
The IUPAC name of compound $C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH{{\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}}$ is:
A) 1, 1-dimethyl-2-propane
B) 2-vinyl propene
C) 3-methyl-1-butene
D) 2-vinyl propane
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: In IUPAC naming system, unsaturated hydrocarbons are named in such a way that the parent chain containing multiple bonds has the lowest number.
Complete step by step answer:
$C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)$is an alkene molecule.
First of all we need to understand what IUPAC nomenclature is. In chemical nomenclature, IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
One needs to follow certain rules while naming alkenes in IUPAC naming system.
1. The parent chain chosen is the longest chain that must include both carbon atoms of the double bond.
2. The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a double bond carbon atom. If the double bond is in the center of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts.
3. Double bonds in hydrocarbon are indicated by replacing the suffix – ane with ene.
4. If more than one double bond is present the compound is named as a diene, triene or equivalent prefix indicating the number of double bonds, and each double bond is assigned a locator number.
Considering the following information we can now name the organic compound.
Considering the parent chain and numbering the organic molecule
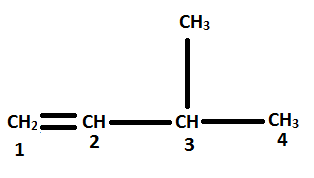
Thus, the name of the organic compound is 3-methyl-1-butene. Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
A student might write 3-methyl-1-butene as 3-methyl-but-1-ene as well. Both are correct. Also, students must be very careful while naming unsaturated hydrocarbons containing both double and triple bonds. While assigning priority, double bonds are given more priority than triple bonds. The location of double bond is indicated before the parent name while the location of the triple bond is indicated between the -en and –yne suffixes (notice that the e is left off, -en is used instead of -ene).
For example,
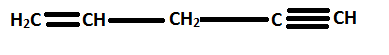 is named as pent-1-en-4-yne.
is named as pent-1-en-4-yne.
Complete step by step answer:
$C{{H}_{2}}=CH-CH\left( C{{H}_{3}} \right)$is an alkene molecule.
First of all we need to understand what IUPAC nomenclature is. In chemical nomenclature, IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
One needs to follow certain rules while naming alkenes in IUPAC naming system.
1. The parent chain chosen is the longest chain that must include both carbon atoms of the double bond.
2. The root chain must be numbered from the end nearest a double bond carbon atom. If the double bond is in the center of the chain, the nearest substituent rule is used to determine the end where numbering starts.
3. Double bonds in hydrocarbon are indicated by replacing the suffix – ane with ene.
4. If more than one double bond is present the compound is named as a diene, triene or equivalent prefix indicating the number of double bonds, and each double bond is assigned a locator number.
Considering the following information we can now name the organic compound.
Considering the parent chain and numbering the organic molecule

Thus, the name of the organic compound is 3-methyl-1-butene. Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
A student might write 3-methyl-1-butene as 3-methyl-but-1-ene as well. Both are correct. Also, students must be very careful while naming unsaturated hydrocarbons containing both double and triple bonds. While assigning priority, double bonds are given more priority than triple bonds. The location of double bond is indicated before the parent name while the location of the triple bond is indicated between the -en and –yne suffixes (notice that the e is left off, -en is used instead of -ene).
For example,
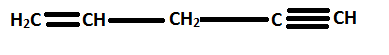
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




