
The horizontal distance between two towers is \[60m\] and the angle of depression of the top of the first tower as seen from the top of the second is \[{30^ \circ }\]. If the height of the second tower is \[90m\] then the height of the first tower is
A. \[90m\]
B. \[(150 - 60\sqrt 3 )m\]
C. \[(150 - 20\sqrt 3 )m\]
D. None of these
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: It is given that the angle of the depression is seen from the second tower which concludes that the height of the second is more than that of the first tower . Always draw a figure with given data. We have made use of trigonometric ratios to find out the height of the first tower. Different ratios have different values like perpendicular , base hypotenuse .
Complete step-by-step answer:
For better understanding we have to draw a figure with given measurements .
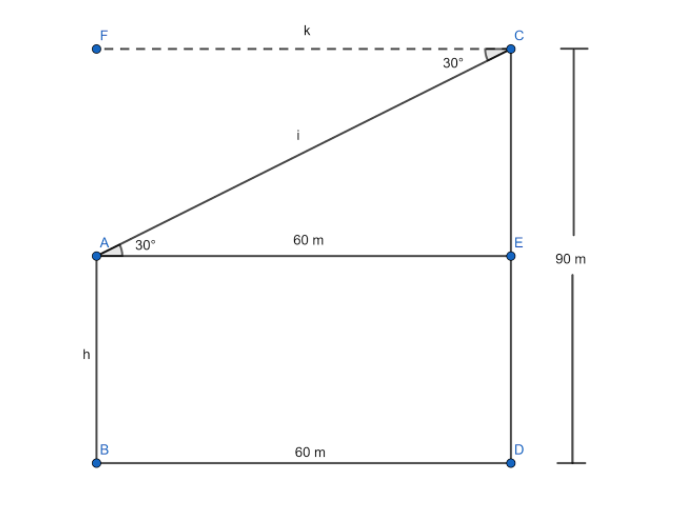
Here \[A\] is the point at the top of the first tower . C is the point of top of the second tower with an angle of depression of \[{30^ \circ }\]towards the top of the first tower . Now the \[\angle CAE = {30^ \circ }\] ( by alternate interior angle property ) . Now in \[\vartriangle CAE\] we have
\[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{CE}}{{AE}}\] , now \[CE = CD - ED\] , which is \[CE = 90 - h\]
Therefore , \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{90 - h}}{{60}}\] ,
now as we know the value of \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] we get ,
\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{90 - h}}{{60}}\]
On solving we get
\[\dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 90 - h\] ,
on rationalizing the RHS we get ,
\[\dfrac{{60\sqrt 3 }}{3} = 90 - h\] ,
on solving we get
\[90 - h = 20\sqrt 3 \]
On simplifying we get
\[h = 90 - 20\sqrt 3 \] ,
putting the value of \[\sqrt 3 \] as \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\] we get ,
\[h = 90 - 20 \times 1.732\]
On solving we get
\[h = 90 - 34.64\] ,
on solving we get
\[h = 55.36m\]
Which is the height of the first tower and the required answer . Therefore , option (4) is the correct answer .
So, the correct answer is “Option 4”.
Note: These questions related to angle of depression and angle of elevation are related to applications of the trigonometric identities which are also applied practically . Trigonometry is widely used in navigation and geography to locate different places in relation to the latitude and longitude .
Complete step-by-step answer:
For better understanding we have to draw a figure with given measurements .

Here \[A\] is the point at the top of the first tower . C is the point of top of the second tower with an angle of depression of \[{30^ \circ }\]towards the top of the first tower . Now the \[\angle CAE = {30^ \circ }\] ( by alternate interior angle property ) . Now in \[\vartriangle CAE\] we have
\[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{CE}}{{AE}}\] , now \[CE = CD - ED\] , which is \[CE = 90 - h\]
Therefore , \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{90 - h}}{{60}}\] ,
now as we know the value of \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\] we get ,
\[\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{90 - h}}{{60}}\]
On solving we get
\[\dfrac{{60}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = 90 - h\] ,
on rationalizing the RHS we get ,
\[\dfrac{{60\sqrt 3 }}{3} = 90 - h\] ,
on solving we get
\[90 - h = 20\sqrt 3 \]
On simplifying we get
\[h = 90 - 20\sqrt 3 \] ,
putting the value of \[\sqrt 3 \] as \[\sqrt 3 = 1.732\] we get ,
\[h = 90 - 20 \times 1.732\]
On solving we get
\[h = 90 - 34.64\] ,
on solving we get
\[h = 55.36m\]
Which is the height of the first tower and the required answer . Therefore , option (4) is the correct answer .
So, the correct answer is “Option 4”.
Note: These questions related to angle of depression and angle of elevation are related to applications of the trigonometric identities which are also applied practically . Trigonometry is widely used in navigation and geography to locate different places in relation to the latitude and longitude .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




