
The frequency corresponding to the wavelengths $4000{A^0}$ is :
A. $6.5 \times {10^{14}}{s^{ - 1}}$
B. $7.5 \times {10^{14}}{s^{ - 1}}$
C. $5.5 \times {10^{14}}{s^{ - 1}}$
D. $4.5 \times {10^{14}}{s^{ - 1}}$
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: All electromagnetic waves travel with the same speed of $3 \times {10^8}$ m/s. Although not mentioned, waves with such low wavelengths could be interpreted as electromagnetic waves. Use $c = \lambda \times \nu $ to find the frequency.
Complete step by step solution:
We know the wavelength of a wave is the length of one complete wave cycle. Waves have a periodic /repeating pattern. It repeats itself. The length of one such wave cycle is called wavelength.
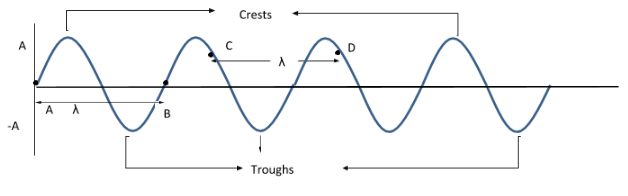
Wavelength can be easily measured by finding the distance between two adjacent crests or trough. Crests are the point in the wave cycle with maximum displacement from equilibrium. And troughs are the point of minimum displacement. In a wave cycle both will have equal magnitude but have opposite signs since the direction is different. It can also be measured as a distance between a point and corresponding point on the next wave cycle (like CD from the figure).
Here in the figure we can see that the length AD represents one wavelength.
Frequency denotes the number of wave cycles in one second.
Frequency is calculated by $\dfrac{1}{T}$ where $T$ is the time period of the wave that is the time required to complete one wave cycle.
As we know all electromagnetic waves travel with a speed of $3 \times {10^8}$ m/s
$c = \dfrac{\lambda }{T}$
$c = \lambda \times \nu $
Substituting $c = 3 \times {10^8}$ m/s and $\lambda = 4000 \times {10^{ - 10}}m$
$1{A^0} = {10^{ - 10}}m$
$3 \times {10^8} = 4000 \times {10^{ - 10}} \times \nu $
$\nu = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^8}}}{{4000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}} = \dfrac{3}{4} \times {10^{15}}$
$\nu = 0.75 \times {10^{15}}$
$\nu = 7.5 \times {10^{14}}$
Additional Knowledge:
The speed of a wave need not always be a constant independent of frequency and wavelength. Even in the case of light travelling through glass, we see that different wavelengths have different refractive indices, which implies different speeds. This is called dispersion. Dispersion is the reason for splitting of white light when passed through prism, formation of rainbows, acceleration of pulses in vertical strings and much more.
Note: Only electromagnetic waves travel with speed of $3 \times {10^8}$m/s. The general equation is $v = \lambda \times \nu $ where v is the speed of the wave. Here we have assumed it to be electromagnetic waves because of its very short wavelength.
Complete step by step solution:
We know the wavelength of a wave is the length of one complete wave cycle. Waves have a periodic /repeating pattern. It repeats itself. The length of one such wave cycle is called wavelength.

Wavelength can be easily measured by finding the distance between two adjacent crests or trough. Crests are the point in the wave cycle with maximum displacement from equilibrium. And troughs are the point of minimum displacement. In a wave cycle both will have equal magnitude but have opposite signs since the direction is different. It can also be measured as a distance between a point and corresponding point on the next wave cycle (like CD from the figure).
Here in the figure we can see that the length AD represents one wavelength.
Frequency denotes the number of wave cycles in one second.
Frequency is calculated by $\dfrac{1}{T}$ where $T$ is the time period of the wave that is the time required to complete one wave cycle.
As we know all electromagnetic waves travel with a speed of $3 \times {10^8}$ m/s
$c = \dfrac{\lambda }{T}$
$c = \lambda \times \nu $
Substituting $c = 3 \times {10^8}$ m/s and $\lambda = 4000 \times {10^{ - 10}}m$
$1{A^0} = {10^{ - 10}}m$
$3 \times {10^8} = 4000 \times {10^{ - 10}} \times \nu $
$\nu = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^8}}}{{4000 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}}} = \dfrac{3}{4} \times {10^{15}}$
$\nu = 0.75 \times {10^{15}}$
$\nu = 7.5 \times {10^{14}}$
Additional Knowledge:
The speed of a wave need not always be a constant independent of frequency and wavelength. Even in the case of light travelling through glass, we see that different wavelengths have different refractive indices, which implies different speeds. This is called dispersion. Dispersion is the reason for splitting of white light when passed through prism, formation of rainbows, acceleration of pulses in vertical strings and much more.
Note: Only electromagnetic waves travel with speed of $3 \times {10^8}$m/s. The general equation is $v = \lambda \times \nu $ where v is the speed of the wave. Here we have assumed it to be electromagnetic waves because of its very short wavelength.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




