
The intercept made by the circle ${x^2} + {y^2} - 14x - 10y + 23 = 0$ on the line \[7x + y - 4 = 0\] is
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D)4
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint- In order to find the intercept made by the given circle and the line first we have to find the radius and center of the circle by comparing the given equation with the general equation of circle, then we will proceed further by using the distance formula from a centre to the given line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given Circle equation is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 14x - 10y + 23 = 0$
And line equation is \[7x + y - 4 = 0\]
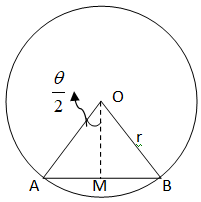
From the given figure
AB is the intercept made by circle and line
So we have to find the length of AB
First we will find the radius of the given circle
We know that
The General Form of the equation of a circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\] and the centre of the circle is \[\left( { - g, - f} \right)\] and the radius is \[\sqrt {\left( {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} \right)} \]
By comparing the given circle equation to the general circle equation we have
Centre as \[\left( {7,5} \right)\]
And the radius will be
Radius $ = \sqrt {\left( {{7^2} + {5^2} - 23} \right)} = \sqrt {\left( {49 + 25 - 23} \right)} = \sqrt {51} $
In right angle triangle AOM, we have OA as a radius, and to find AM, we have to find OM
So, as we know that distance from the point \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] on the line \[ax + by + c = 0\] is given as
$D = \dfrac{{\left| {a{x_1} + b{y_1} + c} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}$
Therefore the distance from the centre \[\left( {7,5} \right)\] to the line will be
$
D = \dfrac{{\left| {7\left( 7 \right) + \left( 5 \right) + \left( { - 4} \right)} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{7^2} + {1^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow D = \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt {50} }} = \sqrt {50} \\
$
$\therefore OM = \sqrt {50} $
In right angle triangle AOM, we will apply Pythagoras theorem in order to find AM
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {AO} \right)^2} = {\left( {MO} \right)^2} + {\left( {AM} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {AM} \right)^2} = {\left( {AO} \right)^2} - {\left( {MO} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {AO} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {MO} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AM = \sqrt {51 - 50} \\
\Rightarrow AM = 1 \\
$
And we know that AB = 2AM
So intercept AB is given as:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 2 \times 1 = 2$
Hence the value of intercept made by the line on the circle is 2
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- The intercepts of a line are the points where the line intercepts, or crosses, the horizontal and vertical axes. The straight line on the graph below intercepts the two coordinate axes. The point where the line crosses the x-axis is called the [x-intercept]. In order to solve such problems students must remember the distance formula in coordinate geometry for different conditions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given Circle equation is ${x^2} + {y^2} - 14x - 10y + 23 = 0$
And line equation is \[7x + y - 4 = 0\]

From the given figure
AB is the intercept made by circle and line
So we have to find the length of AB
First we will find the radius of the given circle
We know that
The General Form of the equation of a circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\] and the centre of the circle is \[\left( { - g, - f} \right)\] and the radius is \[\sqrt {\left( {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} \right)} \]
By comparing the given circle equation to the general circle equation we have
Centre as \[\left( {7,5} \right)\]
And the radius will be
Radius $ = \sqrt {\left( {{7^2} + {5^2} - 23} \right)} = \sqrt {\left( {49 + 25 - 23} \right)} = \sqrt {51} $
In right angle triangle AOM, we have OA as a radius, and to find AM, we have to find OM
So, as we know that distance from the point \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] on the line \[ax + by + c = 0\] is given as
$D = \dfrac{{\left| {a{x_1} + b{y_1} + c} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2}} }}$
Therefore the distance from the centre \[\left( {7,5} \right)\] to the line will be
$
D = \dfrac{{\left| {7\left( 7 \right) + \left( 5 \right) + \left( { - 4} \right)} \right|}}{{\sqrt {{7^2} + {1^2}} }} \\
\Rightarrow D = \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt {50} }} = \sqrt {50} \\
$
$\therefore OM = \sqrt {50} $
In right angle triangle AOM, we will apply Pythagoras theorem in order to find AM
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {AO} \right)^2} = {\left( {MO} \right)^2} + {\left( {AM} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {AM} \right)^2} = {\left( {AO} \right)^2} - {\left( {MO} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow AM = \sqrt {{{\left( {AO} \right)}^2} - {{\left( {MO} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow AM = \sqrt {51 - 50} \\
\Rightarrow AM = 1 \\
$
And we know that AB = 2AM
So intercept AB is given as:
$ \Rightarrow AB = 2 \times 1 = 2$
Hence the value of intercept made by the line on the circle is 2
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- The intercepts of a line are the points where the line intercepts, or crosses, the horizontal and vertical axes. The straight line on the graph below intercepts the two coordinate axes. The point where the line crosses the x-axis is called the [x-intercept]. In order to solve such problems students must remember the distance formula in coordinate geometry for different conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




