
The gas used in the hydrogenation of oils in presence of nickel as a catalyst is:
A.Methane
B.Ethane
C.Ozone
D.Hydrogen
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Here we have been asked to name the gas which is used in the hydrogenation of oils. Hydrogenation, as the name suggests should be related to the addition of hydrogen gas itself. Although, the reaction of different kinds of gases with hydrocarbons would lead to the formation of different products.
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrogenation is the chemical reaction in which a hydrocarbon reacts with molecular hydrogen in the presence of metal catalysts like platinum, palladium, or nickel. This process is used for the reduction of unsaturated organic compounds to saturated organic compounds. Hydrogenation takes place by addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to the unsaturated compound. This reaction occurs in the presence of a metal catalyst, where the ${H_2}$ bond cleaves and two $H$ atoms attach to the catalytic surface, leading to the formation of metal-hydrogen bonds. The unsaturated alkene also gets absorbed on to the catalytic surface, where the hydrogen addition takes place.
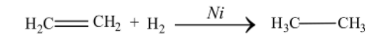
Similar reaction occurs in the case of hydrogenation of oils. Vegetable oils are mainly derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids. In food industries, hydrogenation of oils is mostly done in order to convert the liquid oil into solid or semi-solid fats. Hydrogenation of oil increases the shelf life of oils and various other products used in the food industry.
Hence, option (D) Hydrogen is the correct answer.
Note:
Partially or fully hydrogenated cooking vegetable oil is synthesised by this process of hydrogenation, where palm oil or palm olein oil is treated with hydrogen gas in presence of nickel catalyst under low pressure in reactors. This is commonly known as vanaspati. It contains saturated trans-fat which is an unhealthy substitute for oil and ghee.
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrogenation is the chemical reaction in which a hydrocarbon reacts with molecular hydrogen in the presence of metal catalysts like platinum, palladium, or nickel. This process is used for the reduction of unsaturated organic compounds to saturated organic compounds. Hydrogenation takes place by addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to the unsaturated compound. This reaction occurs in the presence of a metal catalyst, where the ${H_2}$ bond cleaves and two $H$ atoms attach to the catalytic surface, leading to the formation of metal-hydrogen bonds. The unsaturated alkene also gets absorbed on to the catalytic surface, where the hydrogen addition takes place.
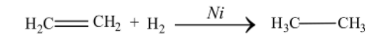
Similar reaction occurs in the case of hydrogenation of oils. Vegetable oils are mainly derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids. In food industries, hydrogenation of oils is mostly done in order to convert the liquid oil into solid or semi-solid fats. Hydrogenation of oil increases the shelf life of oils and various other products used in the food industry.
Hence, option (D) Hydrogen is the correct answer.
Note:
Partially or fully hydrogenated cooking vegetable oil is synthesised by this process of hydrogenation, where palm oil or palm olein oil is treated with hydrogen gas in presence of nickel catalyst under low pressure in reactors. This is commonly known as vanaspati. It contains saturated trans-fat which is an unhealthy substitute for oil and ghee.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




