
: The IUPAC name of the crotonaldehyde is
A. Butenaldehyde
B. Butanal-1
C. But-2-en-1-al
D. prop-2-en-1-ol
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint:IUPAC name is used for the nomenclature of a compound. The nomenclature is done taking in count the number of carbon atoms existing in the longest chain and the substituents attached to it.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of crotonaldehyde is as follows-

The IUPAC name of the crotonaldehyde is But-2-en-1-al.
-Crotonaldehyde is a colorless liquid having a pungent, suffocating odor and has the chemical formula ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CH = CHCHO}}$. Crotonaldehyde are also commonly called as Crotonic aldehyde, 2-butenal, ${\rm{\beta }} - $Methacrolein, ${\rm{\beta }} - $Methyl acrolein, Propylene aldehyde etc. The Crotonaldehyde is found as either E-isomer and Z-isomer. Crotonaldehyde has a molar mass of 70.091 g.mol-1. It has a boiling point of ${\rm{104}}{\rm{.}}{{\rm{0}}^{\rm{^\circ }}}{\rm{C}}$and melting point $ - {76.5^{\rm{^\circ }}}{\rm{C}}$. Crotonaldehyde is soluble in ethyl ether, ethanol, acetone, chloroform etc. It is miscible in benzene.
-Crotonaldehyde works as an excellent prochiral dienophile. Crotonaldehyde is also used as an intermediate in the organic synthesis, it is used as a Precursor to fine chemicals, for the production of sorbic acid.
-Crotonaldehyde can be prepared from acetaldehyde in the following way:
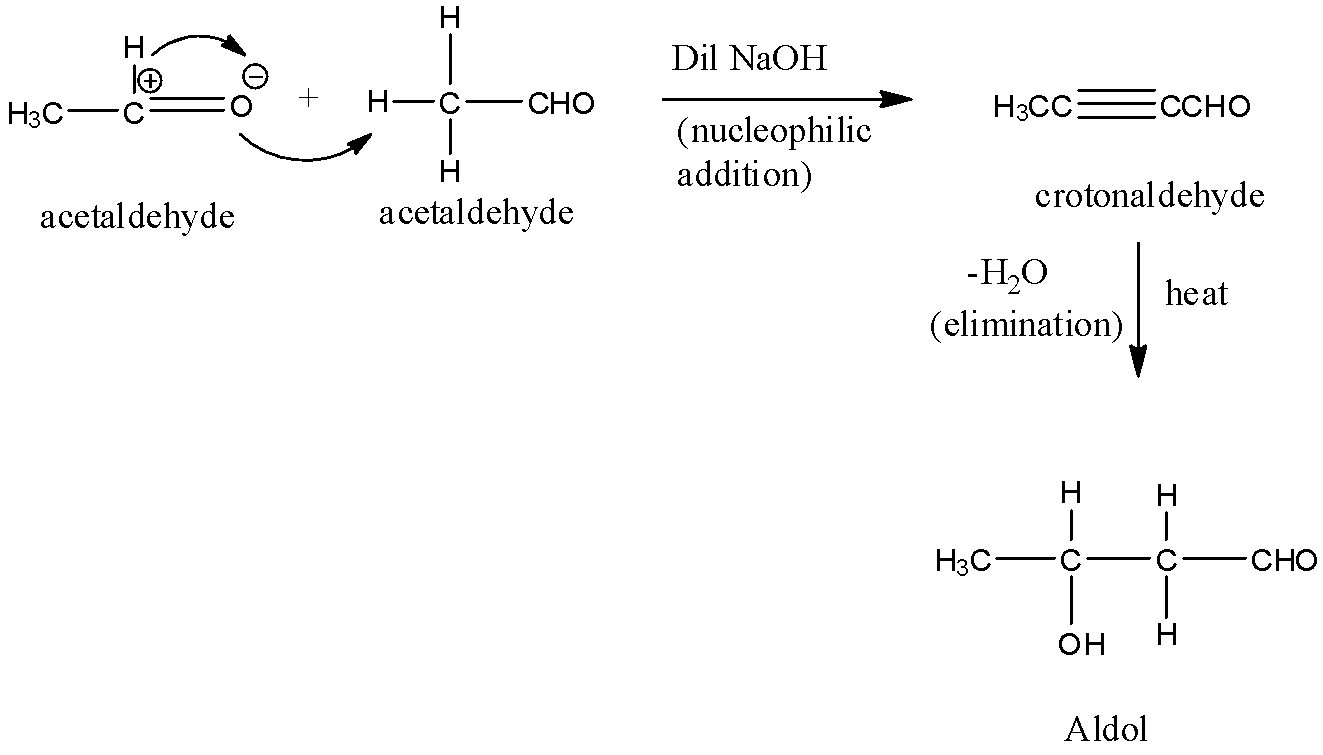
Two acetaldehyde reacts with dilute NaOH by the process of nucleophilic addition to produce crotonaldehyde. The crotonaldehyde on further heating leads to the generation of an aldol by the elimination of the water molecule.
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
Crotonaldehyde has the chemical formula ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{O}}$. According to IUPAC nomenclature, Crotonaldehyde is called or named as But-2-en-1-al. Crotonaldehyde is colorless and it has a pungent and suffocating odor.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of crotonaldehyde is as follows-

The IUPAC name of the crotonaldehyde is But-2-en-1-al.
-Crotonaldehyde is a colorless liquid having a pungent, suffocating odor and has the chemical formula ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CH = CHCHO}}$. Crotonaldehyde are also commonly called as Crotonic aldehyde, 2-butenal, ${\rm{\beta }} - $Methacrolein, ${\rm{\beta }} - $Methyl acrolein, Propylene aldehyde etc. The Crotonaldehyde is found as either E-isomer and Z-isomer. Crotonaldehyde has a molar mass of 70.091 g.mol-1. It has a boiling point of ${\rm{104}}{\rm{.}}{{\rm{0}}^{\rm{^\circ }}}{\rm{C}}$and melting point $ - {76.5^{\rm{^\circ }}}{\rm{C}}$. Crotonaldehyde is soluble in ethyl ether, ethanol, acetone, chloroform etc. It is miscible in benzene.
-Crotonaldehyde works as an excellent prochiral dienophile. Crotonaldehyde is also used as an intermediate in the organic synthesis, it is used as a Precursor to fine chemicals, for the production of sorbic acid.
-Crotonaldehyde can be prepared from acetaldehyde in the following way:

Two acetaldehyde reacts with dilute NaOH by the process of nucleophilic addition to produce crotonaldehyde. The crotonaldehyde on further heating leads to the generation of an aldol by the elimination of the water molecule.
Hence, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
Crotonaldehyde has the chemical formula ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{O}}$. According to IUPAC nomenclature, Crotonaldehyde is called or named as But-2-en-1-al. Crotonaldehyde is colorless and it has a pungent and suffocating odor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




