
The inclusive class interval are also called:
(A) discontinuous class intervals
(B) continuous class intervals
(C) unequal class intervals
(D) higher class intervals
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: We will first write the general form of inclusive class interval. Then, determine its nature by writing its roaster form. Also, we will plot the interval by taking any relevant example of inclusive class interval to select the correct option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The inclusive class interval is of the form $\left[ {a,b} \right]$.
Here, both the numbers are included in the sets, that is, \[a\] and \[b\].
In the roaster form, we can write it as $\left\{ {x:a \leqslant x \leqslant b} \right\}$
The above representation does not represent a discontinuous class as it includes all the elements from $a$ to $b$.
If we have an interval for example, $\left[ {2,3} \right]$, then it includes all the real numbers from point 2 to 3.
If we represent this on a number line, we will get,
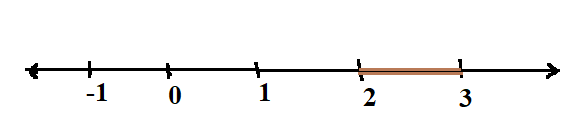
The interval $\left( {2,3} \right)$ is represented by a continuous line.
Hence, the inclusive intervals are also known as continuous class intervals.
Thus, option B is correct.
Note: The interval of the type $\left( {a,b} \right)$ is when $a$ and $b$ are included in the interval but still is a continuous class interval. Unequal class interval is the case when the length of class intervals are not the same.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The inclusive class interval is of the form $\left[ {a,b} \right]$.
Here, both the numbers are included in the sets, that is, \[a\] and \[b\].
In the roaster form, we can write it as $\left\{ {x:a \leqslant x \leqslant b} \right\}$
The above representation does not represent a discontinuous class as it includes all the elements from $a$ to $b$.
If we have an interval for example, $\left[ {2,3} \right]$, then it includes all the real numbers from point 2 to 3.
If we represent this on a number line, we will get,

The interval $\left( {2,3} \right)$ is represented by a continuous line.
Hence, the inclusive intervals are also known as continuous class intervals.
Thus, option B is correct.
Note: The interval of the type $\left( {a,b} \right)$ is when $a$ and $b$ are included in the interval but still is a continuous class interval. Unequal class interval is the case when the length of class intervals are not the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




