
The following figure shows the stomatal apparatus. Identify the parts labelled as a, b, c, d. Choose the correct answer from the following
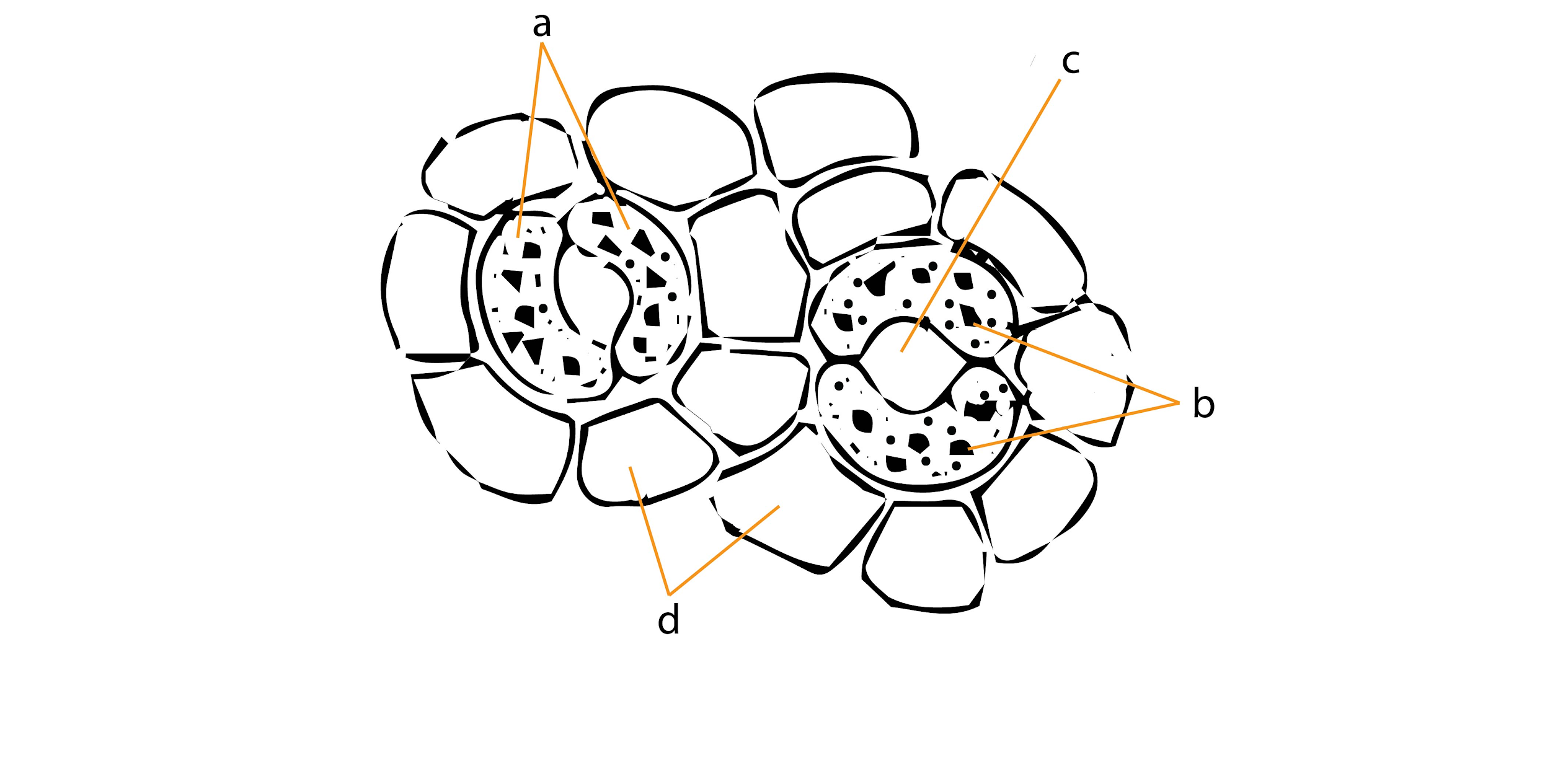
(a) a-subsidiary cells, b-chloroplasts, c-stoma, d-guard cells
(b) a-guard cells, b-stoma, c-chloroplasts, d-subsidiary cells
(c) a-guard cells, b-chloroplasts, c-stoma, d-subsidiary cells
(d) a-subsidiary cells, b-stoma, c-chloroplasts, d-guard cells

Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Stomatal apparatus of plants is a very important system for gaseous exchange. They are guard cells for regulation and are surrounded by subsidiary cells for support.
Complete answer:
The Stomatal apparatus consists of a pair of guard cells with or without the surrounding subsidiary cells which function as a value to open or close the stomatal pore for gaseous exchange and transpiration whenever required.
Each stoma is made up of two bean- shaped guard cells. They contain numerous chloroplasts and small vacuoles. They are thick- walled in the areas of contact and thin- walled in other places. As the guard cells swell up because of endosmosis, their thin- walled side expands. The thick walls of the two guard cells also bend outwards to create a pore in between them called the stoma.
This is the main pore through which gases escape the plant body and excess water leaves too as vapors during transpiration.
The stomatal apparatus has the innermost stoma or the opening, which is controlled by the guard cells. The guard cells have many chloroplasts which help in photosynthesis. This whole apparatus is surrounded by the subsidiary cells which help in the regulation of stomatal opening.
So, the answer is ‘a-guard cells, b-chloroplasts, c-stoma, d-subsidiary cells.’
Note:
- The shape of the guard cells varies in different plants. In dicot plants they are kidney- shaped. - In monocot plants like grasses, however, they are dumb- bell shaped cells. - This is believed to be a more effective and water- efficient gaseous exchange is possible in changing environments and savannahs where they are found in higher numbers.
Complete answer:
The Stomatal apparatus consists of a pair of guard cells with or without the surrounding subsidiary cells which function as a value to open or close the stomatal pore for gaseous exchange and transpiration whenever required.
Each stoma is made up of two bean- shaped guard cells. They contain numerous chloroplasts and small vacuoles. They are thick- walled in the areas of contact and thin- walled in other places. As the guard cells swell up because of endosmosis, their thin- walled side expands. The thick walls of the two guard cells also bend outwards to create a pore in between them called the stoma.
This is the main pore through which gases escape the plant body and excess water leaves too as vapors during transpiration.
The stomatal apparatus has the innermost stoma or the opening, which is controlled by the guard cells. The guard cells have many chloroplasts which help in photosynthesis. This whole apparatus is surrounded by the subsidiary cells which help in the regulation of stomatal opening.
So, the answer is ‘a-guard cells, b-chloroplasts, c-stoma, d-subsidiary cells.’
Note:
- The shape of the guard cells varies in different plants. In dicot plants they are kidney- shaped. - In monocot plants like grasses, however, they are dumb- bell shaped cells. - This is believed to be a more effective and water- efficient gaseous exchange is possible in changing environments and savannahs where they are found in higher numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




