
The given graph shows various pulmonary air volumes and capacities. What is depicted by X and Y in the graph?
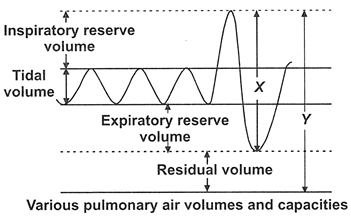
A.Functional residual capacity and vital capacity
B.Total lung capacity and inspiratory capacity
C.Vital capacity and total lung capacity
D.Inspiratory capacity and functional residual capacity

Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: Respiratory starts when start to take in the air via our nostrils to the nasal cavity. After passing through the nasal cavity the air passes through the trachea. The air then reaches the lungs. Lung volume refers to the total volume of air that is present in the lung during different phases of the respiratory cycle. There are four standard volumes of the lung that include inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. We can look into these definitions and see what X and Y represent in the given graph.
Complete answer:
Similar to the four standard lung volumes there are four lung capacities : inspiratory capacity, functional residual capacity, vital capacity, and total lung capacity.
Tidal volume is defined as the volume that enters and leaves during each normal breath that we take. Inspiratory reserve volume can be defined as the extra amount of volume that we can intake during each inspiration. This inspiratory reserve above the tidal volume is from normal quiet inspiration to maximum inspiration. Similarly, expiratory reserve volume is the extra amount of volume that we release during each expiration. Residual volume is defined as the volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum expiration.
Lung capacities consist of two or more lung volumes. We can see how each of the four vital lung capacities is calculated.
Vital capacity is defined as the volume that can be exhaled after maximum inspiration to that of the maximum expiration. It can be calculated as Vital capacity \[ = \] Expiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Inspiratory reserve volume\[ + \] Tidal volume
Inspiratory capacity is defined as the volume breathed in from normal expiration to maximum inspiration. It can be calculated as,
Inspiratory capacity \[ = \]Tidal volume \[ + \] Inspiratory reserve volume
Functional residual capacity can be defined as the total volume remaining in the lungs after normal expiration. It can be calculated as Functional residual capacity\[ = \]Expiratory reserve volume\[ + \]Residual volume
Total lung capacity can be defined as the total volume of the air that is present in the lungs after maximum inspiration. It can be calculated as, Total lung capacity\[ = \]sum of all the volumes.
In the graph the area that is comprised by X\[ = \] Inspiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Tidal volume \[ + \]expiratory reserve volume
Therefore from the above-discussed capacities, we know that this is equal to vital capacity.
Now the area is covered by the Y\[ = \] sum of all the volumes. That is,
Y\[ = \]Inspiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Tidal volume \[ + \]expiratory reserve volume\[ + \] residual volume.
Therefore Y represents total lung capacity.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Note:
Human lung capacities are usually determined by many factors including genetics, gender, and height. On average, the maximum capacity of air that the lung can hold is almost six liters. However, they do not always work on this maximal capacity. Lung volume only measures any one function and lung capacity comprises any two or more volumes.
Complete answer:
Similar to the four standard lung volumes there are four lung capacities : inspiratory capacity, functional residual capacity, vital capacity, and total lung capacity.
Tidal volume is defined as the volume that enters and leaves during each normal breath that we take. Inspiratory reserve volume can be defined as the extra amount of volume that we can intake during each inspiration. This inspiratory reserve above the tidal volume is from normal quiet inspiration to maximum inspiration. Similarly, expiratory reserve volume is the extra amount of volume that we release during each expiration. Residual volume is defined as the volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum expiration.
Lung capacities consist of two or more lung volumes. We can see how each of the four vital lung capacities is calculated.
Vital capacity is defined as the volume that can be exhaled after maximum inspiration to that of the maximum expiration. It can be calculated as Vital capacity \[ = \] Expiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Inspiratory reserve volume\[ + \] Tidal volume
Inspiratory capacity is defined as the volume breathed in from normal expiration to maximum inspiration. It can be calculated as,
Inspiratory capacity \[ = \]Tidal volume \[ + \] Inspiratory reserve volume
Functional residual capacity can be defined as the total volume remaining in the lungs after normal expiration. It can be calculated as Functional residual capacity\[ = \]Expiratory reserve volume\[ + \]Residual volume
Total lung capacity can be defined as the total volume of the air that is present in the lungs after maximum inspiration. It can be calculated as, Total lung capacity\[ = \]sum of all the volumes.
In the graph the area that is comprised by X\[ = \] Inspiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Tidal volume \[ + \]expiratory reserve volume
Therefore from the above-discussed capacities, we know that this is equal to vital capacity.
Now the area is covered by the Y\[ = \] sum of all the volumes. That is,
Y\[ = \]Inspiratory reserve volume \[ + \]Tidal volume \[ + \]expiratory reserve volume\[ + \] residual volume.
Therefore Y represents total lung capacity.
Therefore the correct option is C.
Note:
Human lung capacities are usually determined by many factors including genetics, gender, and height. On average, the maximum capacity of air that the lung can hold is almost six liters. However, they do not always work on this maximal capacity. Lung volume only measures any one function and lung capacity comprises any two or more volumes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




