
What will be the IUPAC name of the Acetic acid compound?
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: Monocarboxylic acid or alkanoic acids are organic compounds with $ - COOH$ as its functional group, where one hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by a carboxyl group. The IUPAC system recommends that alkanoic acids are named by replacing the terminal ‘-e’ of the alkane by ‘-oic acid’ to name the alkanoic acid
Complete answer:
The IUPAC name of acetic acid is ethanoic acid with chemical formula $C{H_3}COOH$. Acetic acid is the simplest monocarboxylic acid containing only two carbon atoms bonded by single bonds.
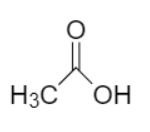
In earlier days, the organic compounds were used to be named after the source from which they were obtained. Acetic acid is produced naturally when excreted by bacteria like Acetobacter genus and Clostridium acetobutylicum making it the common or trivial name of ethanoic acid.
Ethanoic acid or acetic acid belongs to the family of organic fatty acid and carboxylic groups. It contains carboxylic acid as a functional group. Acetic acid or ethanoic acid is a compound in which one hydrogen atom in a methane molecule is replaced by a carboxyl group. Moreover, in Ethanoic acid the word root is ‘eth’, while the primary suffix is ‘ane’ and the secondary suffix is ‘oic acid’. Ethanoic acid is considered as the second simplest carboxylic acid.
Note:
Acetic acid plays a role of protic solvent, food acidity regulator and even an antimicrobial food preservative. Acetic acid is the conjugate acid of acetate. Ethanoic acid is a colourless organic compound with a strong vinegar-like odor. It is also a very important chemical reagent and industrial chemical used in the production of cellulose acetate, polyvinyl acetate and in synthetic fibers and fabrics.
Complete answer:
The IUPAC name of acetic acid is ethanoic acid with chemical formula $C{H_3}COOH$. Acetic acid is the simplest monocarboxylic acid containing only two carbon atoms bonded by single bonds.

In earlier days, the organic compounds were used to be named after the source from which they were obtained. Acetic acid is produced naturally when excreted by bacteria like Acetobacter genus and Clostridium acetobutylicum making it the common or trivial name of ethanoic acid.
Ethanoic acid or acetic acid belongs to the family of organic fatty acid and carboxylic groups. It contains carboxylic acid as a functional group. Acetic acid or ethanoic acid is a compound in which one hydrogen atom in a methane molecule is replaced by a carboxyl group. Moreover, in Ethanoic acid the word root is ‘eth’, while the primary suffix is ‘ane’ and the secondary suffix is ‘oic acid’. Ethanoic acid is considered as the second simplest carboxylic acid.
Note:
Acetic acid plays a role of protic solvent, food acidity regulator and even an antimicrobial food preservative. Acetic acid is the conjugate acid of acetate. Ethanoic acid is a colourless organic compound with a strong vinegar-like odor. It is also a very important chemical reagent and industrial chemical used in the production of cellulose acetate, polyvinyl acetate and in synthetic fibers and fabrics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




