
The ground state electronic configuration of \[{\text{CO}}\] molecule is:
A.\[1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}\]
B.\[1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}3{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^2}2{\pi ^2}\]
C.\[1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^2}3{\sigma ^2}2{\pi ^2}\]
D.\[1{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^4}2{\sigma ^2}3{\sigma ^2}\]
Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: For this question we must have the knowledge about making molecular orbital diagrams for hetro molecules. The electronic configuration will be written in the same way as an electron is being filled in MO diagrams from bottom to top.
Complete step-by-step answer: Molecular orbital is basically the mixing of atomic orbital. The orbits are mixed according to the principle called linear combination of atomic orbital. It states that when two atomic orbital approaches each other they interfere linearly. Every orbital has a wave function. If the two wave functions have the same phase that is plus and plus or minus and minus then they will have constructive interference. Due to this bonding molecular orbital forms which are of lower energy than the original orbital. Now if the orbital combines in an opposite phase that is plus and minus or minus and plus then they will have destructive interference. . Due to these anti-bonding molecular orbital forms which are of higher energy than the original orbital.
For mixing of atomic orbital they must have the same or comparable energy.
In MO diagram of \[{\text{CO}}\] , since oxygen is more electronegative so 2s orbital of oxygen has very low energy due to penetration. Hence it will directly go to non-bonding. Then first mixing will occur in 2p orbital of oxygen and 2s orbital of carbon. When two atomic orbital mixes one sigma bonding and one sigma anti-bonding orbital will form. This is an example of pre sp mixing or non ideal mixing, a sp orbital form by missing 2s orbital and 2p orbital of carbon and this orbital on interaction with one p orbital of oxygen form a non bonding. In diatomic molecules only one sigma bond can be formed which we have already formed. The two remaining p orbital will form \[\pi \] bonding and anti bonding molecular orbital. Hence the diagram will be like:
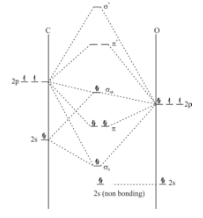
The configuration will be \[1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}\]
The correct option is A.
Note: The bond order of carbon monoxide is 3. When \[{\text{CO}}\] interacts with metal, it donates electrons to metals, but it is a pi acceptor ligand and takes electron density from metal through back bonding. Since \[{\text{CO}}\] has vacant anti bonding molecular orbital to accept electron and so bond order of \[{\text{CO}}\] reduces and become \[{\text{2}}{\text{.5}}\]
Complete step-by-step answer: Molecular orbital is basically the mixing of atomic orbital. The orbits are mixed according to the principle called linear combination of atomic orbital. It states that when two atomic orbital approaches each other they interfere linearly. Every orbital has a wave function. If the two wave functions have the same phase that is plus and plus or minus and minus then they will have constructive interference. Due to this bonding molecular orbital forms which are of lower energy than the original orbital. Now if the orbital combines in an opposite phase that is plus and minus or minus and plus then they will have destructive interference. . Due to these anti-bonding molecular orbital forms which are of higher energy than the original orbital.
For mixing of atomic orbital they must have the same or comparable energy.
In MO diagram of \[{\text{CO}}\] , since oxygen is more electronegative so 2s orbital of oxygen has very low energy due to penetration. Hence it will directly go to non-bonding. Then first mixing will occur in 2p orbital of oxygen and 2s orbital of carbon. When two atomic orbital mixes one sigma bonding and one sigma anti-bonding orbital will form. This is an example of pre sp mixing or non ideal mixing, a sp orbital form by missing 2s orbital and 2p orbital of carbon and this orbital on interaction with one p orbital of oxygen form a non bonding. In diatomic molecules only one sigma bond can be formed which we have already formed. The two remaining p orbital will form \[\pi \] bonding and anti bonding molecular orbital. Hence the diagram will be like:

The configuration will be \[1{\sigma ^2}2{\sigma ^2}1{\pi ^4}3{\sigma ^2}\]
The correct option is A.
Note: The bond order of carbon monoxide is 3. When \[{\text{CO}}\] interacts with metal, it donates electrons to metals, but it is a pi acceptor ligand and takes electron density from metal through back bonding. Since \[{\text{CO}}\] has vacant anti bonding molecular orbital to accept electron and so bond order of \[{\text{CO}}\] reduces and become \[{\text{2}}{\text{.5}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




