
The IUPAC name of \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}\left( {{\text{Cl}}} \right){\text{ = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right) - {\text{CH}}\left( {{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\] is:
(A) \[6 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 5 - methylhept - 5 - en - 1 - yne\]
(B) \[6 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 5 - methylhept - 1 - yn - 5 - ene\]
(C) \[2 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhept - 2 - yn - 6 - ene\]
(D) \[2 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhept - 6 - yn - 2 - ene\]
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: In the IUPAC name, find out the longest continuous carbon atom chain. It will be a parent chain. Decide the priority order of functional groups, and number the chain from the side which gives lowest possible locants. Write the names of substituents in alphabetical order.
Complete step by step answer:
Write the structure of the given compound and identify the parent chain:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}\left( {{\text{Cl}}} \right){\text{ = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right) - {\text{CH}}\left( {{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\]
The parent chain contains 7 carbon atoms. Hence, it is derivative of heptane. Also it contains a carbon-carbon double bond and carbon-carbon triple bond. Hence, it is a derivative of heptynene.
When several functional groups are present in a molecule, certain functional groups have priority over the above functional group.
In the given molecule, carbon-carbon double bond, carbon-carbon triple bond and chloro groups are present as the functional groups. Chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond gets priority over carbon-carbon triple bond.
The parent chain can be numbered from either the right hand side containing carbon-carbon triple bond or from left hand side containing chlorine substituent and carbon-carbon double bond.
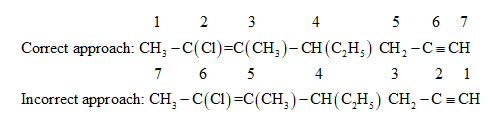
If the parent chain is numbered from the right hand side containing a carbon-carbon triple bond, the IUPAC name will be \[6 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 5 - methylhept - 5 - en - 1 - yne\] .
If the parent chain is numbered from the left hand side containing chlorine substituent and carbon-carbon double bond, the IUPAC name will be \[2 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhept - 2 - yn - 6 - ene\] .
Since the chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond gets priority over the carbon-carbon triple bond, the parent chain is numbered from the end containing the chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond.
While writing the IUPAC name, write the substituent names in the alphabetical order.
The alphabetical order of substituent names is chloro group, ethyl group followed by methyl group. The positions of double and triple bond are represented in the name of parent hydrocarbon itself as \[hept - 2 - yn - 6 - ene\] . Here, ‘yn’ represents a carbon-carbon triple bond and ‘en’ represents a carbon-carbon double bond.
Hence, the correct option is the option (C).
Note: Ensure correct numbering of each and every carbon atom bearing the substituents. Make sure that substituents are named in the alphabetical order. Identify the correct order for the priority of various functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Write the structure of the given compound and identify the parent chain:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}\left( {{\text{Cl}}} \right){\text{ = C}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right) - {\text{CH}}\left( {{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\]
The parent chain contains 7 carbon atoms. Hence, it is derivative of heptane. Also it contains a carbon-carbon double bond and carbon-carbon triple bond. Hence, it is a derivative of heptynene.
When several functional groups are present in a molecule, certain functional groups have priority over the above functional group.
In the given molecule, carbon-carbon double bond, carbon-carbon triple bond and chloro groups are present as the functional groups. Chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond gets priority over carbon-carbon triple bond.
The parent chain can be numbered from either the right hand side containing carbon-carbon triple bond or from left hand side containing chlorine substituent and carbon-carbon double bond.
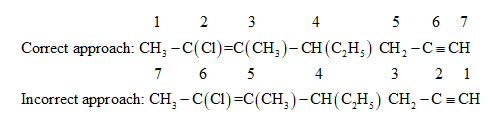
If the parent chain is numbered from the right hand side containing a carbon-carbon triple bond, the IUPAC name will be \[6 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 5 - methylhept - 5 - en - 1 - yne\] .
If the parent chain is numbered from the left hand side containing chlorine substituent and carbon-carbon double bond, the IUPAC name will be \[2 - chloro - 4 - ethyl - 3 - methylhept - 2 - yn - 6 - ene\] .
Since the chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond gets priority over the carbon-carbon triple bond, the parent chain is numbered from the end containing the chloro group and carbon-carbon double bond.
While writing the IUPAC name, write the substituent names in the alphabetical order.
The alphabetical order of substituent names is chloro group, ethyl group followed by methyl group. The positions of double and triple bond are represented in the name of parent hydrocarbon itself as \[hept - 2 - yn - 6 - ene\] . Here, ‘yn’ represents a carbon-carbon triple bond and ‘en’ represents a carbon-carbon double bond.
Hence, the correct option is the option (C).
Note: Ensure correct numbering of each and every carbon atom bearing the substituents. Make sure that substituents are named in the alphabetical order. Identify the correct order for the priority of various functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




