
The height of a tower is h and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is $\alpha $ on moving a distance h/2 towards the tower, the angle of elevation becomes $\beta $. What is the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: In this particular question first draw the pictorial representation of the give problem it will give us a clear picture of what we have to find out later in the solution use the concept that (tan x = perpendicular/base) in a right triangle and tan x = (1/cot x), so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
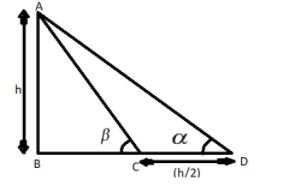
Let us consider the tower AB as shown in the figure, it is given that the height of the tower is h.
So AB = h (as shown in the figure).
Now the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is $\alpha $as shown in the figure.
Now it is given when we move towards the tower i.e. from point D to point C as shown in the figure the angle of elevation changes to $\beta $ and the distance DC is (h/2).
Now we have to find out the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $.
Now in triangle ABC,
Tan is tan of the angle is the ratio of perpendicular to base.
Therefore, $\tan \beta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
Now substitute the value of AB we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{h}{{BC}}$
Now as we know that tan x = 1/cot x, so use this property in the above equation we have.
$ \Rightarrow \cot \beta = \dfrac{{BC}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow h\cot \beta = BC$.................. (1)
Now in triangle ABD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}}$
Now, BD = BC + CD
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC + CD}}$
Now substitute the value of, AB, BC and CD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{h}{{h\cot \beta + \dfrac{h}{2}}}$
Now simplify i.e. cancel out h from numerator and denominator we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha = \dfrac{{\cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}}}{1}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha = \cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha - \cot \beta = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So this is the required answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that in trigonometry sin x = perpendicular to hypotenuse, cos x = base to hypotenuse and tan x = perpendicular to base and always remember that sin x = (1/cosec x), cos x = (1/sec x) and tan x = (1/cot x).
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let us consider the tower AB as shown in the figure, it is given that the height of the tower is h.
So AB = h (as shown in the figure).
Now the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is $\alpha $as shown in the figure.
Now it is given when we move towards the tower i.e. from point D to point C as shown in the figure the angle of elevation changes to $\beta $ and the distance DC is (h/2).
Now we have to find out the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $.
Now in triangle ABC,
Tan is tan of the angle is the ratio of perpendicular to base.
Therefore, $\tan \beta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
Now substitute the value of AB we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \beta = \dfrac{h}{{BC}}$
Now as we know that tan x = 1/cot x, so use this property in the above equation we have.
$ \Rightarrow \cot \beta = \dfrac{{BC}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow h\cot \beta = BC$.................. (1)
Now in triangle ABD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}}$
Now, BD = BC + CD
Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC + CD}}$
Now substitute the value of, AB, BC and CD we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{h}{{h\cot \beta + \dfrac{h}{2}}}$
Now simplify i.e. cancel out h from numerator and denominator we have,
$ \Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha = \dfrac{{\cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}}}{1}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha = \cot \beta + \dfrac{1}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \cot \alpha - \cot \beta = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So this is the required answer.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall that in trigonometry sin x = perpendicular to hypotenuse, cos x = base to hypotenuse and tan x = perpendicular to base and always remember that sin x = (1/cosec x), cos x = (1/sec x) and tan x = (1/cot x).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




