
The geometry of ${H_2}S$ and its dipole moment are:
(A) Angular and non zero
(B) Angular and zero
(C) Linear and non zero
(D) Linear and zero
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The geometry of ${H_2}S$ is the same as the molecule in which we replace sulphur atom by oxygen atom in ${H_2}S$. Dipole moment is the net magnetic moment generated in the molecule by difference in electronegativity in the atoms forming bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first find the shape of ${H_2}S$ with the help of the VSEPR theory and then we will find the dipole moment of the molecule whether it is zero or non zero.
- The electronic configuration of the sulphur atom is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^4}$. It is placed under an oxygen atom in the periodic table.
- We can see that two hydrogen atoms are bonded with sulphur atoms. So, they will form a bond with sulphur using two p orbitals of sulphur. Thus, if we see the valence orbital of a sulphur atom, there are two lone pairs and two bond pairs. So, the structure of the compound will be as shown below.
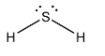
- We know that there is repulsion between the lone pairs and bond pairs. So, they will arrange in a manner that minimum repulsion is there. So, we get the angular shape of the molecule.
- In case you do not know the shape of this molecule, then you can predict its shape by comparing it with ${H_2}O$ where oxygen is from the same group as sulphur. So, both will have the same shape.
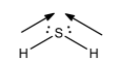
- Now, dipole moment is the magnetic moment produced in the molecule as a result of difference in electronegativity in the atom forming bonds.
- Here, we know that sulphur is more electronegative than hydrogen and thus both bonds will have dipole moment. The direction of both the moments generated is not exactly opposite to each other. So, there will be some resultant dipole moment there in the molecule. So, we can conclude that ${H_2}S$ is angular in shape and its dipole moment will be non zero.
So, the correct answer is (A).
Note: Remember that even if only two atoms are bonded with sulphur atoms in ${H_2}S$, its shape is not linear. This is because a sulphur atom also has two lone pairs of electrons in its valence shell. This will not allow the molecule to be linear as it will repel the bond pairs.
Complete step by step solution:
We will first find the shape of ${H_2}S$ with the help of the VSEPR theory and then we will find the dipole moment of the molecule whether it is zero or non zero.
- The electronic configuration of the sulphur atom is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^4}$. It is placed under an oxygen atom in the periodic table.
- We can see that two hydrogen atoms are bonded with sulphur atoms. So, they will form a bond with sulphur using two p orbitals of sulphur. Thus, if we see the valence orbital of a sulphur atom, there are two lone pairs and two bond pairs. So, the structure of the compound will be as shown below.

- We know that there is repulsion between the lone pairs and bond pairs. So, they will arrange in a manner that minimum repulsion is there. So, we get the angular shape of the molecule.
- In case you do not know the shape of this molecule, then you can predict its shape by comparing it with ${H_2}O$ where oxygen is from the same group as sulphur. So, both will have the same shape.

- Now, dipole moment is the magnetic moment produced in the molecule as a result of difference in electronegativity in the atom forming bonds.
- Here, we know that sulphur is more electronegative than hydrogen and thus both bonds will have dipole moment. The direction of both the moments generated is not exactly opposite to each other. So, there will be some resultant dipole moment there in the molecule. So, we can conclude that ${H_2}S$ is angular in shape and its dipole moment will be non zero.
So, the correct answer is (A).
Note: Remember that even if only two atoms are bonded with sulphur atoms in ${H_2}S$, its shape is not linear. This is because a sulphur atom also has two lone pairs of electrons in its valence shell. This will not allow the molecule to be linear as it will repel the bond pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




