
The hybridization and shape of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ is.
A) $s{p^3}$, tetrahedron.
B) $s{p^3}$, trigonal pyramidal.
C) $s{p^3}{d^2}$, trigonal bipyramidal.
D) $s{p^3}{d^3}$, pentagonal planar.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: We know that, The Hybridization is that the concept in which atomic orbitals combine to make a new hybridized orbital which successively, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties.
We know that the electrons which are present at the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons and the valency of an electron is that the number of electrons through which atom accepts or donate to make a bond.
Complete step by step answer:
We can discover the geometry of an atom by finding the steric number of a particle. The steric number of particle is determined utilizing the equation,
Steric number $ = \dfrac{{{\text{Valence electron of central atom}} + {\text{No}}{\text{.of bonded atom}} + {\text{Charge of compound}}}}{2}$
The steric number of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ can be calculated as,
Steric number $ = \dfrac{{{\text{Valence electron of central atom}} + {\text{No}}{\text{.of bonded atom}} + {\text{Charge of compound}}}}{2}$
In case of $XeF_5^ - $,
Valence electron of central atom Xe is=8
No. of bonded atom = 5
Charge of the compound = -1
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
Steric number \[ = \dfrac{{8 + 5 + 1}}{2} = 7\]
The steric number of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ is Six. Number of bond pairs is five. Number of lone pairs is two.
As lone pairs are available pivotally to limit the repulsion, henceforth, the shape is planar.
The structure of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ is,
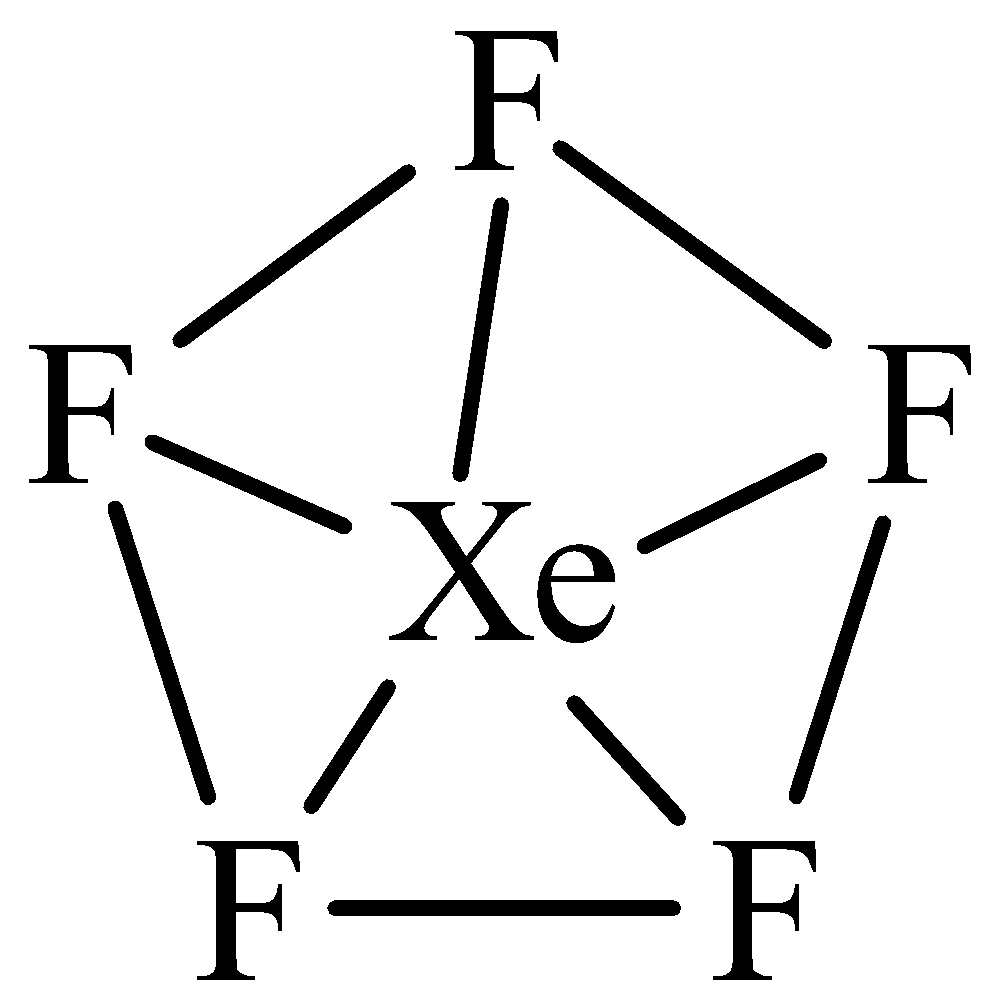
The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybridization:
The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybridization has 1s, 3p and 3d orbitals they undergo intermixing to form 7 identical ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybrid orbitals. These six orbitals are located at the corners of a pentagonal planar. They are inclined at an angle of ${72^{\text{o}}}$ to one another. The central atoms which have ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybrid orbitals forms the bonds with bond angle of ${72^{\text{o}}}$
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We have to remember that the steric number is an amount of the quantity of ligands and solitary sets encompassing the focal molecule.
${\text{Steric number}} = \left( {m + n} \right)$
Where m is the number of ligands and n is the number of lone pairs.
