
The formula of 3- chloro- 2, 2- dimethyl butane is:
(A) $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH}}\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right){\text{C}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} $
(B) $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} $
(C) $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Cl}} $
(D) $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}} $
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the rules for the nomenclature of organic compounds given by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry or IUPAC. We are given the IUPAC name of the compound. The rules for the nomenclature set for organic compounds by IUPAC are in such a way that each compound has a unique name for it. The parent chain is the longest chain and its substituents are written as prefixes with the carbon number they are attached to.
Complete step by step solution
To draw the structure of the given compound, we must follow these steps:
First, we need to identify the parent carbon chain or the longest carbon chain on which we then arrange the functional groups and substituents. The parent carbon chain is represented by the word root of the compound. The word root in this case is the butan- . But- represents a four carbon parent chain and – ane represents an alkane, i.e. the bonds between the carbon atoms of the principal chain are singly bonded.
There are no principal functions that can be added to the name of the compound as a suffix. Chloro group is considered as a substitute and mentioned in the prefix.
Now, we must identify the positions of the remaining substituent groups given in the prefix of the word root of the compound. We are given that two methyl groups are attached to the second carbon atom in the chain and a chloro group is bonded to the third carbon atom. This gives us the formula of 3- chloro- 2, 2- dimethyl butane as $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}} $
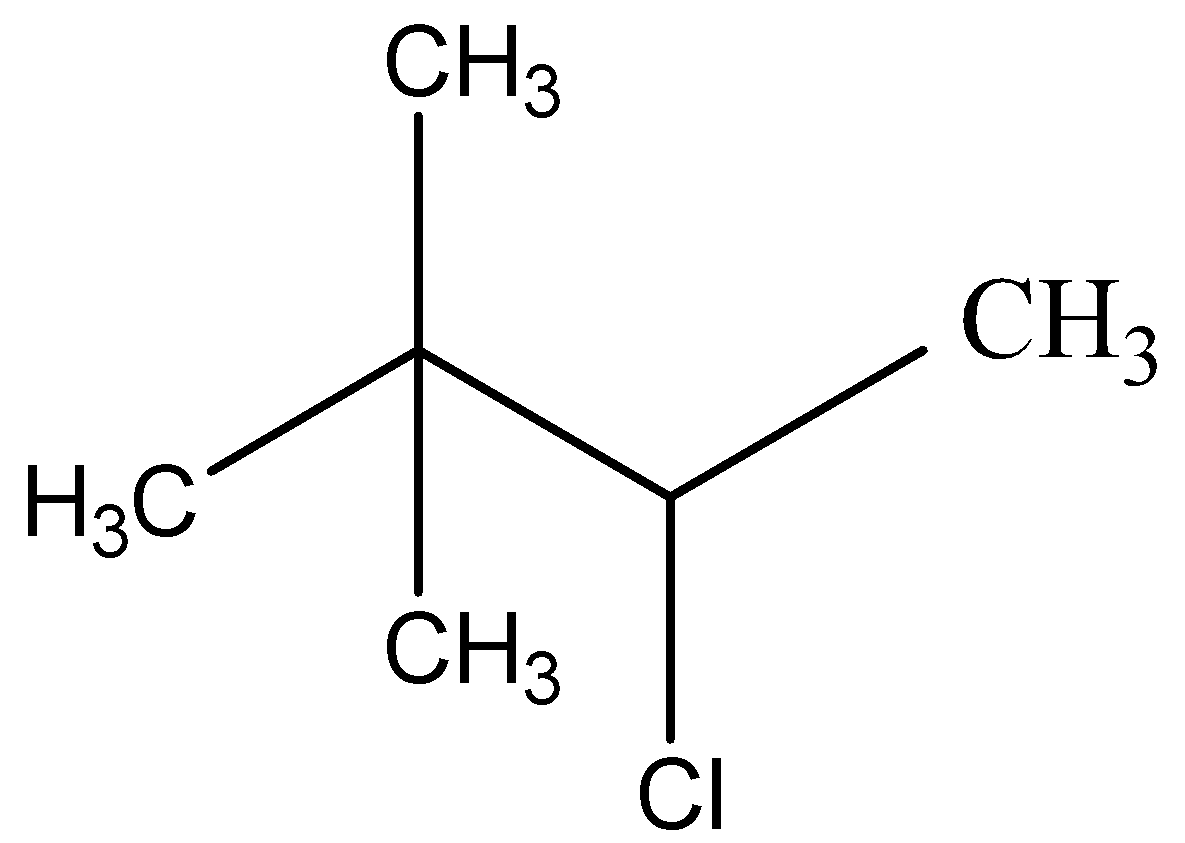
The correct answer is D.
Note
To represent the position of the substituent groups in the IUPAC name of the compound, we must first number the parent carbon chain after its identification. The parent carbon chain must be numbered in such a way so that the majority of the substituent groups get the lowest possible numbers.
Complete step by step solution
To draw the structure of the given compound, we must follow these steps:
First, we need to identify the parent carbon chain or the longest carbon chain on which we then arrange the functional groups and substituents. The parent carbon chain is represented by the word root of the compound. The word root in this case is the butan- . But- represents a four carbon parent chain and – ane represents an alkane, i.e. the bonds between the carbon atoms of the principal chain are singly bonded.
There are no principal functions that can be added to the name of the compound as a suffix. Chloro group is considered as a substitute and mentioned in the prefix.
Now, we must identify the positions of the remaining substituent groups given in the prefix of the word root of the compound. We are given that two methyl groups are attached to the second carbon atom in the chain and a chloro group is bonded to the third carbon atom. This gives us the formula of 3- chloro- 2, 2- dimethyl butane as $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHClC}}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}} $

The correct answer is D.
Note
To represent the position of the substituent groups in the IUPAC name of the compound, we must first number the parent carbon chain after its identification. The parent carbon chain must be numbered in such a way so that the majority of the substituent groups get the lowest possible numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




