
The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is $ 3\sqrt{10} $ . If the smaller side is tripled and the larger side is doubled, the new hypotenuse will be $ 9\sqrt{10} $ . Find the length of each side of the triangle.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Assume that the length of the legs of the right-angled triangle be a and b, with a being the smaller side. Form an equation in a and b using the fact that the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of its legs. Again find the length of the hypotenuse using Pythagora’s theorem when the smaller side is tripled, and the longer side is doubled and equate it to $ 9\sqrt{5} $ and hence form another equation in a and b. Put $ {{a}^{2}}=x $ and $ {{b}^{2}}=y $ and hence form a system of linear equations in two variables x and y. Solve the system using any of the known methods like elimination, substitution, etc. and hence find the value of x and y. Hence find the length of each side of the triangles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
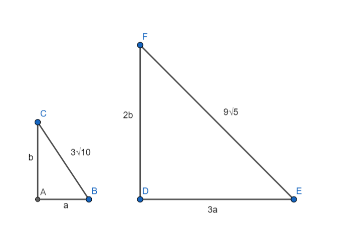
Let the length of the smaller side of the triangle be a and the length of the larger side be b.
We know that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of its sides. This is known as Pythagora’s theorem.
Hence, we have
$ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{\left( 3\sqrt{10} \right)}^{2}} $
Simplifying, we get
$ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=90\text{ }\left( i \right) $
The lengths of the sides when the smaller side is tripled, and the larger side is doubled are 3a and 2b.
Again using Pythagora’s theorem, we get
$ {{\left( 3a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 9\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}} $
Simplifying, we get
$ 9{{a}^{2}}+4{{b}^{2}}=405\text{ }\left( ii \right) $
Put $ {{a}^{2}}=x $ and $ {{b}^{2}}=y $ , we have
Equation (i) becomes
$ x+y=90\text{ }\left( iii \right) $
Equation (ii) becomes
$ 9x+4y=405\text{ }\left( iv \right) $
Multiplying equation (iii) by 4 and subtracting the resulting equation from equation (iv), we get
$ \begin{align}
& 9x+4y-4x-4y=405-360 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=45 \\
\end{align} $
Dividing both sides by 5, we get
$ x=9 $
Substituting the value of x in equation (iii), we get
$ 9+y=90 $
Subtracting 9 from both sides, we get
$ y=81 $
Reverting to original variables, we get
$ \begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\pm 3 \\
\end{align} $
Since a is the length of the side of the triangle, a>0
Hence, we have a =3.
Also, we have
$ \begin{align}
& {{b}^{2}}=81 \\
& \Rightarrow b=\pm 9 \\
\end{align} $
Since b is the length of the side of the triangle, b>0.
Hence, we have b = 9.
Hence the sides of the triangle are 3 and 9.
Note: Verification:
Length of hypotenuse $ =\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{9}^{2}}}=\sqrt{9+81}=\sqrt{90}=3\sqrt{10} $
Length of hypotenuse when the smaller side is tripled and the larger side is doubled $ =\sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{18}^{2}}}=9\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}=9\sqrt{5} $
Hence our answer is verified to be correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let the length of the smaller side of the triangle be a and the length of the larger side be b.
We know that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of its sides. This is known as Pythagora’s theorem.
Hence, we have
$ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{\left( 3\sqrt{10} \right)}^{2}} $
Simplifying, we get
$ {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=90\text{ }\left( i \right) $
The lengths of the sides when the smaller side is tripled, and the larger side is doubled are 3a and 2b.
Again using Pythagora’s theorem, we get
$ {{\left( 3a \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2b \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 9\sqrt{5} \right)}^{2}} $
Simplifying, we get
$ 9{{a}^{2}}+4{{b}^{2}}=405\text{ }\left( ii \right) $
Put $ {{a}^{2}}=x $ and $ {{b}^{2}}=y $ , we have
Equation (i) becomes
$ x+y=90\text{ }\left( iii \right) $
Equation (ii) becomes
$ 9x+4y=405\text{ }\left( iv \right) $
Multiplying equation (iii) by 4 and subtracting the resulting equation from equation (iv), we get
$ \begin{align}
& 9x+4y-4x-4y=405-360 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x=45 \\
\end{align} $
Dividing both sides by 5, we get
$ x=9 $
Substituting the value of x in equation (iii), we get
$ 9+y=90 $
Subtracting 9 from both sides, we get
$ y=81 $
Reverting to original variables, we get
$ \begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}=9 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\pm 3 \\
\end{align} $
Since a is the length of the side of the triangle, a>0
Hence, we have a =3.
Also, we have
$ \begin{align}
& {{b}^{2}}=81 \\
& \Rightarrow b=\pm 9 \\
\end{align} $
Since b is the length of the side of the triangle, b>0.
Hence, we have b = 9.
Hence the sides of the triangle are 3 and 9.
Note: Verification:
Length of hypotenuse $ =\sqrt{{{3}^{2}}+{{9}^{2}}}=\sqrt{9+81}=\sqrt{90}=3\sqrt{10} $
Length of hypotenuse when the smaller side is tripled and the larger side is doubled $ =\sqrt{{{9}^{2}}+{{18}^{2}}}=9\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}}=9\sqrt{5} $
Hence our answer is verified to be correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





