
The given relation is cotAcotBcotC$ \leqslant $0 in a triangle ABC
A. true
B. false
Answer
597.6k+ views
HINT- The concept used in this question is that we have to understand the difference between right angle, acute angle and obtuse angle triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
Right angled triangle- a triangle is said to be right angled if one of its three angles is ${90^0}$
Acute angled triangle – a triangle is said to be acute angled triangle if all the three angles of triangle is less than ${90^0}$
Obtuse angled triangle – a triangle is said to be obtuse angled if its one angle is greater than ${90^0}$
Now, moving on to the question,
Given, cotAcotBcotC$ \leqslant $0
Since ABC is a triangle we have three possible cases
i) Right angled triangle
Let A = ${90^0}$
cotAcotBcotC = 0
ii) Acute angled triangle
A, B, C are in Ist quadrant
cotAcotBcotC > 0
iii) Obtuse angled triangle
Let angle A > ${90^0}$, but angle B and C < ${90^0}$
cotA < 0 but cotBcotC > 0
cotAcotBcotC < 0
Therefore, cotAcotBcotC$ \leqslant $0 is only possible for right angles and obtuse angled triangles, but it is false for acute angled triangles.
Therefore, the statement
cotAcotBcotC $ \leqslant $ 0 is false for A, B, C are angles in triangle ABC.
NOTE- The trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right angled triangles to ratios of two side lengths. The most widely used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent. Their reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant and the cotangent.
In a right triangle ABC right angled at B, we have hypotenuse = AC, base = BC and perpendicular = AB
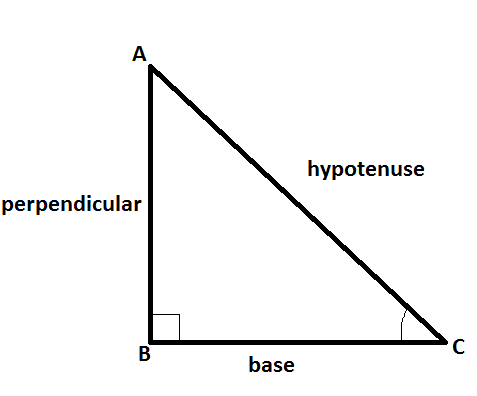
$\sin C = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}$
$\cos C = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}}$
$\tan C = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Right angled triangle- a triangle is said to be right angled if one of its three angles is ${90^0}$
Acute angled triangle – a triangle is said to be acute angled triangle if all the three angles of triangle is less than ${90^0}$
Obtuse angled triangle – a triangle is said to be obtuse angled if its one angle is greater than ${90^0}$
Now, moving on to the question,
Given, cotAcotBcotC$ \leqslant $0
Since ABC is a triangle we have three possible cases
i) Right angled triangle
Let A = ${90^0}$
cotAcotBcotC = 0
ii) Acute angled triangle
A, B, C are in Ist quadrant
cotAcotBcotC > 0
iii) Obtuse angled triangle
Let angle A > ${90^0}$, but angle B and C < ${90^0}$
cotA < 0 but cotBcotC > 0
cotAcotBcotC < 0
Therefore, cotAcotBcotC$ \leqslant $0 is only possible for right angles and obtuse angled triangles, but it is false for acute angled triangles.
Therefore, the statement
cotAcotBcotC $ \leqslant $ 0 is false for A, B, C are angles in triangle ABC.
NOTE- The trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right angled triangles to ratios of two side lengths. The most widely used trigonometric functions are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent. Their reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant and the cotangent.
In a right triangle ABC right angled at B, we have hypotenuse = AC, base = BC and perpendicular = AB

$\sin C = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse}}$
$\cos C = \dfrac{{base}}{{hypotenuse}}$
$\tan C = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




