
The height of a tower is ‘h’ and α is the angle of elevation of the top of the tower. On moving a distance $\dfrac{h}{2}$ towards the tower, the angle of elevation becomes β. What is the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $?
A. $\dfrac{1}{2}$
B. $\dfrac{2}{3}$
C. 1
D. 2
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: Given the height of the tower is h and the angle of elevation is α. When we move a distance of $\dfrac{h}{2}$ towards the tower the angle of elevation becomes β. The tower is perpendicular to the ground so it makes a right triangle. Find the value of cot α in terms of h, x and also cot β in terms of h and x and solve for its value. The result must be in terms of either h or a constant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
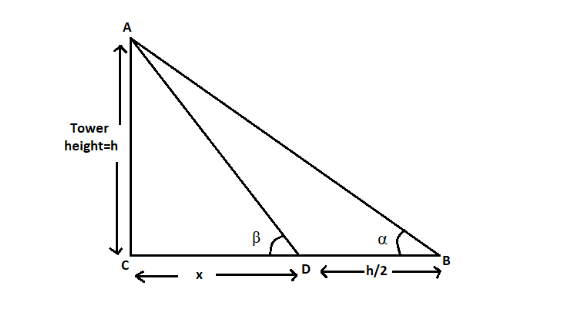
We are given that the height of a tower is ‘h’ and α is the angle of elevation of the top of the tower. On moving a distance $\dfrac{h}{2}$ towards the tower, the angle of elevation becomes β.
We have to find the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $
As we can see in the diagram, triangles ABC and ADC are right triangles with hypotenuses AB and AD respectively.
The function Cot (cotangent) of angle x is the ratio of the adjacent side to angle x and opposite side to angle x.
Therefore, in triangle ABC
$
\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{CB}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{CD + DB}}{{AC}} \\
CB = x + \dfrac{h}{2},AC = h \\
\to \cot \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {x + \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)}}{h} \\
\to h\cot \alpha = x + \dfrac{h}{2} \\
\therefore x = h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2} \to eq(1) \\
$
In triangle ADC,
$
\cot \beta = \dfrac{{CD}}{{AC}} \\
CD = x,AC = h \\
\to \cot \beta = \dfrac{x}{h} \\
\therefore x = h\cot \beta \to eq(2) \\
$
Subtracting equations 1 and 2, we get
$
0 = \left( {h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right) - \left( {h\cot \beta } \right) \\
\to h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2} - h\cot \beta = 0 \\
\to h\left( {\cot \alpha - \cot \beta } \right) - \dfrac{h}{2} = 0 \\
\to h\left( {\cot \alpha - \cot \beta } \right) = \dfrac{h}{2} \\
\therefore \cot \alpha - \cot \beta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
$
The value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $ is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, the correct option is Option A, $\dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: An alternate way to find the value of cot.
Function Sine of x is the ratio of its opposite side and hypotenuse. Function Cosine of x is the ratio of its adjacent side and hypotenuse.
Tangent function is the ratio of the above sine and cosine functions.
And the cot (cotangent) function is the reciprocal of the above tangent function or the ratio of cosine and sine functions. Thus we can find the value of cot using sine and cosines instead of directly using its definition.
Complete step-by-step answer:

We are given that the height of a tower is ‘h’ and α is the angle of elevation of the top of the tower. On moving a distance $\dfrac{h}{2}$ towards the tower, the angle of elevation becomes β.
We have to find the value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $
As we can see in the diagram, triangles ABC and ADC are right triangles with hypotenuses AB and AD respectively.
The function Cot (cotangent) of angle x is the ratio of the adjacent side to angle x and opposite side to angle x.
Therefore, in triangle ABC
$
\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{CB}}{{AC}} = \dfrac{{CD + DB}}{{AC}} \\
CB = x + \dfrac{h}{2},AC = h \\
\to \cot \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {x + \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)}}{h} \\
\to h\cot \alpha = x + \dfrac{h}{2} \\
\therefore x = h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2} \to eq(1) \\
$
In triangle ADC,
$
\cot \beta = \dfrac{{CD}}{{AC}} \\
CD = x,AC = h \\
\to \cot \beta = \dfrac{x}{h} \\
\therefore x = h\cot \beta \to eq(2) \\
$
Subtracting equations 1 and 2, we get
$
0 = \left( {h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right) - \left( {h\cot \beta } \right) \\
\to h\cot \alpha - \dfrac{h}{2} - h\cot \beta = 0 \\
\to h\left( {\cot \alpha - \cot \beta } \right) - \dfrac{h}{2} = 0 \\
\to h\left( {\cot \alpha - \cot \beta } \right) = \dfrac{h}{2} \\
\therefore \cot \alpha - \cot \beta = \dfrac{1}{2} \\
$
The value of $\cot \alpha - \cot \beta $ is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, the correct option is Option A, $\dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: An alternate way to find the value of cot.
Function Sine of x is the ratio of its opposite side and hypotenuse. Function Cosine of x is the ratio of its adjacent side and hypotenuse.
Tangent function is the ratio of the above sine and cosine functions.
And the cot (cotangent) function is the reciprocal of the above tangent function or the ratio of cosine and sine functions. Thus we can find the value of cot using sine and cosines instead of directly using its definition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




