
The IUPAC name of the following compound is:
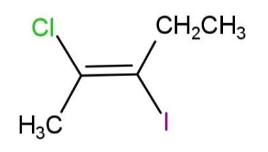
A. trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene
B. cis-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
C. trans-3-iodo-4-chloro-3-pentene
D. cis-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint:IUPAC is the international union for pure and applied chemistry. It has made certain rules for the naming of organic compounds. Cis and trans are known as two different isomers of the same compound, they are position isomers.
Complete step-by-step answer:The naming of organic compounds is done by following the norms and standards given by IUPAC. According to IUPAC, some of the nomenclature rules followed in compounds with double or triple bonds, and functional groups, are:
-the longest possible carbon chain is selected for naming that contains functional groups and maximum multiple bonds.
- numbering is done in a way that functional groups get the lowest possible numbers, followed by multiple bonds.
- two or more similar groups are given the prefix, di, tri, tetra, etc.
- among more than two functional groups, one is taken as principal group while others as substituent groups.
- when unsaturated compounds contain atoms on the same adjacent carbon, then it is called as cis, while when on the opposite side, it is called trans.
We are given a compound that has chlorine and iodine as functional groups. We will number the longest chain. Starting from the methyl group, and ending on the ethyl group, we will number them 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 carbons. Carbon-2 and 3 appear with a double bond. Since the functional groups are on opposite sides, it will be named as trans.
So, the name will be trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene. Hence, option A is correct.
Note:The parent hydrocarbon chain consists of 5 carbons, with a double bond at carbon-2, so it is named as 2-pentene. For, naming a continuous carbon chain is selected, so this chain cannot start from the carbon having Cl, or I atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:The naming of organic compounds is done by following the norms and standards given by IUPAC. According to IUPAC, some of the nomenclature rules followed in compounds with double or triple bonds, and functional groups, are:
-the longest possible carbon chain is selected for naming that contains functional groups and maximum multiple bonds.
- numbering is done in a way that functional groups get the lowest possible numbers, followed by multiple bonds.
- two or more similar groups are given the prefix, di, tri, tetra, etc.
- among more than two functional groups, one is taken as principal group while others as substituent groups.
- when unsaturated compounds contain atoms on the same adjacent carbon, then it is called as cis, while when on the opposite side, it is called trans.
We are given a compound that has chlorine and iodine as functional groups. We will number the longest chain. Starting from the methyl group, and ending on the ethyl group, we will number them 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 carbons. Carbon-2 and 3 appear with a double bond. Since the functional groups are on opposite sides, it will be named as trans.
So, the name will be trans-2-chloro-3-iodo-2-pentene. Hence, option A is correct.
Note:The parent hydrocarbon chain consists of 5 carbons, with a double bond at carbon-2, so it is named as 2-pentene. For, naming a continuous carbon chain is selected, so this chain cannot start from the carbon having Cl, or I atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




