
The hydrolysis of $NC{l_3}$ results in the formation of _______ and _______.
(A) Hydrogen chloride, Hypochlorous acid
(B) Ammonia, Hypochlorous acid
(C) Ammonia, Chlorous acid
(D) Chloric acid, Ammonia
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The N-Cl bonds in nitrogen trichloride are non-polar. Nitrogen atoms react with water by the donation of its lone pair to the positively charged part of the molecule. The acid produced has a chlorine atom in +1 oxidation state.
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrolysis is the process of breaking bonds of the molecule by its reaction with water. So, water is used as a reagent in the hydrolysis reaction.
-We are here asked about the hydrolysis products of Nitrogen trichloride ($NC{l_3}$). We will need to figure out how water will react with nitrogen trichloride.
-Water has protons as its positively charged part and hydroxide ions as negatively charged parts. This is the reason why water can act as both acid as well as a base depending upon the reactant.
-In nitrogen trichloride, three N-Cl single bonds are there. Nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell and is a second-period element. Chlorine has seven electrons in its valence shell and it is a third-period element. So, we can say that there is not much difference between the electronegativity between them.
- So, N-Cl bonds will be non-polar. So, nitrogen atoms will attack the protons with their lone pair of electrons as shown below.
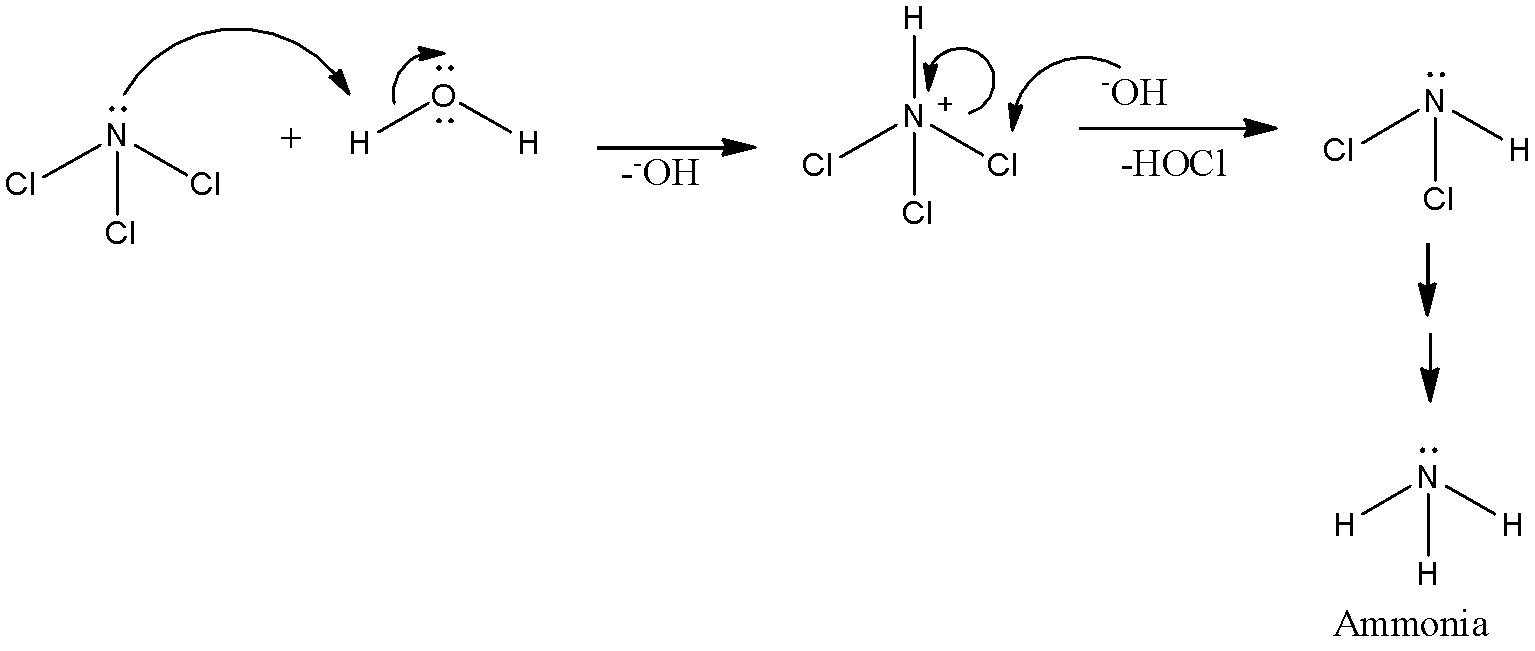
Here, the same way all three chlorine atoms are replaced by protons and we obtain ammonia as a final product. Alongside ammonia, we also obtain Hypochlorous acid.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is (B).
Note: Note that the acids of chlorine are named depending upon the different oxidation states of the chlorine atom present in it. e.g. HOCl : Hypochlorous acid, $HCl{O_2}$: Chlorous acid, $HCl{O_3}$: Chloric acid, $HCl{O_4}$: Perchloric acid
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrolysis is the process of breaking bonds of the molecule by its reaction with water. So, water is used as a reagent in the hydrolysis reaction.
-We are here asked about the hydrolysis products of Nitrogen trichloride ($NC{l_3}$). We will need to figure out how water will react with nitrogen trichloride.
-Water has protons as its positively charged part and hydroxide ions as negatively charged parts. This is the reason why water can act as both acid as well as a base depending upon the reactant.
-In nitrogen trichloride, three N-Cl single bonds are there. Nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell and is a second-period element. Chlorine has seven electrons in its valence shell and it is a third-period element. So, we can say that there is not much difference between the electronegativity between them.
- So, N-Cl bonds will be non-polar. So, nitrogen atoms will attack the protons with their lone pair of electrons as shown below.

Here, the same way all three chlorine atoms are replaced by protons and we obtain ammonia as a final product. Alongside ammonia, we also obtain Hypochlorous acid.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is (B).
Note: Note that the acids of chlorine are named depending upon the different oxidation states of the chlorine atom present in it. e.g. HOCl : Hypochlorous acid, $HCl{O_2}$: Chlorous acid, $HCl{O_3}$: Chloric acid, $HCl{O_4}$: Perchloric acid
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




