
The girth of the stem or root increases due to?
(a) Apical meristem
(b) Cambium
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) Epidermis
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The increase in girth and diameter of the plant is known as secondary growth. The tissues responsible for the secondary growth are mainly found beneath the bark and in the vascular bundles of dicot roots and stems.
Complete answer:
The girth of the stem or root increases because of ‘Cambium’. Cambiums are the lateral meristems that participate in the secondary growth of dicots. Generally, secondary growth does not occur in monocots due to a lack of vascular cambium in them.
Lateral meristem: These are the meristems that are present along the lateral sides of roots and shoots of many plants. They are found in the mature regions of roots and shoots. These do not occur in all plants. They occur only in those plants that produce the woody axis or show secondary growth. These are generally not present from the very beginning of the life of a plant and appear later than the primary meristems that are why they are called secondary meristems. The lateral meristems are the cylindrical meristems that divide in the radial direction resulting in the increase in girth of the stems and roots.
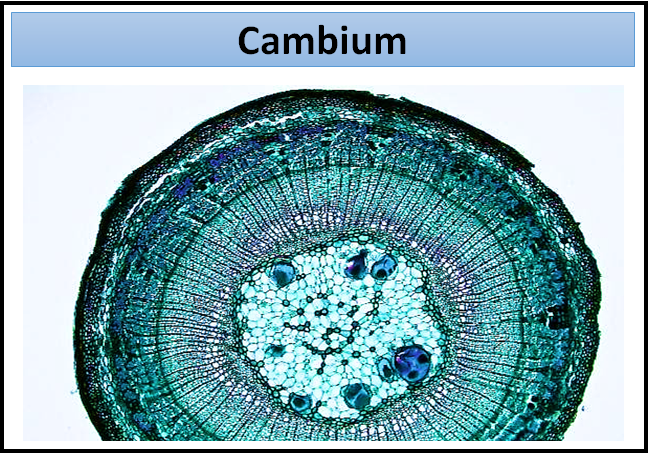
So, the correct answer is ‘Cambium’.
Additional Information:
The various examples of lateral meristems or cambium are:
- Fascicular vascular cambium: It is the meristematic tissues that develop within the vascular bundles. It is also known as intrafascicular cambium.
- Interfascicular cambium: The meristematic tissue which develops between the vascular bundles is known as interfascicular cambium.
- Cork cambium: This lateral meristem forms the cork, a tough protective material during the secondary growth.
Note: Meristems are the specialized areas in the plant body that possess the meristematic tissue. These are the areas of active cell division as the cells present in them keep on dividing to form other cells. Meristem is of three types based on their position, they are apical meristem, intercalary meristem, and lateral meristem.
Complete answer:
The girth of the stem or root increases because of ‘Cambium’. Cambiums are the lateral meristems that participate in the secondary growth of dicots. Generally, secondary growth does not occur in monocots due to a lack of vascular cambium in them.
Lateral meristem: These are the meristems that are present along the lateral sides of roots and shoots of many plants. They are found in the mature regions of roots and shoots. These do not occur in all plants. They occur only in those plants that produce the woody axis or show secondary growth. These are generally not present from the very beginning of the life of a plant and appear later than the primary meristems that are why they are called secondary meristems. The lateral meristems are the cylindrical meristems that divide in the radial direction resulting in the increase in girth of the stems and roots.

So, the correct answer is ‘Cambium’.
Additional Information:
The various examples of lateral meristems or cambium are:
- Fascicular vascular cambium: It is the meristematic tissues that develop within the vascular bundles. It is also known as intrafascicular cambium.
- Interfascicular cambium: The meristematic tissue which develops between the vascular bundles is known as interfascicular cambium.
- Cork cambium: This lateral meristem forms the cork, a tough protective material during the secondary growth.
Note: Meristems are the specialized areas in the plant body that possess the meristematic tissue. These are the areas of active cell division as the cells present in them keep on dividing to form other cells. Meristem is of three types based on their position, they are apical meristem, intercalary meristem, and lateral meristem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




