
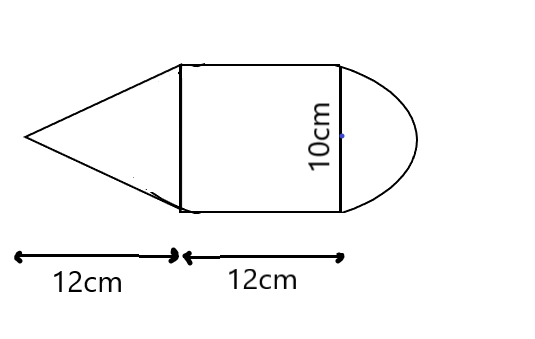
The given figure shows the cross section of a cone, a cylinder and a hemisphere all which diameter $10cm$, and the other dimensions are as shown. Calculate:
a) The total surface area
b) The total volume of the solid.
c) The density of the material if its total weight is $1.7kg$.

Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: In order to find the total surface area, we need to sum the surface area of the cone, surface area of the cylinder and surface area of the hemisphere. Similarly, for the total volume of the solid, sum the volume of the cone, volume of cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere. The volume and total surface area can be found out from the formulas of mensuration for these solids.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three parts of a solid that is a cone, a cylinder and a hemisphere, each having a diameter of $10cm$.
And we know, the radius is: $\dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5cm$
The diagram according to the details:
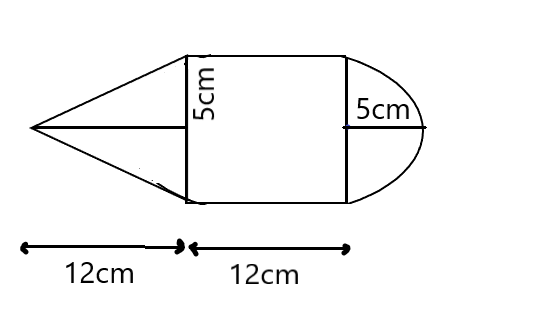
From the figure, the values given for each solid part is:
Cone:
Height$ = 12cm$
Radius$ = 5cm$
To find the surface area of cone, we need slant height$\left( l \right)$ which is equal to $l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {r^2}} $.
Substituting the values of height and radius to obtain slant height, and we get:
$
l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {r^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {12} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 5 \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {144 + 25} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {169} \\
$
Since, we know that $\sqrt {169} = 13$
So, the slant height of the cone$\left( l \right)$ is $13cm$.
Cylinder:
Height$ = 12cm$
Radius$ = 5cm$
Hemisphere:
Radius$ = 5cm$
From mensuration, we know the formulas for the solids for surface area, which are:
Surface area of cone$ = \pi rl$
Surface area of cylinder$ = 2\pi rh$
Surface area of cone$ = 2\pi {r^2}$
(a).The total surface area of solid is equal to the sum of surface area of cone, surface area of cylinder and the surface area of hemisphere:
Total surface area
$
TSA\left( {Cone} \right) + TSA\left( {Cylinder} \right) + TSA\left( {Hemisphere} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \pi rl + 2\pi rh + 2\pi {r^2} \\
$
Taking $\pi r$common:
$\pi r\left( {l + 2h + 2r} \right)$
Substituting the values, obtained and given above in the equation, and we get:
$
TSA = \pi r\left( {l + 2h + 2r} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 2 \times 12 + 2 \times 5} \right) \\
$
Solving the parenthesis, and multiplying it outside the brackets, we get:
$
TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 2 \times 12 + 2 \times 5} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 24 + 10} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {47} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22 \times 5 \times 47}}{7} = \dfrac{{5170}}{7} \\
\Rightarrow TSA = 738.57 \\
$
Therefore, the total surface area of the solid is $738.57c{m^2}$.
(b) Total Volume of the solid:
From mensuration, we know the formulas for the solids for volume, which are:
Volume of cone$ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Volume of cylinder$ = \pi {r^2}h$
Volume of hemisphere$ = \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}$
The total Volume of solid is equal to the sum of volume of cone, volume of cylinder and the volume of hemisphere:
Total Volume:
\[
Volume\left( {Cone} \right) + Volume\left( {Cylinder} \right) + Volume\left( {Hemisphere} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h + \pi {r^2}h + \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3} \\
\]
Taking $\pi r$common:
$\pi r\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}rh + rh + \dfrac{2}{3}{r^2}} \right)$
Substituting the values, obtained and given above in the equation, and we get:
$
Volume = \pi r\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}rh + rh + \dfrac{2}{3}{r^2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times 5 \times 12 + 5 \times 12 + \dfrac{2}{3} \times 5 \times 5} \right) \\
$
Solving the parenthesis, and multiplying it with values outside the brackets, we get:
\[
Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times 5 \times 12 + 5 \times 12 + \dfrac{2}{3} \times 5 \times 5} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{3} + 60 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{60 + 180 + 50}}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{290}}{3}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22 \times 5 \times 290}}{{7 \times 3}} = \dfrac{{31900}}{{21}} \\
\Rightarrow Volume = 1519.05 \\
\]
Therefore, The Volume of the solid is $1519.05c{m^3}$.
(c) Density
For density we know that density is the mass of an object that is divided by volume.
So, the mass given: \[1.7kg\]
Since, \[1kg = 1000g\] .So, \[1.7kg = 1.7 \times 1000g = 1700g\].
