen bonding in maleic acid is shown as follows:
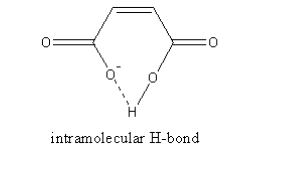
So, the maleic acid does not lose the second proton whereas the fumaric acid can lose the second proton easily so, ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ fumaric acid is more than the ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ maleic acid.
So, ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ of maleic acid is lesser than of ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ fumaric acid due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid.
Therefore, option (B) intramolecular hydrogen in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid is correct.
Note:The hydrogen is bonded between two most electronegative fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen atoms, the bond is known as hydrogen bonding. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is more stable than intermolecular hydrogen bonding. On adding a non-polar solvent the intermolecular hydrogen bonding breaks. The addition of non-polar solvent does not affect intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete answer:
The structure of the maleic and fumaric acid is as follows:

By releasing one proton maleic acid forms anion. Because both carboxylic groups are on the same side. The anionic oxygen forms hydrogen bonding with nearby hydrogen available at another carboxylic group. Similarly fumaric acid also forms anion but as both carboxylic groups are on the different side. So, the anion of fumaric acid cannot form hydrogen bonding. Hence anion of maleic acid is more stable than the anion of fumaric acid.
>The hydrogen bonding between two carboxylic groups of a maleic molecule, is known as intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
>The hydrogen bonding between two carboxylic groups of two fumaric acid molecules is known as intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
The intramolecular hydrogen bonding in maleic acid is shown as follows:

So, the maleic acid does not lose the second proton whereas the fumaric acid can lose the second proton easily so, ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ fumaric acid is more than the ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ maleic acid.
So, ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ of maleic acid is lesser than of ${{\text{K}}_{{\text{a2}}}}$ fumaric acid due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid.
Therefore, option (B) intramolecular hydrogen in the ion formed after one proton removal in maleic acid is correct.
Note:The hydrogen is bonded between two most electronegative fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen atoms, the bond is known as hydrogen bonding. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is more stable than intermolecular hydrogen bonding. On adding a non-polar solvent the intermolecular hydrogen bonding breaks. The addition of non-polar solvent does not affect intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




