
The IUPAC name of allyl chloride is:
(A) 1-chloroethane
(B) 3-chloro-1-propyne
(C) 3-chloro-1-propene
(D) 1-chloropropene
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The organic molecule with chemical formula $C{{H}_{2}}=CHC{{H}_{2}}Cl$ is known as Allyl chloride. Allyl chloride is colourless and water-insoluble liquid but is soluble in other common solvents.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structure of allyl chloride is given below-
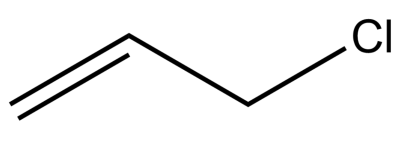
-Since, allyl chloride has a parent chain with three carbons and one double bond, hence the name of the parent chain will be propene. As according to IUPAC nomenclature, the priority for numbering is given to double bond, rather than chlorine atom.
-So, the IUPAC nomenclature of allyl chloride is- 3-Chloroprop-1-ene
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
-Allyl chloride was first produced by reacting allyl alcohol with phosphorous trichloride.
-Allyl chloride on the industrial scale is produced by chlorination of propylene. At lower temperatures, the main product formed is 1,2-dichloropropane, but at higher temperatures (at about $500{}^\circ C$), allyl chloride predominates which is formed by a free radical reaction.
$C{{H}_{3}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to ClC{{H}_{2}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl$
Note: Let us now see the uses and safety of allyl chloride. Allyl chloride is an alkylating agent that is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and pesticides. The maximum of the allyl chloride produced is converted to epichlorohydrin. Some other commercially available allyl derivatives include allyl alcohol, allylamine, allyl isothiocyanate (which is also called synthetic mustard oil), and 1-bromo-3-chloropropane. Allyl cyanide is a reactive halide which is a derivative of allyl chloride. Allyl cyanide undergoes reductive coupling to give diallyl.
$2ClC{{H}_{2}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+Mg\to {{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}{{(CH=C{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}+MgC{{l}_{2}}$
Allyl chloride is highly toxic and flammable, hence needs to handled with safety while using. Allyl chloride can cause eye effect may be delayed and may lead to the possible impairment of vision.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structure of allyl chloride is given below-

-Since, allyl chloride has a parent chain with three carbons and one double bond, hence the name of the parent chain will be propene. As according to IUPAC nomenclature, the priority for numbering is given to double bond, rather than chlorine atom.
-So, the IUPAC nomenclature of allyl chloride is- 3-Chloroprop-1-ene
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Additional information:
-Allyl chloride was first produced by reacting allyl alcohol with phosphorous trichloride.
-Allyl chloride on the industrial scale is produced by chlorination of propylene. At lower temperatures, the main product formed is 1,2-dichloropropane, but at higher temperatures (at about $500{}^\circ C$), allyl chloride predominates which is formed by a free radical reaction.
$C{{H}_{3}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to ClC{{H}_{2}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl$
Note: Let us now see the uses and safety of allyl chloride. Allyl chloride is an alkylating agent that is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and pesticides. The maximum of the allyl chloride produced is converted to epichlorohydrin. Some other commercially available allyl derivatives include allyl alcohol, allylamine, allyl isothiocyanate (which is also called synthetic mustard oil), and 1-bromo-3-chloropropane. Allyl cyanide is a reactive halide which is a derivative of allyl chloride. Allyl cyanide undergoes reductive coupling to give diallyl.
$2ClC{{H}_{2}}CH=C{{H}_{2}}+Mg\to {{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}{{(CH=C{{H}_{2}})}_{2}}+MgC{{l}_{2}}$
Allyl chloride is highly toxic and flammable, hence needs to handled with safety while using. Allyl chloride can cause eye effect may be delayed and may lead to the possible impairment of vision.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