And, the volume obtained above is $1519.05c{m^3}$.
So, Density$ = \dfrac{{mass}}{{volume}}$
Substituting the values:
$
Density = \dfrac{{mass}}{{volume}} \\
Density = \dfrac{{1700}}{{1519.05}}g/c{m^3} \\
Density = 1.12g/c{m^3} \\
$
Therefore, the values obtained are:
a) The total surface area-$738.57c{m^2}$
b) The total volume of the solid-$1519.05c{m^3}$
c) The density of the material if its total weight is $1.7kg = 1.12g/c{m^3}$
Note:
> It’s very important to remember the mensuration formula of solids to solve this type of question. A single wrong formula can make the whole answer wrong.
> Hemisphere is nothing but half of the sphere.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given three parts of a solid that is a cone, a cylinder and a hemisphere, each having a diameter of $10cm$.
And we know, the radius is: $\dfrac{{diameter}}{2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5cm$
The diagram according to the details:

From the figure, the values given for each solid part is:
Cone:
Height$ = 12cm$
Radius$ = 5cm$
To find the surface area of cone, we need slant height$\left( l \right)$ which is equal to $l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {r^2}} $.
Substituting the values of height and radius to obtain slant height, and we get:
$
l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {r^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {{{\left( {12} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 5 \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {144 + 25} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {169} \\
$
Since, we know that $\sqrt {169} = 13$
So, the slant height of the cone$\left( l \right)$ is $13cm$.
Cylinder:
Height$ = 12cm$
Radius$ = 5cm$
Hemisphere:
Radius$ = 5cm$
From mensuration, we know the formulas for the solids for surface area, which are:
Surface area of cone$ = \pi rl$
Surface area of cylinder$ = 2\pi rh$
Surface area of cone$ = 2\pi {r^2}$
(a).The total surface area of solid is equal to the sum of surface area of cone, surface area of cylinder and the surface area of hemisphere:
Total surface area
$
TSA\left( {Cone} \right) + TSA\left( {Cylinder} \right) + TSA\left( {Hemisphere} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \pi rl + 2\pi rh + 2\pi {r^2} \\
$
Taking $\pi r$common:
$\pi r\left( {l + 2h + 2r} \right)$
Substituting the values, obtained and given above in the equation, and we get:
$
TSA = \pi r\left( {l + 2h + 2r} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 2 \times 12 + 2 \times 5} \right) \\
$
Solving the parenthesis, and multiplying it outside the brackets, we get:
$
TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 2 \times 12 + 2 \times 5} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {13 + 24 + 10} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {47} \right) \\
\Rightarrow TSA = \dfrac{{22 \times 5 \times 47}}{7} = \dfrac{{5170}}{7} \\
\Rightarrow TSA = 738.57 \\
$
Therefore, the total surface area of the solid is $738.57c{m^2}$.
(b) Total Volume of the solid:
From mensuration, we know the formulas for the solids for volume, which are:
Volume of cone$ = \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Volume of cylinder$ = \pi {r^2}h$
Volume of hemisphere$ = \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}$
The total Volume of solid is equal to the sum of volume of cone, volume of cylinder and the volume of hemisphere:
Total Volume:
\[
Volume\left( {Cone} \right) + Volume\left( {Cylinder} \right) + Volume\left( {Hemisphere} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h + \pi {r^2}h + \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3} \\
\]
Taking $\pi r$common:
$\pi r\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}rh + rh + \dfrac{2}{3}{r^2}} \right)$
Substituting the values, obtained and given above in the equation, and we get:
$
Volume = \pi r\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}rh + rh + \dfrac{2}{3}{r^2}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times 5 \times 12 + 5 \times 12 + \dfrac{2}{3} \times 5 \times 5} \right) \\
$
Solving the parenthesis, and multiplying it with values outside the brackets, we get:
\[
Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} \times 5 \times 12 + 5 \times 12 + \dfrac{2}{3} \times 5 \times 5} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{60}}{3} + 60 + \dfrac{{50}}{3}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{60 + 180 + 50}}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{{22}}{7} \times 5\left( {\dfrac{{290}}{3}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow Volume = \dfrac{{22 \times 5 \times 290}}{{7 \times 3}} = \dfrac{{31900}}{{21}} \\
\Rightarrow Volume = 1519.05 \\
\]
Therefore, The Volume of the solid is $1519.05c{m^3}$.
(c) Density
For density we know that density is the mass of an object that is divided by volume.
So, the mass given: \[1.7kg\]
Since, \[1kg = 1000g\] .So, \[1.7kg = 1.7 \times 1000g = 1700g\].
And, the volume obtained above is $1519.05c{m^3}$.
So, Density$ = \dfrac{{mass}}{{volume}}$
Substituting the values:
$
Density = \dfrac{{mass}}{{volume}} \\
Density = \dfrac{{1700}}{{1519.05}}g/c{m^3} \\
Density = 1.12g/c{m^3} \\
$
Therefore, the values obtained are:
a) The total surface area-$738.57c{m^2}$
b) The total volume of the solid-$1519.05c{m^3}$
c) The density of the material if its total weight is $1.7kg = 1.12g/c{m^3}$
Note:
> It’s very important to remember the mensuration formula of solids to solve this type of question. A single wrong formula can make the whole answer wrong.
> Hemisphere is nothing but half of the sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




