
The gas molecules randomly move in all directions and collide with each other and with the wall of the container. It is difficult to determine the speed of an individual molecule but it has become possible to work out the distribution of molecules among different molecular speeds. This is known as Maxwell Boltzmann distribution.
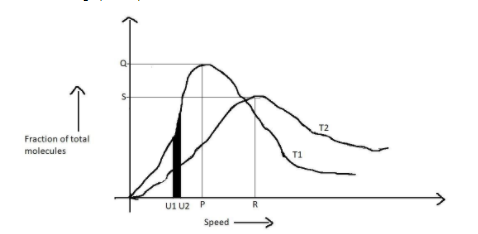
Consider the following graph about Maxwell’s distribution of speeds at two different temperatures \[{{{T}}_1}\] and ${{{T}}_2}$.
In the above graph the point P refers to:
A. root mean square speed at ${{{T}}_1}$
B. average speed at ${{{T}}_1}$
C. most probable speed at ${{{T}}_1}$
D. highest possible speed at ${{{T}}_1}$

Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint:We know that different molecules have different speeds. The given graph is about Maxwell’s distribution of speeds of molecules at different temperatures. This is based on the kinetic molecular theory of gases. This theory is based on the motion of gas molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The gas molecules are continuously and randomly moving with high velocities. These gas molecules collide with each other. In these collisions, kinetic energy is not lost. Thus they are said to be elastic. Due to these collisions, pressure is produced on the walls of the container. Moreover, the average kinetic energy increases when the absolute temperature is increased.
There are three types of velocities. They are probable velocity, average velocity and root mean square velocity. When the mean of the velocities is taken, it is known as the average velocity. When we take the mean square of the velocities, it is known as the root mean square velocity. When we consider the largest number of gas molecules, its velocity is known as the probable velocity.
At temperature ${{{T}}_1}$, the highest peak is obtained than that at temperature ${{{T}}_2}$. Therefore the speed under ${{{T}}_1}$ is called the probable velocity, i.e. P represents probable velocity at ${{{T}}_1}$. R represents the probable velocity at temperature ${{{T}}_2}$. Q and S represents the fraction of total molecules corresponding to the probable velocities at temperatures ${{{T}}_1}$ and ${{{T}}_2}$.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
The equation representing Maxwell’s law of distribution of velocities is given below:
\[\dfrac{{d{{{N}}_{{C}}}}}{{{N}}} = 4\pi {\left( {\dfrac{{{M}}}{{2\pi {{RT}}}}} \right)^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}{{{e}}^{\dfrac{{ - {{MC}}}}{{2{{RT}}}}}}{{{C}}^2}d{{C}}\], where $d{{{N}}_{{C}}}$ is the number of molecules which have velocities between ${{C}}$ and ${{C}} + d{{C}}$, ${{N}}$ is the total number of molecules, ${{M}}$ is the molecular mass and ${{T}}$ is the absolute temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
The gas molecules are continuously and randomly moving with high velocities. These gas molecules collide with each other. In these collisions, kinetic energy is not lost. Thus they are said to be elastic. Due to these collisions, pressure is produced on the walls of the container. Moreover, the average kinetic energy increases when the absolute temperature is increased.
There are three types of velocities. They are probable velocity, average velocity and root mean square velocity. When the mean of the velocities is taken, it is known as the average velocity. When we take the mean square of the velocities, it is known as the root mean square velocity. When we consider the largest number of gas molecules, its velocity is known as the probable velocity.
At temperature ${{{T}}_1}$, the highest peak is obtained than that at temperature ${{{T}}_2}$. Therefore the speed under ${{{T}}_1}$ is called the probable velocity, i.e. P represents probable velocity at ${{{T}}_1}$. R represents the probable velocity at temperature ${{{T}}_2}$. Q and S represents the fraction of total molecules corresponding to the probable velocities at temperatures ${{{T}}_1}$ and ${{{T}}_2}$.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:
The equation representing Maxwell’s law of distribution of velocities is given below:
\[\dfrac{{d{{{N}}_{{C}}}}}{{{N}}} = 4\pi {\left( {\dfrac{{{M}}}{{2\pi {{RT}}}}} \right)^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}{{{e}}^{\dfrac{{ - {{MC}}}}{{2{{RT}}}}}}{{{C}}^2}d{{C}}\], where $d{{{N}}_{{C}}}$ is the number of molecules which have velocities between ${{C}}$ and ${{C}} + d{{C}}$, ${{N}}$ is the total number of molecules, ${{M}}$ is the molecular mass and ${{T}}$ is the absolute temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




