
The graph of the function \[\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] is a
(A) straight line passing through the point \[\left( 0,-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] with slope 2.
(B) straight line passing through the origin.
(C) parabola with vertex \[\left( 1,-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\]
(D) straight line passing through the point \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] and parallel to the x-axis.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: We know the formula, \[\cos \left( A-B \right)\cos \left( A+B \right)={{\cos }^{2}}A-{{\sin }^{2}}B\] . Replace A by (x+1) and B by 1, in this formula and get the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] . Now, put the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] in the equation \[\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] and the equation of the curve. Now, plot the graph and after plotting we get a line parallel to x-axis. When a line is parallel to the x-axis then the x-coordinate of points which is on the straight line can be any real number. Now, conclude the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have the equation of the curve,
\[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
The given equation is not in a simplified way. Therefore, we need to simplify it. The, only we will be able to plot its graph.
Now, simplifying equation (1), we get
\[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\cos \left( x+1-1 \right).\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] …………………..(2)
We know the identity, \[\cos \left( A-B \right)\cos \left( A+B \right)={{\cos }^{2}}A-{{\sin }^{2}}B\] ……………..(3)
Replacing A by (x+1) and B by 1, in equation (3), we get
\[\cos \left( x+1-1 \right)\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] ……………………….(4)
From equation (4), we have the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] .
Now, putting the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] in equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\cos \left( x+1-1 \right).\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got the equation of the curve which is, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
We can see that the equation of the curve is of straight line.
Now, plotting the graph of the curve, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
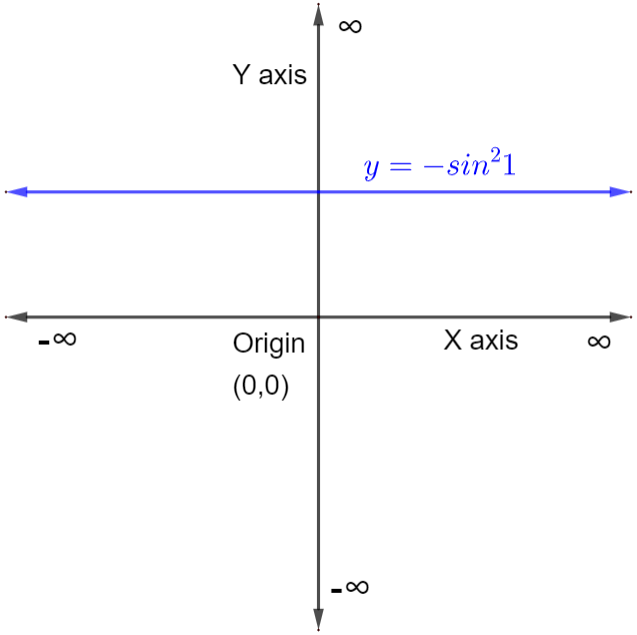
From the graph we can see that the slope of the straight line is zero and also parallel to x-axis.
Any point on the straight line has y coordinate always equal to \[-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] and the x coordinate of the point is any real number.
That is, \[x\in R\] and \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
From the graph, we can see that the straight line is passing through the point \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] and parallel to the x-axis.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We can also solve this question by another method. Using the formula, \[\cos A.\cos B=\dfrac{\cos \left( A+B \right)+\cos \left( A-B \right)}{2}\] for the simplification of the equation \[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] .
Now, simplifying we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\cos \left( 2x+2 \right)+\cos 2}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\cos 2\left( x+1 \right)+\cos 2\left( 1 \right)}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
We know the formula, \[\cos 2A=2{{\cos }^{2}}A-1\] and \[\cos 2A=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}A\] .
Using this formula in equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-1+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}1}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2\left( {{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-y={{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got the equation of the curve which is, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
We can see that the equation of the curve is of straight line.
