
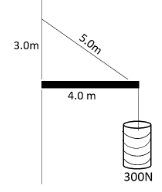
The horizontal beam in figure weights $150N$, and its centre of gravity is at its centre. Find the horizontal and the vertical component of the forces exerted on the beam at the wall.
A. horizontal component is $500N$ towards left and vertical component $75N$ downwards.
B. horizontal component is $500N$ towards right and vertical component $75N$ .
C. horizontal component is $625N$ towards left and vertical component $150N$.
D. Horizontal component is $625N$ towards right and vertical component $150N$ downwards.

Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Torque is the quantity of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Force is what makes an object to accelerate in linear kinematics. In the same way, torque is what causes an angular acceleration. Hence, torque can be described as the rotational equivalent of linear force.
Complete answer:
Here the resultant torque on the beam about the hinge becomes zero.

Let the horizontal component & vertical component of tension be ${{T}_{H}},{{T}_{V}}$ respectively. And the horizontal component & vertical component of forces exerted on the beam at the wall are ${{F}_{H}},{{F}_{V}}$ respectively. Therefore we can write that,
$\begin{align}
& {{T}_{V}}\times 4-300\times 4-150\times 2=0 \\
& {{T}_{V}}=375N \\
\end{align}$
This tension will be acting upwards.
By geometry, the relation between ${{T}_{H}},{{T}_{V}}$ will be,
$\dfrac{{{T}_{V}}}{{{T}_{H}}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
Hence we will get,
${{T}_{H}}=400N$
This is acting on the left side.
Now let us balance the force,
${{T}_{H}}+{{F}_{H}}=0$
Therefore
${{F}_{H}}=500N$
This is acting on the right side.
And also we can write that,
${{F}_{V}}+{{T}_{V}}-300-150=0$
${{F}_{V}}=450-375=75N$
This is acting upwards.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The centre of gravity is the average location on the basis of the weight of an object. We can completely define the motion of any object through space in terms of the movement of the centre of gravity of the object from one place to another, and the rotation of the object about its centre of gravity when it is free to rotate.
Complete answer:
Here the resultant torque on the beam about the hinge becomes zero.

Let the horizontal component & vertical component of tension be ${{T}_{H}},{{T}_{V}}$ respectively. And the horizontal component & vertical component of forces exerted on the beam at the wall are ${{F}_{H}},{{F}_{V}}$ respectively. Therefore we can write that,
$\begin{align}
& {{T}_{V}}\times 4-300\times 4-150\times 2=0 \\
& {{T}_{V}}=375N \\
\end{align}$
This tension will be acting upwards.
By geometry, the relation between ${{T}_{H}},{{T}_{V}}$ will be,
$\dfrac{{{T}_{V}}}{{{T}_{H}}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
Hence we will get,
${{T}_{H}}=400N$
This is acting on the left side.
Now let us balance the force,
${{T}_{H}}+{{F}_{H}}=0$
Therefore
${{F}_{H}}=500N$
This is acting on the right side.
And also we can write that,
${{F}_{V}}+{{T}_{V}}-300-150=0$
${{F}_{V}}=450-375=75N$
This is acting upwards.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
The centre of gravity is the average location on the basis of the weight of an object. We can completely define the motion of any object through space in terms of the movement of the centre of gravity of the object from one place to another, and the rotation of the object about its centre of gravity when it is free to rotate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




