
The IUPAC name of \[C{H_3} - C\left( {C{H_3}} \right)\left( {OH} \right)C{H_2} - CH{\left( {CH{}_3} \right)_2}\] is
A. \[2,4\]-dimethylpenta-\[2\]-ol
B. \[2,4\]-dimethylpenta-\[4\]-ol
C. \[2,2\]-dimethylbutane
D. \[2,4,4\]-trimethylbutan-\[2\]-ol
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The carbon which is attached to the preferred functional group will begin the numbering of carbon atoms. The lower the number bearing the functional group is lowered.
Complete step by step answer:
There are certain rules for naming the compounds following IUPAC nomenclature. At first the functional group has to be identified. In this case it is an alcohol specifically a tertiary alcohol. Also the given hydrocarbon is a branched chain hydrocarbon.
For naming branched chain numbering is done so that the maximum number of carbon atoms is numbered leading to a longest possible chain. Thus the maximum of carbon atoms is five for the given compound. So it is a pentane alkane chain.
The alcohol is named by replacing the suffix –ane with -anol. The position of the hydroxyl group written on the parent chain is indicated by placing the number in front of the base alkane name.
The hydroxyl group takes precedence over other alkyl or halogen substituents attached to the parent chain. If double bonds and hydroxyl groups are present the –en suffix is followed by ol.
Thus the numbering of the carbon atom is done as follows:
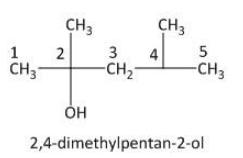
From the above picture the hydroxyl group is attached to the \[C_2\] carbon atom. Two methyl groups are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain, one at \[C_2\] and one at\[C_4\]. Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is \[2,4\]-dimethylpenta-\[2\]-ol.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
A molecule’s longest chain of carbons connected by single bonds is considered as the base for naming compounds by IUPAC nomenclature. The chain can be a continuous chain or a ring.
Complete step by step answer:
There are certain rules for naming the compounds following IUPAC nomenclature. At first the functional group has to be identified. In this case it is an alcohol specifically a tertiary alcohol. Also the given hydrocarbon is a branched chain hydrocarbon.
For naming branched chain numbering is done so that the maximum number of carbon atoms is numbered leading to a longest possible chain. Thus the maximum of carbon atoms is five for the given compound. So it is a pentane alkane chain.
The alcohol is named by replacing the suffix –ane with -anol. The position of the hydroxyl group written on the parent chain is indicated by placing the number in front of the base alkane name.
The hydroxyl group takes precedence over other alkyl or halogen substituents attached to the parent chain. If double bonds and hydroxyl groups are present the –en suffix is followed by ol.
Thus the numbering of the carbon atom is done as follows:

From the above picture the hydroxyl group is attached to the \[C_2\] carbon atom. Two methyl groups are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain, one at \[C_2\] and one at\[C_4\]. Thus the IUPAC name of the given compound is \[2,4\]-dimethylpenta-\[2\]-ol.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
A molecule’s longest chain of carbons connected by single bonds is considered as the base for naming compounds by IUPAC nomenclature. The chain can be a continuous chain or a ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




