
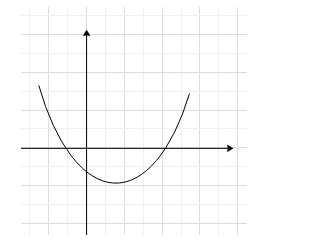
The graph of the quadratic polynomial : $ y=a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $ is as shown in the figure.
Then
A. $ {{b}^{2}}-4ac>0 $
B. $ b<0 $
C. $ a>0 $
D. All of these

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: In the options we can see that there are some conditions on the coefficients a, b and c. We can find the correct conditions for the given graph by differentiation. For minima, the second derivative of the function $ f(x)=y $ with respect x must be positive.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We can see that the function (value of y) is first decreasing. Then it reaches a minimum value then it starts to increase from that value of x.
Therefore, the graph has a minimum. For minima, the second derivative of the function $ f(x)=y $ with respect x must be positive, i.e. $ y''>0 $ .
Now differentiate y with rest to x.
$ \Rightarrow y'=2ax+b $ …. (i)
Differentiate the above equation with respect to x again.
$ \Rightarrow y''=2a $ .
But we know that $ y''>0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 2a>0 $
$ \Rightarrow a>0 $ .
Therefore, option C is correct.
We can see that the y has a minimum value for a positive value of x. Let that x-coordinate be $ x={{x}_{0}} $ .
Also, when the value of y is minimum, the first derivative of y with respect to x is zero.
i.e. $ y'=0 $ .
So, substitute $ y'=0 $ and $ x={{x}_{0}} $ in (i).
$ \Rightarrow 0=2a{{x}_{0}}+b $
$ \Rightarrow b=-2a{{x}_{0}} $ …. (ii)
We found that ‘a’ is positive and $ {{x}_{0}} $ is also positive. And the product of two positive numbers is always positive.
Therefore, $ -2a{{x}_{0}} $ is negative.
This means that ‘b’ is negative.
$ \Rightarrow b<0 $ .
Therefore, the option B is also correct.
When $ x={{x}_{0}} $ , we can see that the value of y is negative.
i.e. at $ x={{x}_{0}} $ , $ y<0 $ .
This means that $ ax_{0}^{2}+b{{x}_{0}}+c<0 $ …. (iii)
From (ii) we get that $ {{x}_{0}}=\dfrac{-b}{2a} $ .
Substitute this value in (iii).
$ \Rightarrow a{{\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right)}^{2}}+b\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right)+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+\dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}}{2a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+\dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}+4ac}{4a}<0 $
Here, since ‘a’ is positive, $ -{{b}^{2}}+4ac<0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}-4ac>0 $ .
Therefore, option A is also correct.
Hence, all first three options are correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Though we solved the question with differentiation method, we can also solve by using properties of quadratic function.
In the graph, we can see that for $ y=0 $ , the values of x are real.
i.e. the roots of the equation $ y=0 $ are real.
Therefore, the discriminant ( $ D={{b}^{2}}-4ac $ ) must be positive.
$ \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}-4ac>0 $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We can see that the function (value of y) is first decreasing. Then it reaches a minimum value then it starts to increase from that value of x.
Therefore, the graph has a minimum. For minima, the second derivative of the function $ f(x)=y $ with respect x must be positive, i.e. $ y''>0 $ .
Now differentiate y with rest to x.
$ \Rightarrow y'=2ax+b $ …. (i)
Differentiate the above equation with respect to x again.
$ \Rightarrow y''=2a $ .
But we know that $ y''>0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow 2a>0 $
$ \Rightarrow a>0 $ .
Therefore, option C is correct.
We can see that the y has a minimum value for a positive value of x. Let that x-coordinate be $ x={{x}_{0}} $ .
Also, when the value of y is minimum, the first derivative of y with respect to x is zero.
i.e. $ y'=0 $ .
So, substitute $ y'=0 $ and $ x={{x}_{0}} $ in (i).
$ \Rightarrow 0=2a{{x}_{0}}+b $
$ \Rightarrow b=-2a{{x}_{0}} $ …. (ii)
We found that ‘a’ is positive and $ {{x}_{0}} $ is also positive. And the product of two positive numbers is always positive.
Therefore, $ -2a{{x}_{0}} $ is negative.
This means that ‘b’ is negative.
$ \Rightarrow b<0 $ .
Therefore, the option B is also correct.
When $ x={{x}_{0}} $ , we can see that the value of y is negative.
i.e. at $ x={{x}_{0}} $ , $ y<0 $ .
This means that $ ax_{0}^{2}+b{{x}_{0}}+c<0 $ …. (iii)
From (ii) we get that $ {{x}_{0}}=\dfrac{-b}{2a} $ .
Substitute this value in (iii).
$ \Rightarrow a{{\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right)}^{2}}+b\left( \dfrac{-b}{2a} \right)+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+\dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}}{2a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+\dfrac{-2{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}}{4a}+c<0 $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{b}^{2}}+4ac}{4a}<0 $
Here, since ‘a’ is positive, $ -{{b}^{2}}+4ac<0 $ .
$ \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}-4ac>0 $ .
Therefore, option A is also correct.
Hence, all first three options are correct.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Though we solved the question with differentiation method, we can also solve by using properties of quadratic function.
In the graph, we can see that for $ y=0 $ , the values of x are real.
i.e. the roots of the equation $ y=0 $ are real.
Therefore, the discriminant ( $ D={{b}^{2}}-4ac $ ) must be positive.
$ \Rightarrow {{b}^{2}}-4ac>0 $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




