
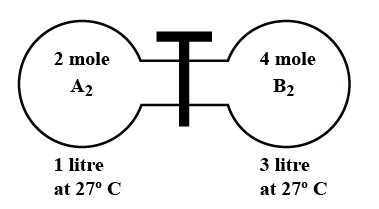
The gas ${{A}_{2}}$ in the left flask allowed to react with gas ${{B}_{2}}$ present in right flask at
${{A}_{2}}(g)+{{B}_{2}}(g)\rightleftharpoons 2AB(g),\text{ }{{\text{K}}_{c}}=4$ at ${{27}^{\circ }}C$
What is the concentration of AB when equilibrium is established?
(a)- 1.33 M
(b)- 0.66 M
(c)- 0.33 M
(d)- 2.66 M

Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: We can solve this by using the formula ${{K}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{[AB]}^{2}}}{[{{A}_{2}}][{{B}_{2}}]}$. Given the volume is 1 liter of ${{A}_{2}}$ and 3 liters of ${{B}_{2}}$, so the total volume of the system will be 3 + 1 = 4 liters.
Complete step-by-step answer:We are given the reaction as:
${{A}_{2}}(g)+{{B}_{2}}(g)\rightleftharpoons 2AB(g)$
1 mole of ${{A}_{2}}$ reacts with 1 mole of ${{B}_{2}}$ will produce 2 moles of AB. Given, the value of equilibrium constant is${{K}_{c}}=4$. The ${{K}_{c}}$ means the value of the compounds are taken in concentrations.
In the diagram given above, there are 2 moles of ${{A}_{2}}$ and 4 moles of ${{B}_{2}}$. Initially, the moles of A are 2, moles of B are 4, and mole of AB is 0. After time t, the moles of A will be 2-x, the moles of B will be 4-x, and the moles of AB will be 2x.
Given the volume is 1 liter of ${{A}_{2}}$ and 3 liters of ${{B}_{2}}$, so the total volume of the system will be 3 + 1 = 4 liters.
We have to use the formula:
${{K}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{[AB]}^{2}}}{[{{A}_{2}}][{{B}_{2}}]}$
The concentration of [AB] will be:
$\dfrac{2x}{4}=\dfrac{x}{2}$
The concentration of $[{{B}_{2}}]$ will be:
$\dfrac{4-x}{4}$
The concentration of $[{{A}_{2}}]$ will be:
$\dfrac{2-x}{4}$
Putting these values in the formula, will be:
${{K}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{\left[ \dfrac{x}{2} \right]}^{2}}}{\left[ \dfrac{2-x}{4} \right]\left[ \dfrac{4-x}{4} \right]}$
$4=\dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{(4-x)(2-x)}$
${{x}^{2}}=(4-x)(2-x)$
Now, solving the equation will be:
${{x}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-6x+8$
6x = 8
The value of x will be:
$x=\dfrac{4}{3}$
The concentration of AB is $\dfrac{x}{2}$, putting the value of x:
$[AB]=\dfrac{2}{3}=0.66M$
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (b)- 0.66M.
Note: While writing the value of the equilibrium constant, then you have to take the concentration value only in which the number of moles of the compound must be divided with the total volume of the system.
Complete step-by-step answer:We are given the reaction as:
${{A}_{2}}(g)+{{B}_{2}}(g)\rightleftharpoons 2AB(g)$
1 mole of ${{A}_{2}}$ reacts with 1 mole of ${{B}_{2}}$ will produce 2 moles of AB. Given, the value of equilibrium constant is${{K}_{c}}=4$. The ${{K}_{c}}$ means the value of the compounds are taken in concentrations.
In the diagram given above, there are 2 moles of ${{A}_{2}}$ and 4 moles of ${{B}_{2}}$. Initially, the moles of A are 2, moles of B are 4, and mole of AB is 0. After time t, the moles of A will be 2-x, the moles of B will be 4-x, and the moles of AB will be 2x.
Given the volume is 1 liter of ${{A}_{2}}$ and 3 liters of ${{B}_{2}}$, so the total volume of the system will be 3 + 1 = 4 liters.
We have to use the formula:
${{K}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{[AB]}^{2}}}{[{{A}_{2}}][{{B}_{2}}]}$
The concentration of [AB] will be:
$\dfrac{2x}{4}=\dfrac{x}{2}$
The concentration of $[{{B}_{2}}]$ will be:
$\dfrac{4-x}{4}$
The concentration of $[{{A}_{2}}]$ will be:
$\dfrac{2-x}{4}$
Putting these values in the formula, will be:
${{K}_{c}}=\dfrac{{{\left[ \dfrac{x}{2} \right]}^{2}}}{\left[ \dfrac{2-x}{4} \right]\left[ \dfrac{4-x}{4} \right]}$
$4=\dfrac{4{{x}^{2}}}{(4-x)(2-x)}$
${{x}^{2}}=(4-x)(2-x)$
Now, solving the equation will be:
${{x}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-6x+8$
6x = 8
The value of x will be:
$x=\dfrac{4}{3}$
The concentration of AB is $\dfrac{x}{2}$, putting the value of x:
$[AB]=\dfrac{2}{3}=0.66M$
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (b)- 0.66M.
Note: While writing the value of the equilibrium constant, then you have to take the concentration value only in which the number of moles of the compound must be divided with the total volume of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