Now, plotting the graph of the curve, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
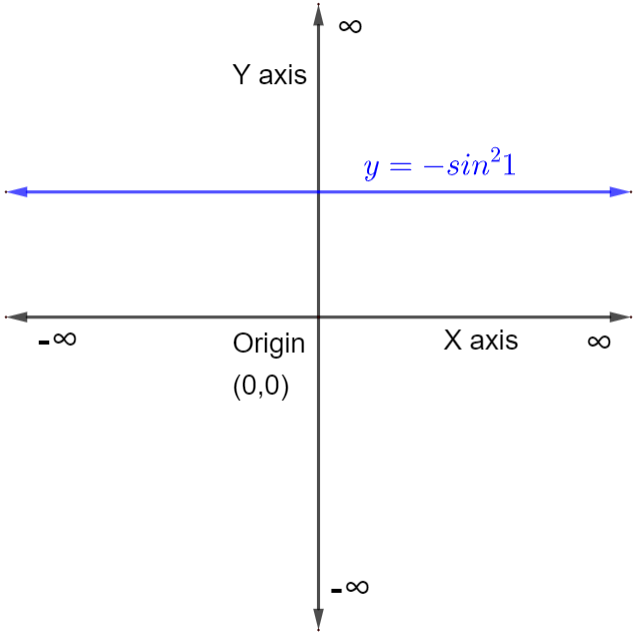
From the graph we can see that the slope of the straight line is zero and also parallel to x-axis.
Any point on the straight line has y coordinate always equal to \[-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] and the x coordinate of the point is any real number.
That is, \[x\in R\] and \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
From the graph, we can see that the straight line is passing through the point \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] and parallel to the x-axis.
Hence, option (D) is the correct one.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have the equation of the curve,
\[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
The given equation is not in a simplified way. Therefore, we need to simplify it. The, only we will be able to plot its graph.
Now, simplifying equation (1), we get
\[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\cos \left( x+1-1 \right).\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] …………………..(2)
We know the identity, \[\cos \left( A-B \right)\cos \left( A+B \right)={{\cos }^{2}}A-{{\sin }^{2}}B\] ……………..(3)
Replacing A by (x+1) and B by 1, in equation (3), we get
\[\cos \left( x+1-1 \right)\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] ……………………….(4)
From equation (4), we have the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] .
Now, putting the value of \[\cos \left( x \right)\cos \left( x+2 \right)\] in equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\cos \left( x+1-1 \right).\cos \left( x+1+1 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got the equation of the curve which is, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
We can see that the equation of the curve is of straight line.
Now, plotting the graph of the curve, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .

From the graph we can see that the slope of the straight line is zero and also parallel to x-axis.
Any point on the straight line has y coordinate always equal to \[-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] and the x coordinate of the point is any real number.
That is, \[x\in R\] and \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
From the graph, we can see that the straight line is passing through the point \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] and parallel to the x-axis.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We can also solve this question by another method. Using the formula, \[\cos A.\cos B=\dfrac{\cos \left( A+B \right)+\cos \left( A-B \right)}{2}\] for the simplification of the equation \[y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] .
Now, simplifying we get
\[\begin{align}
& y=\cos x.\cos \left( x+2 \right)-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\cos \left( 2x+2 \right)+\cos 2}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{\cos 2\left( x+1 \right)+\cos 2\left( 1 \right)}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
We know the formula, \[\cos 2A=2{{\cos }^{2}}A-1\] and \[\cos 2A=1-2{{\sin }^{2}}A\] .
Using this formula in equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-1+1-2{{\sin }^{2}}1}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{2\left( {{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-y={{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)}{2}-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y={{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right)-{{\sin }^{2}}1-{{\cos }^{2}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have got the equation of the curve which is, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
We can see that the equation of the curve is of straight line.
Now, plotting the graph of the curve, \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .

From the graph we can see that the slope of the straight line is zero and also parallel to x-axis.
Any point on the straight line has y coordinate always equal to \[-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] and the x coordinate of the point is any real number.
That is, \[x\in R\] and \[y=-{{\sin }^{2}}1\] .
From the graph, we can see that the straight line is passing through the point \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2},-{{\sin }^{2}}1 \right)\] and parallel to the x-axis.
Hence, option (D) is the correct one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




