
The I – V characteristics of an LED is,
(A)
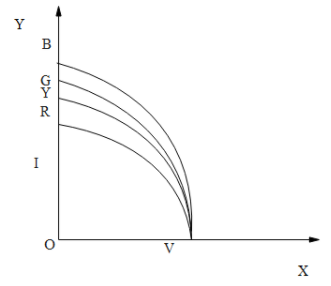
(B)
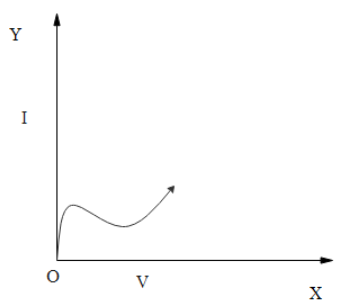
(C)
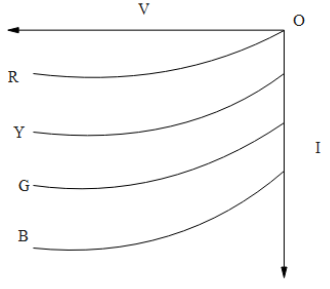
(D)
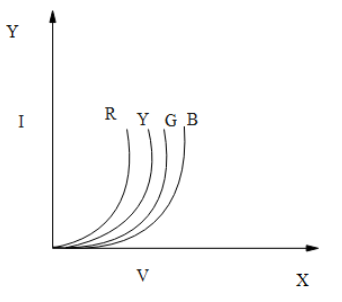




Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: LED or light emitting diode works in forward biased condition. The recombination of electrons and holes at the junction leads to the production of light energy. A light emitting diode (LED) may be a semiconductor light that emits light when current flows through it. The LED can never be connected in reverse-biased mode. Because there is a chance to cause damage to the LEDs in that condition.
Complete answer:
The Light-emitting diode (LED) may be always a forward biased contact diode which emits light when energized. The recombination of electrons and holes at the junction leads to the production of light energy . Emit radiation in the infrared region. If light – emitting diode is reverse-biased, then no light would be emitted in the least. The LED can be damaged on being reverse-biased.
The emission of light from a light-emitting diode is by the mechanism of spontaneous emission. There are two energy bands in a semiconductor. The conduction which is of higher energy and therefore the valence which is lower energy bands. There may also be new energy bands (ED) due to donor impurities near the conductor band or acceptor impurities (EA) near the valence band. When an electron falls from higher to lower energy level, the energy in the form of light is released. Generally, radiative transitions occur. Sometimes, non-radiative transitions may occur.
Thus option (D) is correct.
Note:
LED or light emitting diodes always work in forward biased conditions. The LED can be damaged on being reverse-biased. Electrons within the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy within the form of photons. The LED can never be connected in reverse-biased mode. Because there is a chance to cause damage to the LEDs in that condition.
Complete answer:
The Light-emitting diode (LED) may be always a forward biased contact diode which emits light when energized. The recombination of electrons and holes at the junction leads to the production of light energy . Emit radiation in the infrared region. If light – emitting diode is reverse-biased, then no light would be emitted in the least. The LED can be damaged on being reverse-biased.
The emission of light from a light-emitting diode is by the mechanism of spontaneous emission. There are two energy bands in a semiconductor. The conduction which is of higher energy and therefore the valence which is lower energy bands. There may also be new energy bands (ED) due to donor impurities near the conductor band or acceptor impurities (EA) near the valence band. When an electron falls from higher to lower energy level, the energy in the form of light is released. Generally, radiative transitions occur. Sometimes, non-radiative transitions may occur.
Thus option (D) is correct.
Note:
LED or light emitting diodes always work in forward biased conditions. The LED can be damaged on being reverse-biased. Electrons within the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy within the form of photons. The LED can never be connected in reverse-biased mode. Because there is a chance to cause damage to the LEDs in that condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




