
The information source for making proteins is
(a) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(b) DNA
(c) Hormones
(d) Enzymes
Answer
530.3k+ views
Hint: Central dogma model has three main processes: Replication, Transcription, and Translation used by all cells to maintain their genetic information.
Complete answer:
Francis Crick proposed the Central dogma in molecular biology, which states that the genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to Protein.
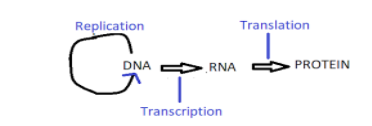
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the basic source of making proteins in the cells. First DNA replicates itself, then DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA - ribonucleic acid) molecule during transcription, lastly the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. In translation, mRNA along with transfer RNA (tRNA- adapter molecule) and ribosome’s (also acts as catalyst) work together to produce proteins.
Additional Information:
Let’s see how the other options are connected to protein synthesis. In the eukaryotic cells, rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is a series of connected flattened sacs and a part of the continuous membrane organelle. The rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosome’s on top and these ribosomes are called 'membrane bound' and are responsible for the assembly of protein.
Chemical substances that affect the activity of another part of the body (target site) are known as hormones. Hormones are useful for messengers, controlling and coordinating activities throughout the body. Anabolic hormones stimulate the human muscle growth mainly by increasing protein synthesis (growth hormone and testosterone) or by reducing protein breakdown (insulin).
Proteins that speed up the rate of a chemical reaction in a living organism are known as enzymes. An enzyme basically acts as a catalyst for specific chemical reactions, converting from a set of reactants (called substrates) into specific products. Enzymes like tRNA help in protein synthesis.
So, the correct answer is “DNA”.
Note: In some viruses the flow of information is in reverse direction; from RNA to DNA. DNA is the genetic material passed from parents to offspring.
Catalyst is a substance used for making the reaction faster.
Complete answer:
Francis Crick proposed the Central dogma in molecular biology, which states that the genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to Protein.

DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the basic source of making proteins in the cells. First DNA replicates itself, then DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA - ribonucleic acid) molecule during transcription, lastly the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. In translation, mRNA along with transfer RNA (tRNA- adapter molecule) and ribosome’s (also acts as catalyst) work together to produce proteins.
Additional Information:
Let’s see how the other options are connected to protein synthesis. In the eukaryotic cells, rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is a series of connected flattened sacs and a part of the continuous membrane organelle. The rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosome’s on top and these ribosomes are called 'membrane bound' and are responsible for the assembly of protein.
Chemical substances that affect the activity of another part of the body (target site) are known as hormones. Hormones are useful for messengers, controlling and coordinating activities throughout the body. Anabolic hormones stimulate the human muscle growth mainly by increasing protein synthesis (growth hormone and testosterone) or by reducing protein breakdown (insulin).
Proteins that speed up the rate of a chemical reaction in a living organism are known as enzymes. An enzyme basically acts as a catalyst for specific chemical reactions, converting from a set of reactants (called substrates) into specific products. Enzymes like tRNA help in protein synthesis.
So, the correct answer is “DNA”.
Note: In some viruses the flow of information is in reverse direction; from RNA to DNA. DNA is the genetic material passed from parents to offspring.
Catalyst is a substance used for making the reaction faster.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




