
The ground state electron configuration of the cobalt atom is characterized by which of the following?
I. Partially filled 3d orbital
II. The presence of unpaired electrons
III. All electrons paired
(a) I only
(b) II only
(c) I and II only
(d) I and III only
(e) I, II and III
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: We know electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom in its atomic orbital or distribution of electrons of a molecule in its molecular orbital. Electron filling occurs from lowest energy orbital to high energy orbital.
Complete answer: -Atomic number of cobalt is \[[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}4{{s}^{2}}\]. Here [Ar] is the electronic configuration of argon. In d orbital out of the four subshells, only 2 subshells are completely filled with 2 electrons of opposite spin. While three subshells have only one electron in each of them. So, cobalt has unpaired electrons in it. The statement II is applicable for the given question.
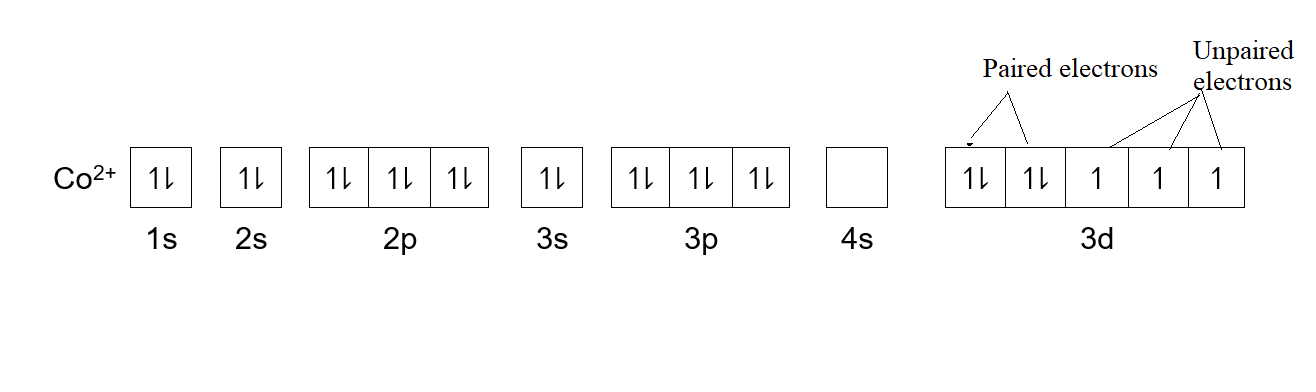
-As there are 7 electrons in its d orbital, so it is partially filled. Thus, statement I is incorrect.
-As mentioned above, not all electrons in the ground state of cobalt are paired, So, statement III is incorrect. Hence, cobalt has unpaired electrons and statement I and II are correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons around the nucleus of an atom or it could in a molecule too. Each electron moves independently in an orbital. Filling of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is based on a set of rules.
-First rule is Aufbau principle which states that the first lower energy orbitals are filled.
-Second rule is Pauli’s Exclusion principle which states that only two electrons are allowed in an orbital and their spins are opposite.
-Hund’s rule, the third rule states that most stable arrangements of electrons in a subshell occurs when the number of unpaired electrons is maximum and has the same spin.
Note: We might get confused with the idea of a half filled and partially filled orbital. Half filled d orbital contains only five electrons in it. Partially filled d orbital can have anywhere between one to nine electrons in them but is not fully occupied.
Complete answer: -Atomic number of cobalt is \[[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}4{{s}^{2}}\]. Here [Ar] is the electronic configuration of argon. In d orbital out of the four subshells, only 2 subshells are completely filled with 2 electrons of opposite spin. While three subshells have only one electron in each of them. So, cobalt has unpaired electrons in it. The statement II is applicable for the given question.

-As there are 7 electrons in its d orbital, so it is partially filled. Thus, statement I is incorrect.
-As mentioned above, not all electrons in the ground state of cobalt are paired, So, statement III is incorrect. Hence, cobalt has unpaired electrons and statement I and II are correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: Electronic configuration is the distribution of electrons around the nucleus of an atom or it could in a molecule too. Each electron moves independently in an orbital. Filling of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is based on a set of rules.
-First rule is Aufbau principle which states that the first lower energy orbitals are filled.
-Second rule is Pauli’s Exclusion principle which states that only two electrons are allowed in an orbital and their spins are opposite.
-Hund’s rule, the third rule states that most stable arrangements of electrons in a subshell occurs when the number of unpaired electrons is maximum and has the same spin.
Note: We might get confused with the idea of a half filled and partially filled orbital. Half filled d orbital contains only five electrons in it. Partially filled d orbital can have anywhere between one to nine electrons in them but is not fully occupied.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




