
The given table shows some information about the trophic levels of a food chain.
Trophic level The energy in the trophic level Number of organisms P 10,000 kJ 1000 Q 200 kJ 10 R 100,000 kJ 1 S 2000 kJ 500
Select the option with the correct order of trophic levels in a food chain.
A. Q →S→P→R
B. S→Q→R→P
C. P→R→Q→S
D. R→P→S→Q
| Trophic level | The energy in the trophic level | Number of organisms |
| P | 10,000 kJ | 1000 |
| Q | 200 kJ | 10 |
| R | 100,000 kJ | 1 |
| S | 2000 kJ | 500 |
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: As per 10% law, during the exchange of natural food energy, starting with one trophic level then onto the next more elevated level, just around a modest amount of the moving energy is put away as flesh. The measure of energy at each trophic level declines as it travels through an environment. As meager as 10% of the energy at any trophic level is moved to the following level; the rest is lost generally through metabolic cycles as heat.
Complete answer:
1. Lindemann (1942) set forth a 10% law for the exchange of energy starting with one trophic level
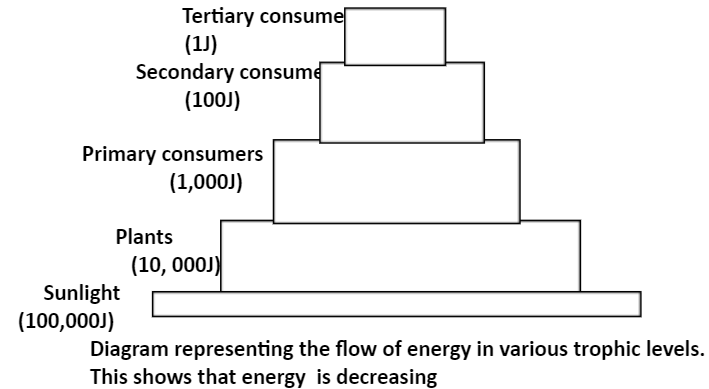 then onto the next.
then onto the next.
2. As per the law, during the exchange of natural food, starting with one trophic level then onto the next, just around a modest amount of the natural issue is put away as tissue.
3. The remaining is lost during a move or separated in a breath.
4. Plants use solar energy for essential creation and can store just 10% of the used energy as net creation accessible for the herbivores.
5. When plants are eaten 10% of energy is transferred. At the point when a carnivore expends that organism, just about 10% of energy is fixed in its tissue for a more elevated level.
So, the correct answer is “Option D (R→P→S→Q)”.
Note: The 10% law was given by Raymond Lindeman. This law expresses that when energy is moved from one trophic level to the next, just 10% energy from the natural issue is passed on. It can be best explained by taking an example of the pyramid of energy. The pyramid of energy portrays the energy stream structure from one trophic level to another trophic level in the food chain. As per 10% law, 90% of the energy caught from the past trophic level is lost as warmth to the earth and just 10% is made accessible to the following trophic level.
Complete answer:
1. Lindemann (1942) set forth a 10% law for the exchange of energy starting with one trophic level

2. As per the law, during the exchange of natural food, starting with one trophic level then onto the next, just around a modest amount of the natural issue is put away as tissue.
3. The remaining is lost during a move or separated in a breath.
4. Plants use solar energy for essential creation and can store just 10% of the used energy as net creation accessible for the herbivores.
5. When plants are eaten 10% of energy is transferred. At the point when a carnivore expends that organism, just about 10% of energy is fixed in its tissue for a more elevated level.
So, the correct answer is “Option D (R→P→S→Q)”.
Note: The 10% law was given by Raymond Lindeman. This law expresses that when energy is moved from one trophic level to the next, just 10% energy from the natural issue is passed on. It can be best explained by taking an example of the pyramid of energy. The pyramid of energy portrays the energy stream structure from one trophic level to another trophic level in the food chain. As per 10% law, 90% of the energy caught from the past trophic level is lost as warmth to the earth and just 10% is made accessible to the following trophic level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




