
The general solution of $\tan 5\theta =\cot 2\theta $ is \[\]
A.$\theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{14}$\[\]
B. $\theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{5}$\[\]
C. $\theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{2}$\[\]
D. $\theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{3}$\[\]
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: We use the complimentary angle relation $\tan \theta =\cot \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-\theta \right)$ and convert cotangent in the given equation $\tan 5\theta =\cot 2\theta $ to tangent and the find the solution for $\theta $ using the information that the solution of the equation $\tan x=\tan \alpha $ is given by $x=n\pi +\alpha $ for some arbitrary integer $n$.\[\]
Complete step by step answer:
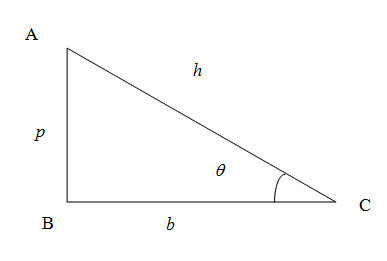
We know that in right angled triangle the side opposite to right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.\[\]
Here in the above diagram of right angled triangle ABC we have,
\[AC=h,AB=p,BC=b\]
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the tangent of the angle is the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side (excluding hypotenuse, also called leg adjacent) . So we have tangent of the angle of angle $\theta $\[\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{p}{b}\]
The ratio reciprocal to tangent of the angle is called co-tangent which means of ratio of leg adjacent to the opposite side is denoted by $\cot \theta $ and is given by
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{b}{p}\]
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. So we have
\[\begin{align}
& A+B+C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow A+C={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow A={{90}^{\circ }}-C={{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \\
\end{align}\]
We use definition of tangent and cotangent to for angles $A,C$ to have,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan C=\tan \theta =\dfrac{p}{b},\cot C=\cot \theta =\dfrac{b}{p} \\
& \cot A=\cot \left( 90-\theta \right)=\dfrac{p}{b},\cot A=\cot \left( 90-\theta \right)=\dfrac{b}{p} \\
\end{align}\]
We have from above,
\[\tan \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\cot \theta ,\cot \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta \]
The above equation is called complementary angle relation of tangent and cotangent or reduction formula of tangent-cotangent.\[\]
We know the solutions of the equation $\tan x=\tan \alpha $ where $x$ is the unknown and $\alpha $ is the known angle is given with some arbitrary integer $n$ as
\[x=n\pi +\alpha \]
We are given in the question the trigonometric equation with unknown angle $\theta $ as,
\[\tan 5\theta =\cot 2\theta \]
We use the complimentary angle relation for $\cot \left( 2\theta \right)$ and convert it into tangent of the angle $2\theta $ to have,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 5\theta =\tan \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-2\theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 5\theta =\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We find the solutions of above equation in tangent function taking unknown $x=5\theta $ and the known $\alpha =\dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta $ as
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 5\theta =n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta \\
& \Rightarrow 7\theta =n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
We divide the above equation by 7 to have the required result as,
\[\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{14},n\in Z\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We note that the tangent function is not defined for $\theta =\left( 2n+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and cotangent function is not defined for $\theta =n\pi $ and hence the obtained result well defined. We must not confuse between complementary and supplementary angle relation which is given by a shift $\pi $ radian as $\tan \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\tan \theta ,\cot \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\cot \theta $.
Complete step by step answer:

We know that in right angled triangle the side opposite to right angled triangle is called hypotenuse denoted as $h$, the vertical side is called perpendicular denoted as $p$ and the horizontal side is called the base denoted as $b$.\[\]
Here in the above diagram of right angled triangle ABC we have,
\[AC=h,AB=p,BC=b\]
We know from the trigonometric ratios in a right angled triangle the tangent of the angle is the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side (excluding hypotenuse, also called leg adjacent) . So we have tangent of the angle of angle $\theta $\[\]
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{p}{b}\]
The ratio reciprocal to tangent of the angle is called co-tangent which means of ratio of leg adjacent to the opposite side is denoted by $\cot \theta $ and is given by
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{b}{p}\]
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$. So we have
\[\begin{align}
& A+B+C={{180}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow A+C={{90}^{\circ }} \\
& \Rightarrow A={{90}^{\circ }}-C={{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \\
\end{align}\]
We use definition of tangent and cotangent to for angles $A,C$ to have,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan C=\tan \theta =\dfrac{p}{b},\cot C=\cot \theta =\dfrac{b}{p} \\
& \cot A=\cot \left( 90-\theta \right)=\dfrac{p}{b},\cot A=\cot \left( 90-\theta \right)=\dfrac{b}{p} \\
\end{align}\]
We have from above,
\[\tan \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\cot \theta ,\cot \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\sin \theta \]
The above equation is called complementary angle relation of tangent and cotangent or reduction formula of tangent-cotangent.\[\]
We know the solutions of the equation $\tan x=\tan \alpha $ where $x$ is the unknown and $\alpha $ is the known angle is given with some arbitrary integer $n$ as
\[x=n\pi +\alpha \]
We are given in the question the trigonometric equation with unknown angle $\theta $ as,
\[\tan 5\theta =\cot 2\theta \]
We use the complimentary angle relation for $\cot \left( 2\theta \right)$ and convert it into tangent of the angle $2\theta $ to have,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 5\theta =\tan \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-2\theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 5\theta =\tan \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We find the solutions of above equation in tangent function taking unknown $x=5\theta $ and the known $\alpha =\dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta $ as
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 5\theta =n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}-2\theta \\
& \Rightarrow 7\theta =n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
We divide the above equation by 7 to have the required result as,
\[\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{n\pi }{7}+\dfrac{\pi }{14},n\in Z\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We note that the tangent function is not defined for $\theta =\left( 2n+1 \right)\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and cotangent function is not defined for $\theta =n\pi $ and hence the obtained result well defined. We must not confuse between complementary and supplementary angle relation which is given by a shift $\pi $ radian as $\tan \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\tan \theta ,\cot \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\cot \theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




