
The greatest positive argument of complex number satisfying $\left| {z - 4} \right| = \operatorname{Re} \left( z \right)$ is-
A. $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
B. $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}$
C. $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
D. $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint:
We know that Re means the real part of the equation then we know that $z = x + iy$ where x is the real part and y is the imaginary part of the equation. And we also know that $\left| z \right| = \sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} $ so using this puts the value of the given equation with real part in place of x and imaginary part as y. Solve the equation. You’ll see that it forms the equation of parabola. Now we have to find $\theta $ which is called the argument. So the value of $\tan \theta $ which has the highest positive value will give you the argument.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, $\left| {z - 4} \right| = \operatorname{Re} \left( z \right)$
Here the Re means real part of z hence we can write given equation as-
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {x - 4} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} = x$
Where x is the real part of the complex number and y is the imaginary part.
On squaring both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 4} \right)^2} + {y^2} = {x^2}$
Now we know that ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {\left( {a - b} \right)^2}$
So on applying this formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {4^2} - 2 \times 4 \times x} \right) + {y^2} = {x^2}$
On solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 16 - 8x + {y^2} = {x^2}$
On cancelling the same terms on both side we get,
$ \Rightarrow 16 - 8x + {y^2} = 0$
Now on adjusting the above equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 16 - 8x = 0$
On rearranging we can write,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 8x - 16$
On taking $8$ common from right side of the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 8\left( {x - 2} \right)$ --- (i)
This equation is in the form of parabola.
It represents the parabola with focus $\left( {4,0} \right)$ lying above the x-axis as both y and x coordinates are positive in it. The imaginary axis is the directrix.
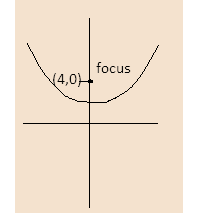
Then the two tangents from the directrix will be at right angles.
And then the greatest positive argument of z will be $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ because at other angles the value of $\tan \theta $ is less than $1$.
Hence the correct answer is D.
Note:
If the question had asked for the imaginary part instead of the real part then we would have put y in the place of x in the right side and solved the equation. Here parabola is upwards as it has both the coordinates on positive x-axis and positive y- axis.
We know that Re means the real part of the equation then we know that $z = x + iy$ where x is the real part and y is the imaginary part of the equation. And we also know that $\left| z \right| = \sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} $ so using this puts the value of the given equation with real part in place of x and imaginary part as y. Solve the equation. You’ll see that it forms the equation of parabola. Now we have to find $\theta $ which is called the argument. So the value of $\tan \theta $ which has the highest positive value will give you the argument.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, $\left| {z - 4} \right| = \operatorname{Re} \left( z \right)$
Here the Re means real part of z hence we can write given equation as-
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {x - 4} \right)}^2} + {y^2}} = x$
Where x is the real part of the complex number and y is the imaginary part.
On squaring both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 4} \right)^2} + {y^2} = {x^2}$
Now we know that ${a^2} - 2ab + {b^2} = {\left( {a - b} \right)^2}$
So on applying this formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} + {4^2} - 2 \times 4 \times x} \right) + {y^2} = {x^2}$
On solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 16 - 8x + {y^2} = {x^2}$
On cancelling the same terms on both side we get,
$ \Rightarrow 16 - 8x + {y^2} = 0$
Now on adjusting the above equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} + 16 - 8x = 0$
On rearranging we can write,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 8x - 16$
On taking $8$ common from right side of the equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = 8\left( {x - 2} \right)$ --- (i)
This equation is in the form of parabola.
It represents the parabola with focus $\left( {4,0} \right)$ lying above the x-axis as both y and x coordinates are positive in it. The imaginary axis is the directrix.

Then the two tangents from the directrix will be at right angles.
And then the greatest positive argument of z will be $\dfrac{\pi }{4}$ because at other angles the value of $\tan \theta $ is less than $1$.
Hence the correct answer is D.
Note:
If the question had asked for the imaginary part instead of the real part then we would have put y in the place of x in the right side and solved the equation. Here parabola is upwards as it has both the coordinates on positive x-axis and positive y- axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




