
The function of meiosis-I is to separate
(a) Homologous chromosomes
(b) Parental chromosomes
(c) Sister chromatids
(d) Cross overs
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Meiosis-I is known as reductional division because after meiosis occurs there is a decrease in the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells. Such a division is usually seen during alternation of generation i.e. from haploid to diploid body.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
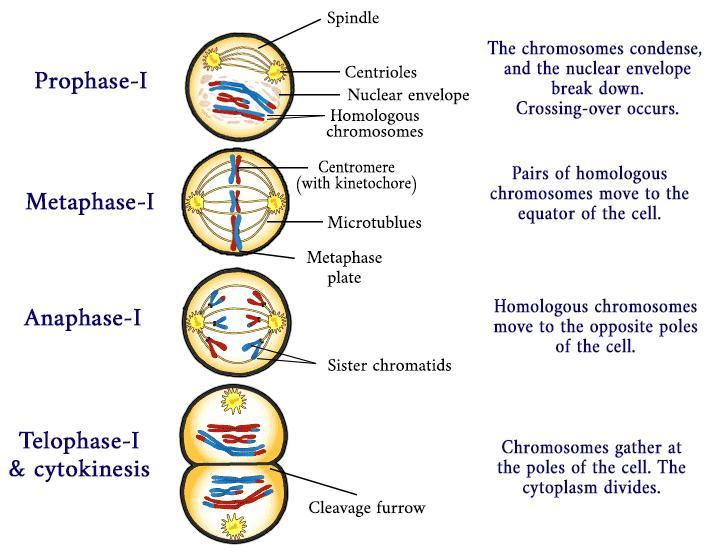
Meiosis is a type of cellular division responsible for causing a change in the ploidy of cells. It is further divided into two types known as meiosis-I and meiosis-II. Meiosis-II is just normally mitosis taking place after meiosis-I. Meiosis-I occurs to separate the homologous chromosomes present and reduce the chromosome number. This separation occurs in the anaphase-I of meiosis-I where the chromosomes are separated by spindle fibers and moved to the poles on either side.
So, the correct option is ‘Homologous chromosomes’.
Additional information:
Let us study meiosis-I in more detail. Meiosis-I is divided into the following phases:
Prophase: Prophase is further divided into:
> Leptotene: Condensation of chromosomes begin
> Zygotene: Association of chromosomes known as synapsis
> Pachytene: Crossing over between two homologous chromosomes takes place
> Diplotene: Dissolution of the synaptonemal complex
> Diakinesis: Terminalization of the chiasmata
Metaphase: Bivalent chromosomes arrange themselves on the equatorial plane.
Anaphase: Separation of the homologous chromosomes
Telophase: Karyokinesis takes place followed by cytokinesis
Note:
- Chiasmata are known as the points of attachment still present between the homologous chromosomes even after the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex.
- Crossing over is responsible for recombination in the genome of cells which leads to variations in a species. These variations with time make way for the evolution of that species.
- Mitosis is known as equational division as the number of chromosomes remains the same in the daughter cells and the parent cell.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Meiosis is a type of cellular division responsible for causing a change in the ploidy of cells. It is further divided into two types known as meiosis-I and meiosis-II. Meiosis-II is just normally mitosis taking place after meiosis-I. Meiosis-I occurs to separate the homologous chromosomes present and reduce the chromosome number. This separation occurs in the anaphase-I of meiosis-I where the chromosomes are separated by spindle fibers and moved to the poles on either side.

So, the correct option is ‘Homologous chromosomes’.
Additional information:
Let us study meiosis-I in more detail. Meiosis-I is divided into the following phases:
Prophase: Prophase is further divided into:
> Leptotene: Condensation of chromosomes begin
> Zygotene: Association of chromosomes known as synapsis
> Pachytene: Crossing over between two homologous chromosomes takes place
> Diplotene: Dissolution of the synaptonemal complex
> Diakinesis: Terminalization of the chiasmata
Metaphase: Bivalent chromosomes arrange themselves on the equatorial plane.
Anaphase: Separation of the homologous chromosomes
Telophase: Karyokinesis takes place followed by cytokinesis
Note:
- Chiasmata are known as the points of attachment still present between the homologous chromosomes even after the dissolution of the synaptonemal complex.
- Crossing over is responsible for recombination in the genome of cells which leads to variations in a species. These variations with time make way for the evolution of that species.
- Mitosis is known as equational division as the number of chromosomes remains the same in the daughter cells and the parent cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




