
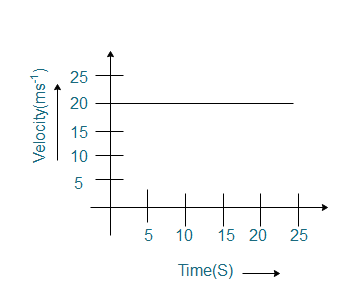
The following velocity-time graph shows the motion of a cyclist. Find (i) its acceleration, (ii) its velocity and (iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds.

Answer
528.4k+ views
Hint: Here, we have a velocity time graph i.e. we have change of velocity with time. From the graph we can directly find the velocity. The acceleration can be found from the graph as the rate of change of the velocity. The distance covered in a time can be found as the area under the curve in the curve for that time.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) acceleration of an object can be defined as the rate of change of velocity of the object with time. If we observe the graph, we will see that, in the velocity-time graph, the velocity of the object is not changing with time. Since, the velocity of the cyclist is constant with time, the rate of change of velocity with time is zero. So, the acceleration of the object will be zero.
(ii) in the graph, we observe that the cyclist is moving with the same velocity all the time. According to the graph, the velocity of the cyclist is $20m{{s}^{-1}}$ .
(iii) now, from the velocity time graph, the distance covered by the cyclist can be obtained as the area under the curve. We need to find the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds. So, we need to find the area under the curve from zero to 15 seconds.
From the velocity time graph, for 15 seconds, in the time axis, $t=15\text{seconds}$
In the velocity axis, the velocity is constant for all the time with value, $v=20m{{s}^{-1}}$
So, the distance covered will be the area under the rectangle which can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& s=vt \\
& s=20m{{s}^{-1}}\times 15s \\
& s=300m \\
\end{align}$
So, the cyclist will cover a distance of 300 m in 15 seconds.
Note: When we have a velocity time graph, for non-accelerating objects or for objects which are moving with constant velocity, the graph will be straight parallel to the time axis. For objects moving with a uniform acceleration, the graph will be a straight line with a slope. For objects with non-uniform acceleration we will get a zigzag line.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) acceleration of an object can be defined as the rate of change of velocity of the object with time. If we observe the graph, we will see that, in the velocity-time graph, the velocity of the object is not changing with time. Since, the velocity of the cyclist is constant with time, the rate of change of velocity with time is zero. So, the acceleration of the object will be zero.
(ii) in the graph, we observe that the cyclist is moving with the same velocity all the time. According to the graph, the velocity of the cyclist is $20m{{s}^{-1}}$ .
(iii) now, from the velocity time graph, the distance covered by the cyclist can be obtained as the area under the curve. We need to find the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds. So, we need to find the area under the curve from zero to 15 seconds.
From the velocity time graph, for 15 seconds, in the time axis, $t=15\text{seconds}$
In the velocity axis, the velocity is constant for all the time with value, $v=20m{{s}^{-1}}$
So, the distance covered will be the area under the rectangle which can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& s=vt \\
& s=20m{{s}^{-1}}\times 15s \\
& s=300m \\
\end{align}$
So, the cyclist will cover a distance of 300 m in 15 seconds.
Note: When we have a velocity time graph, for non-accelerating objects or for objects which are moving with constant velocity, the graph will be straight parallel to the time axis. For objects moving with a uniform acceleration, the graph will be a straight line with a slope. For objects with non-uniform acceleration we will get a zigzag line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