Example: Now we can calculate the steric number of ClF2- as,
${\text{Steric number}} = \left( {2 + 3} \right) = 5$
The steric number of ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ - }}$ is five ,which means that it is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ hybridized, two of them are in bonding and there is lone pairs thus it adopts the linear structure with the bond angle of ${\text{18}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}$.
The structure of ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ - }}$ is,
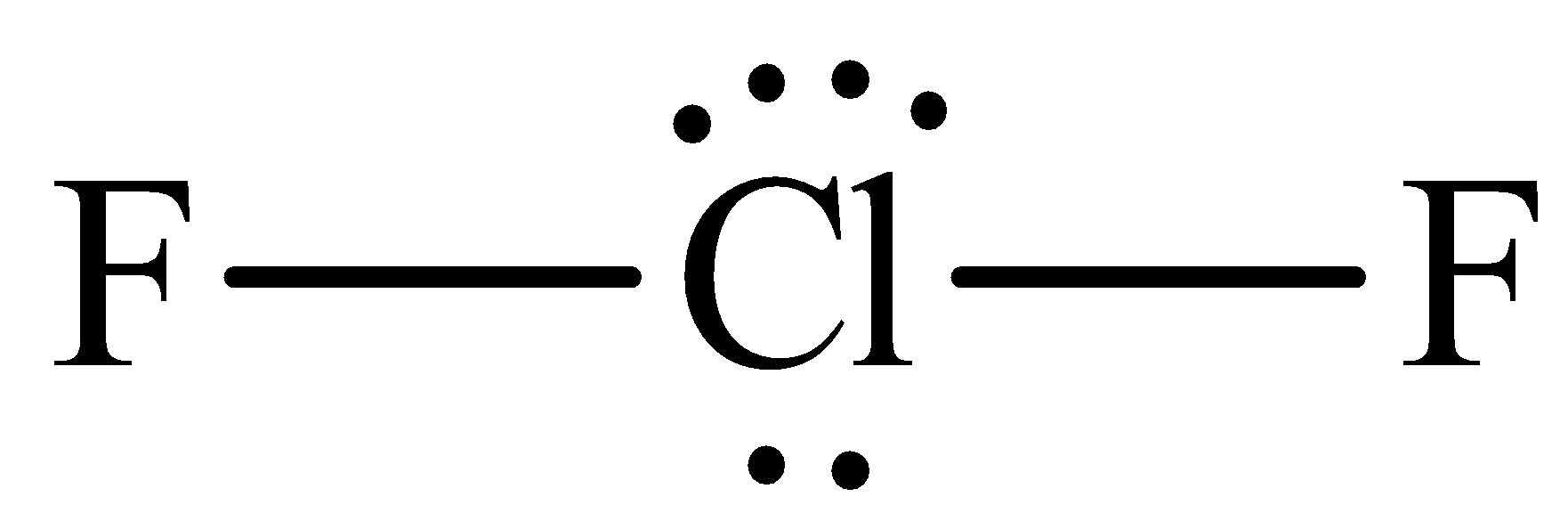
We know that the electrons which are present at the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons and the valency of an electron is that the number of electrons through which atom accepts or donate to make a bond.
Complete step by step answer:
We can discover the geometry of an atom by finding the steric number of a particle. The steric number of particle is determined utilizing the equation,
Steric number $ = \dfrac{{{\text{Valence electron of central atom}} + {\text{No}}{\text{.of bonded atom}} + {\text{Charge of compound}}}}{2}$
The steric number of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ can be calculated as,
Steric number $ = \dfrac{{{\text{Valence electron of central atom}} + {\text{No}}{\text{.of bonded atom}} + {\text{Charge of compound}}}}{2}$
In case of $XeF_5^ - $,
Valence electron of central atom Xe is=8
No. of bonded atom = 5
Charge of the compound = -1
Now we can substitute the known values we get,
Steric number \[ = \dfrac{{8 + 5 + 1}}{2} = 7\]
The steric number of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ is Six. Number of bond pairs is five. Number of lone pairs is two.
As lone pairs are available pivotally to limit the repulsion, henceforth, the shape is planar.
The structure of $Xe{F_5}^ - $ is,

The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybridization:
The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybridization has 1s, 3p and 3d orbitals they undergo intermixing to form 7 identical ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybrid orbitals. These six orbitals are located at the corners of a pentagonal planar. They are inclined at an angle of ${72^{\text{o}}}$ to one another. The central atoms which have ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{{\text{d}}^3}$ hybrid orbitals forms the bonds with bond angle of ${72^{\text{o}}}$
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We have to remember that the steric number is an amount of the quantity of ligands and solitary sets encompassing the focal molecule.
${\text{Steric number}} = \left( {m + n} \right)$
Where m is the number of ligands and n is the number of lone pairs.
Example: Now we can calculate the steric number of ClF2- as,
${\text{Steric number}} = \left( {2 + 3} \right) = 5$
The steric number of ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ - }}$ is five ,which means that it is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ hybridized, two of them are in bonding and there is lone pairs thus it adopts the linear structure with the bond angle of ${\text{18}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}$.
The structure of ${\text{Cl}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}^{\text{ - }}$ is,

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




