
The free-body diagram will be identical to the one we drew in the example of the frictionless plane, except we will have a vector for the force of friction in the negative X-direction. What is the work done on the box by the force of kinetic friction?
A.$\mu mgh \sin {30°}$
B.$\mu mgh \tan {30°}$
C.$\mu mgh \cot {30°}$
D.$\mu mgh \cos {30°}$

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: To find the work done on the box by the force of kinetic friction, use the formula for work done giving the relation between force of friction and displacement of the box in direction that the force is exerted. But, formula for force of friction is given by product of normal force and coefficient of friction. Substitute the values in the formula for work done. This will give the value for work done on the box by the force of kinetic friction.
Complete answer:
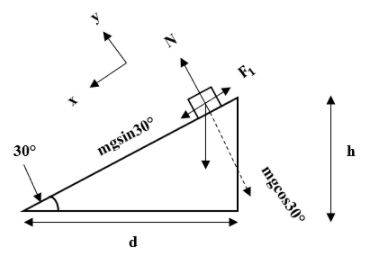
Work done by the force of friction is given by,
$W = F . d$ …(1)
Where, F is the force of friction
d is the displacement of the box in direction that the force is exerted
Force of friction is given by,
$F= \mu. N$
Where, $\mu$ is the coefficient of friction
N is the normal force
Substituting the value in above equation we get,
$F = \mu. mg\cos {30°}$ …(2)
Displacement of the box in direction that the force is exerted is given by,
$d = \dfrac {h}{\sin{30°}}$ …(3)
Substituting equation. (2) and (3) in equation. (1) we get,
$W = \mu. mg\cos {30°} \times \dfrac {h}{\sin{30°}}$
$\Rightarrow W= \mu mgh \cot{30°}$
Thus, the work done on the box by the force of kinetic friction is $\mu mgh \cot {30°}$.
So, the correct answer is option D i.e. $\mu mgh \cot {30°}$.
Note:
Students must know that there are two types of frictional forces namely Kinetic friction and Static friction. Kinetic friction is the friction that acts between two surfaces in contact that are moving. While static friction is the friction that acts between two surfaces that are not moving. Objects that weigh less exert downward force than heavier objects. Close contacts increase friction between the two objects.
Complete answer:
Work done by the force of friction is given by,
$W = F . d$ …(1)
Where, F is the force of friction
d is the displacement of the box in direction that the force is exerted
Force of friction is given by,
$F= \mu. N$
Where, $\mu$ is the coefficient of friction
N is the normal force
Substituting the value in above equation we get,
$F = \mu. mg\cos {30°}$ …(2)
Displacement of the box in direction that the force is exerted is given by,
$d = \dfrac {h}{\sin{30°}}$ …(3)
Substituting equation. (2) and (3) in equation. (1) we get,
$W = \mu. mg\cos {30°} \times \dfrac {h}{\sin{30°}}$
$\Rightarrow W= \mu mgh \cot{30°}$
Thus, the work done on the box by the force of kinetic friction is $\mu mgh \cot {30°}$.
So, the correct answer is option D i.e. $\mu mgh \cot {30°}$.
Note:
Students must know that there are two types of frictional forces namely Kinetic friction and Static friction. Kinetic friction is the friction that acts between two surfaces in contact that are moving. While static friction is the friction that acts between two surfaces that are not moving. Objects that weigh less exert downward force than heavier objects. Close contacts increase friction between the two objects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




