
The intercepts on the straight line $y = mx$ by the lines $y = 2$ and $y = 6$ is less than $5$, then $m$ belongs to which of the following ranges?
A. $\left( {\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3},\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$
B. $\left( {\dfrac{4}{3},\dfrac{8}{3}} \right)$
C. $\left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{4}{3},\infty } \right)$
D. $\left( {\dfrac{4}{3},\infty } \right)$
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given three equations of lines and distance is given between their intersection points. Start by finding the intersection point of the two pairs of lines- $y = 2$ and $y = mx$, $y = 6$ and $y = mx$ by substituting the values of y and then find their x-coordinate. Then we have the distance between the two points. Form an equation using distance formula, and find the range within which m lies.
Formula used: Distance between the two points $\left( {{x_1},{x_2}} \right)$ and $\left( {{y_1},{y_2}} \right)$ is,
$d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given three equations of lines. Let’s start by numbering the equations in order to avoid any confusion.
$y = mx$ …….... (1)
$y = 2$ …...…. (2)
$y = 6$ …….... (3)
Now, to find the intercepts, we will find the intersection points.
Intersection point of equation (1) and (2)
$ \Rightarrow y = mx,y = 2$
Putting $y = 2$ in equation (1),
$ \Rightarrow 2 = mx$
Shifting m to the other side to find x-coordinate.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{2}{m}$
Therefore, the intersection point of equation (1) and (2) is - $\left( {\dfrac{2}{m},2} \right)$
Next, we will find intersection point of equation (1) and (3)-
$ \Rightarrow y = mx,y = 6$
Putting $y = 6$ in equation (1),
$ \Rightarrow 6 = mx$
Shifting m to the other side to find x-coordinate.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{6}{m}$
Therefore, the intersection point of equation (1) and (3) is - $\left( {\dfrac{6}{m},6} \right)$.
It is given that the distance between the two intersection points is less than 5. Using distance formula,$d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $between the two points $\left( {\dfrac{2}{m},2} \right)$ and $\left( {\dfrac{6}{m},6} \right)$, form an equation.
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{6}{m} - \dfrac{2}{m}} \right)}^2} + {{(6 - 2)}^2}} < 5$
Squaring both the sides,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{m}} \right)^2} + {4^2} < 25$
Simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} + 16 < 25$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} < 25 - 16$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} < 9$
Taking everything on one side,
$ \Rightarrow 9{m^2} - 16 > 0$
Making factors on LHS using ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$,
$ \Rightarrow (3m - 4)(3m + 4) > 0$
$ \Rightarrow 3m - 4 > 0,3m + 4 < 0$
$ \Rightarrow m > \dfrac{4}{3},m < \dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}$
Now, let's plot the values of m on the number line and use a wavy curve method to find the range of m.
In this method, we simply plot the points on the number line and start marking + and – in every range that is made due to the points, starting marking + from the right. See how it is done below.
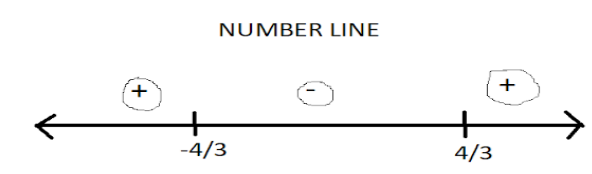
Now, since we are asked for the range greater than 0 as shown in this equation- $ \Rightarrow (3m - 4)(3m + 4) > 0$, we will take the range from the number line which has been marked as positive.
Therefore, $m \in \left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{4}{3},\infty } \right)$.
Option C is the correct answer.
Note: The students might not be aware about the wavy curve method but it is a very simple method and is used to find out the range. While using this method, we should always start marking the ranges as positive starting from right as done in this question.
Formula used: Distance between the two points $\left( {{x_1},{x_2}} \right)$ and $\left( {{y_1},{y_2}} \right)$ is,
$d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given three equations of lines. Let’s start by numbering the equations in order to avoid any confusion.
$y = mx$ …….... (1)
$y = 2$ …...…. (2)
$y = 6$ …….... (3)
Now, to find the intercepts, we will find the intersection points.
Intersection point of equation (1) and (2)
$ \Rightarrow y = mx,y = 2$
Putting $y = 2$ in equation (1),
$ \Rightarrow 2 = mx$
Shifting m to the other side to find x-coordinate.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{2}{m}$
Therefore, the intersection point of equation (1) and (2) is - $\left( {\dfrac{2}{m},2} \right)$
Next, we will find intersection point of equation (1) and (3)-
$ \Rightarrow y = mx,y = 6$
Putting $y = 6$ in equation (1),
$ \Rightarrow 6 = mx$
Shifting m to the other side to find x-coordinate.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{6}{m}$
Therefore, the intersection point of equation (1) and (3) is - $\left( {\dfrac{6}{m},6} \right)$.
It is given that the distance between the two intersection points is less than 5. Using distance formula,$d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $between the two points $\left( {\dfrac{2}{m},2} \right)$ and $\left( {\dfrac{6}{m},6} \right)$, form an equation.
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{6}{m} - \dfrac{2}{m}} \right)}^2} + {{(6 - 2)}^2}} < 5$
Squaring both the sides,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{4}{m}} \right)^2} + {4^2} < 25$
Simplifying,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} + 16 < 25$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} < 25 - 16$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{m^2}}} < 9$
Taking everything on one side,
$ \Rightarrow 9{m^2} - 16 > 0$
Making factors on LHS using ${a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)$,
$ \Rightarrow (3m - 4)(3m + 4) > 0$
$ \Rightarrow 3m - 4 > 0,3m + 4 < 0$
$ \Rightarrow m > \dfrac{4}{3},m < \dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}$
Now, let's plot the values of m on the number line and use a wavy curve method to find the range of m.
In this method, we simply plot the points on the number line and start marking + and – in every range that is made due to the points, starting marking + from the right. See how it is done below.

Now, since we are asked for the range greater than 0 as shown in this equation- $ \Rightarrow (3m - 4)(3m + 4) > 0$, we will take the range from the number line which has been marked as positive.
Therefore, $m \in \left( { - \infty ,\dfrac{{ - 4}}{3}} \right) \cup \left( {\dfrac{4}{3},\infty } \right)$.
Option C is the correct answer.
Note: The students might not be aware about the wavy curve method but it is a very simple method and is used to find out the range. While using this method, we should always start marking the ranges as positive starting from right as done in this question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




